Threads
XF\Mvc\Entity\ArrayCollection Object
(
[entities:protected] => Array
(
[24684] => ThemeHouse\XPress\XF\Entity\Thread Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 57
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\Thread
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[thread_id] => 24684
[node_id] => 2
[title] => Build China’s ASML
[reply_count] => 16
[view_count] => 510
[user_id] => 19450
[username] => user nl
[post_date] => 1772785293
[sticky] => 0
[discussion_state] => visible
[discussion_open] => 1
[discussion_type] => discussion
[first_post_id] => 98120
[first_post_reaction_score] => 0
[first_post_reactions] => []
[last_post_date] => 1772880454
[last_post_id] => 98163
[last_post_user_id] => 5185
[last_post_username] => Fred Chen
[prefix_id] => 0
[tags] => []
[custom_fields] => []
[vote_score] => 0
[vote_count] => 0
[featured] => 0
[type_data] => []
[index_state] => default
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
[User] => ThemeHouse\XLink\XF\Entity\User Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 54
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\User
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[user_id] => 19450
[username] => user nl
[username_date] => 0
[username_date_visible] => 0
[email] => mauricehmjanssen@gmail.com
[custom_title] =>
[language_id] => 1
[style_id] => 0
[style_variation] =>
[timezone] => Europe/Amsterdam
[visible] => 1
[activity_visible] => 1
[user_group_id] => 2
[secondary_group_ids] =>
[display_style_group_id] => 2
[permission_combination_id] => 8
[message_count] => 458
[question_solution_count] => 0
[conversations_unread] => 0
[register_date] => 1424291496
[last_activity] => 1772879938
[last_summary_email_date] =>
[trophy_points] => 63
[alerts_unviewed] => 2
[alerts_unread] => 2
[avatar_date] => 1726169369
[avatar_width] => 384
[avatar_height] => 384
[avatar_highdpi] => 1
[avatar_optimized] => 0
[gravatar] =>
[user_state] => valid
[security_lock] =>
[is_moderator] => 0
[is_admin] => 0
[is_banned] => 0
[reaction_score] => 343
[warning_points] => 0
[is_staff] => 0
[secret_key] => V-1lb5_AW69yhzqA5ok9b64U0fMjJiqf
[privacy_policy_accepted] => 0
[terms_accepted] => 0
[vote_score] => 0
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
[Forum] => XF\Entity\Forum Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 56
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\Forum
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[node_id] => 2
[discussion_count] => 8388
[message_count] => 61505
[last_post_id] => 98163
[last_post_date] => 1772880454
[last_post_user_id] => 5185
[last_post_username] => Fred Chen
[last_thread_id] => 24684
[last_thread_title] => Build China’s ASML
[last_thread_prefix_id] => 0
[moderate_threads] => 0
[moderate_replies] => 0
[allow_posting] => 1
[count_messages] => 1
[auto_feature] => 0
[find_new] => 1
[allow_index] => allow
[index_criteria] =>
[field_cache] => []
[prefix_cache] => []
[prompt_cache] => []
[default_prefix_id] => 0
[default_sort_order] => last_post_date
[default_sort_direction] => desc
[list_date_limit_days] => 0
[require_prefix] => 0
[allowed_watch_notifications] => all
[min_tags] => 0
[forum_type_id] => discussion
[type_config] => {"allowed_thread_types":["poll"]}
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
[Node] => XF\Entity\Node Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 55
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\Node
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[node_id] => 2
[title] => SemiWiki Main Forum ( Ask the Experts! )
[description] => Post your questions to the experts here!
[node_name] =>
[node_type_id] => Forum
[parent_node_id] => 1
[display_order] => 1
[display_in_list] => 1
[lft] => 2
[rgt] => 3
[depth] => 1
[style_id] => 0
[effective_style_id] => 0
[breadcrumb_data] => {"1":{"node_id":1,"title":"Main Category","depth":0,"lft":1,"node_name":null,"node_type_id":"Category","display_in_list":true}}
[navigation_id] =>
[effective_navigation_id] =>
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
[24689] => ThemeHouse\XPress\XF\Entity\Thread Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 61
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\Thread
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[thread_id] => 24689
[node_id] => 2
[title] => Intel’s EMIB Challenges TSMC’s CoWoS as America’s Answer to the AI Packaging Bottleneck
[reply_count] => 1
[view_count] => 96
[user_id] => 5185
[username] => Fred Chen
[post_date] => 1772861237
[sticky] => 0
[discussion_state] => visible
[discussion_open] => 1
[discussion_type] => discussion
[first_post_id] => 98157
[first_post_reaction_score] => 0
[first_post_reactions] => []
[last_post_date] => 1772874024
[last_post_id] => 98158
[last_post_user_id] => 5
[last_post_username] => Daniel Nenni
[prefix_id] => 0
[tags] => []
[custom_fields] => []
[vote_score] => 0
[vote_count] => 0
[featured] => 0
[type_data] => []
[index_state] => default
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
[User] => ThemeHouse\XLink\XF\Entity\User Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 58
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\User
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[user_id] => 5185
[username] => Fred Chen
[username_date] => 0
[username_date_visible] => 0
[email] => chen.t.fred@gmail.com
[custom_title] =>
[language_id] => 1
[style_id] => 0
[style_variation] =>
[timezone] => America/Los_Angeles
[visible] => 1
[activity_visible] => 1
[user_group_id] => 4
[secondary_group_ids] =>
[display_style_group_id] => 4
[permission_combination_id] => 92
[message_count] => 2555
[question_solution_count] => 0
[conversations_unread] => 0
[register_date] => 1333032401
[last_activity] => 1772880818
[last_summary_email_date] => 1605940563
[trophy_points] => 113
[alerts_unviewed] => 0
[alerts_unread] => 1
[avatar_date] => 0
[avatar_width] => 0
[avatar_height] => 0
[avatar_highdpi] => 0
[avatar_optimized] => 0
[gravatar] =>
[user_state] => valid
[security_lock] =>
[is_moderator] => 0
[is_admin] => 0
[is_banned] => 0
[reaction_score] => 1860
[warning_points] => 0
[is_staff] => 0
[secret_key] => 5m-bZq0HRSi9VA-96QONHJeevdQas5S8
[privacy_policy_accepted] => 0
[terms_accepted] => 0
[vote_score] => 0
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
[Forum] => XF\Entity\Forum Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 56
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\Forum
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[node_id] => 2
[discussion_count] => 8388
[message_count] => 61505
[last_post_id] => 98163
[last_post_date] => 1772880454
[last_post_user_id] => 5185
[last_post_username] => Fred Chen
[last_thread_id] => 24684
[last_thread_title] => Build China’s ASML
[last_thread_prefix_id] => 0
[moderate_threads] => 0
[moderate_replies] => 0
[allow_posting] => 1
[count_messages] => 1
[auto_feature] => 0
[find_new] => 1
[allow_index] => allow
[index_criteria] =>
[field_cache] => []
[prefix_cache] => []
[prompt_cache] => []
[default_prefix_id] => 0
[default_sort_order] => last_post_date
[default_sort_direction] => desc
[list_date_limit_days] => 0
[require_prefix] => 0
[allowed_watch_notifications] => all
[min_tags] => 0
[forum_type_id] => discussion
[type_config] => {"allowed_thread_types":["poll"]}
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
[Node] => XF\Entity\Node Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 55
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\Node
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[node_id] => 2
[title] => SemiWiki Main Forum ( Ask the Experts! )
[description] => Post your questions to the experts here!
[node_name] =>
[node_type_id] => Forum
[parent_node_id] => 1
[display_order] => 1
[display_in_list] => 1
[lft] => 2
[rgt] => 3
[depth] => 1
[style_id] => 0
[effective_style_id] => 0
[breadcrumb_data] => {"1":{"node_id":1,"title":"Main Category","depth":0,"lft":1,"node_name":null,"node_type_id":"Category","display_in_list":true}}
[navigation_id] =>
[effective_navigation_id] =>
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
[24680] => ThemeHouse\XPress\XF\Entity\Thread Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 65
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\Thread
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[thread_id] => 24680
[node_id] => 2
[title] => Intel CEO Tan reconsidering fate of chipmaker's new manufacturing tech, CFO says
[reply_count] => 23
[view_count] => 2195
[user_id] => 5
[username] => Daniel Nenni
[post_date] => 1772695350
[sticky] => 0
[discussion_state] => visible
[discussion_open] => 1
[discussion_type] => discussion
[first_post_id] => 98070
[first_post_reaction_score] => 0
[first_post_reactions] => []
[last_post_date] => 1772859543
[last_post_id] => 98156
[last_post_user_id] => 90182
[last_post_username] => siliconbruh999
[prefix_id] => 0
[tags] => []
[custom_fields] => []
[vote_score] => 0
[vote_count] => 0
[featured] => 0
[type_data] => []
[index_state] => default
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
[User] => ThemeHouse\XLink\XF\Entity\User Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 62
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\User
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[user_id] => 5
[username] => Daniel Nenni
[username_date] => 0
[username_date_visible] => 0
[email] => dnenni@semiwiki.com
[custom_title] => Admin
[language_id] => 1
[style_id] => 0
[style_variation] =>
[timezone] => America/Los_Angeles
[visible] => 1
[activity_visible] => 1
[user_group_id] => 3
[secondary_group_ids] => 4,5,132
[display_style_group_id] => 3
[permission_combination_id] => 88
[message_count] => 15330
[question_solution_count] => 0
[conversations_unread] => 0
[register_date] => 1280720820
[last_activity] => 1772877925
[last_summary_email_date] => 1605968657
[trophy_points] => 113
[alerts_unviewed] => 35
[alerts_unread] => 35
[avatar_date] => 1663211649
[avatar_width] => 110
[avatar_height] => 107
[avatar_highdpi] => 0
[avatar_optimized] => 0
[gravatar] =>
[user_state] => valid
[security_lock] =>
[is_moderator] => 1
[is_admin] => 1
[is_banned] => 0
[reaction_score] => 9187
[warning_points] => 0
[is_staff] => 1
[secret_key] => 0HwyUVVHCwJotUUVEpvqAclfYJdGNPpw
[privacy_policy_accepted] => 0
[terms_accepted] => 0
[vote_score] => 0
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
[Forum] => XF\Entity\Forum Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 56
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\Forum
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[node_id] => 2
[discussion_count] => 8388
[message_count] => 61505
[last_post_id] => 98163
[last_post_date] => 1772880454
[last_post_user_id] => 5185
[last_post_username] => Fred Chen
[last_thread_id] => 24684
[last_thread_title] => Build China’s ASML
[last_thread_prefix_id] => 0
[moderate_threads] => 0
[moderate_replies] => 0
[allow_posting] => 1
[count_messages] => 1
[auto_feature] => 0
[find_new] => 1
[allow_index] => allow
[index_criteria] =>
[field_cache] => []
[prefix_cache] => []
[prompt_cache] => []
[default_prefix_id] => 0
[default_sort_order] => last_post_date
[default_sort_direction] => desc
[list_date_limit_days] => 0
[require_prefix] => 0
[allowed_watch_notifications] => all
[min_tags] => 0
[forum_type_id] => discussion
[type_config] => {"allowed_thread_types":["poll"]}
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
[Node] => XF\Entity\Node Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 55
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\Node
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[node_id] => 2
[title] => SemiWiki Main Forum ( Ask the Experts! )
[description] => Post your questions to the experts here!
[node_name] =>
[node_type_id] => Forum
[parent_node_id] => 1
[display_order] => 1
[display_in_list] => 1
[lft] => 2
[rgt] => 3
[depth] => 1
[style_id] => 0
[effective_style_id] => 0
[breadcrumb_data] => {"1":{"node_id":1,"title":"Main Category","depth":0,"lft":1,"node_name":null,"node_type_id":"Category","display_in_list":true}}
[navigation_id] =>
[effective_navigation_id] =>
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
[24686] => ThemeHouse\XPress\XF\Entity\Thread Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 69
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\Thread
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[thread_id] => 24686
[node_id] => 2
[title] => Intel Foundry’s Advanced Packaging Innovations Lead the Industry in Scaling Past Reticle Limits
[reply_count] => 2
[view_count] => 378
[user_id] => 5
[username] => Daniel Nenni
[post_date] => 1772813055
[sticky] => 0
[discussion_state] => visible
[discussion_open] => 1
[discussion_type] => discussion
[first_post_id] => 98137
[first_post_reaction_score] => 0
[first_post_reactions] => []
[last_post_date] => 1772859467
[last_post_id] => 98155
[last_post_user_id] => 90182
[last_post_username] => siliconbruh999
[prefix_id] => 0
[tags] => []
[custom_fields] => []
[vote_score] => 0
[vote_count] => 0
[featured] => 0
[type_data] => []
[index_state] => default
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
[User] => ThemeHouse\XLink\XF\Entity\User Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 62
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\User
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[user_id] => 5
[username] => Daniel Nenni
[username_date] => 0
[username_date_visible] => 0
[email] => dnenni@semiwiki.com
[custom_title] => Admin
[language_id] => 1
[style_id] => 0
[style_variation] =>
[timezone] => America/Los_Angeles
[visible] => 1
[activity_visible] => 1
[user_group_id] => 3
[secondary_group_ids] => 4,5,132
[display_style_group_id] => 3
[permission_combination_id] => 88
[message_count] => 15330
[question_solution_count] => 0
[conversations_unread] => 0
[register_date] => 1280720820
[last_activity] => 1772877925
[last_summary_email_date] => 1605968657
[trophy_points] => 113
[alerts_unviewed] => 35
[alerts_unread] => 35
[avatar_date] => 1663211649
[avatar_width] => 110
[avatar_height] => 107
[avatar_highdpi] => 0
[avatar_optimized] => 0
[gravatar] =>
[user_state] => valid
[security_lock] =>
[is_moderator] => 1
[is_admin] => 1
[is_banned] => 0
[reaction_score] => 9187
[warning_points] => 0
[is_staff] => 1
[secret_key] => 0HwyUVVHCwJotUUVEpvqAclfYJdGNPpw
[privacy_policy_accepted] => 0
[terms_accepted] => 0
[vote_score] => 0
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
[Forum] => XF\Entity\Forum Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 56
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\Forum
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[node_id] => 2
[discussion_count] => 8388
[message_count] => 61505
[last_post_id] => 98163
[last_post_date] => 1772880454
[last_post_user_id] => 5185
[last_post_username] => Fred Chen
[last_thread_id] => 24684
[last_thread_title] => Build China’s ASML
[last_thread_prefix_id] => 0
[moderate_threads] => 0
[moderate_replies] => 0
[allow_posting] => 1
[count_messages] => 1
[auto_feature] => 0
[find_new] => 1
[allow_index] => allow
[index_criteria] =>
[field_cache] => []
[prefix_cache] => []
[prompt_cache] => []
[default_prefix_id] => 0
[default_sort_order] => last_post_date
[default_sort_direction] => desc
[list_date_limit_days] => 0
[require_prefix] => 0
[allowed_watch_notifications] => all
[min_tags] => 0
[forum_type_id] => discussion
[type_config] => {"allowed_thread_types":["poll"]}
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
[Node] => XF\Entity\Node Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 55
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\Node
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[node_id] => 2
[title] => SemiWiki Main Forum ( Ask the Experts! )
[description] => Post your questions to the experts here!
[node_name] =>
[node_type_id] => Forum
[parent_node_id] => 1
[display_order] => 1
[display_in_list] => 1
[lft] => 2
[rgt] => 3
[depth] => 1
[style_id] => 0
[effective_style_id] => 0
[breadcrumb_data] => {"1":{"node_id":1,"title":"Main Category","depth":0,"lft":1,"node_name":null,"node_type_id":"Category","display_in_list":true}}
[navigation_id] =>
[effective_navigation_id] =>
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
[24688] => ThemeHouse\XPress\XF\Entity\Thread Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 73
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\Thread
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[thread_id] => 24688
[node_id] => 2
[title] => Costco is advertising a $4350 Apple MacBook?
[reply_count] => 1
[view_count] => 220
[user_id] => 38697
[username] => blueone
[post_date] => 1772826169
[sticky] => 0
[discussion_state] => visible
[discussion_open] => 1
[discussion_type] => discussion
[first_post_id] => 98144
[first_post_reaction_score] => 0
[first_post_reactions] => []
[last_post_date] => 1772840444
[last_post_id] => 98151
[last_post_user_id] => 712
[last_post_username] => yanfeng
[prefix_id] => 0
[tags] => []
[custom_fields] => []
[vote_score] => 0
[vote_count] => 0
[featured] => 0
[type_data] => []
[index_state] => default
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
[User] => ThemeHouse\XLink\XF\Entity\User Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 70
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\User
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[user_id] => 38697
[username] => blueone
[username_date] => 0
[username_date_visible] => 0
[email] => rob8633@hotmail.com
[custom_title] =>
[language_id] => 1
[style_id] => 0
[style_variation] =>
[timezone] => America/Denver
[visible] => 0
[activity_visible] => 0
[user_group_id] => 2
[secondary_group_ids] =>
[display_style_group_id] => 2
[permission_combination_id] => 8
[message_count] => 2539
[question_solution_count] => 0
[conversations_unread] => 0
[register_date] => 1621824096
[last_activity] => 1772851357
[last_summary_email_date] =>
[trophy_points] => 113
[alerts_unviewed] => 0
[alerts_unread] => 0
[avatar_date] => 0
[avatar_width] => 0
[avatar_height] => 0
[avatar_highdpi] => 0
[avatar_optimized] => 0
[gravatar] =>
[user_state] => valid
[security_lock] =>
[is_moderator] => 0
[is_admin] => 0
[is_banned] => 0
[reaction_score] => 3368
[warning_points] => 0
[is_staff] => 0
[secret_key] => aGlUsVcP2cy-QllnjVLMCtpGT8e-_F_T
[privacy_policy_accepted] => 1621824096
[terms_accepted] => 1621824096
[vote_score] => 0
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
[Forum] => XF\Entity\Forum Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 56
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\Forum
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[node_id] => 2
[discussion_count] => 8388
[message_count] => 61505
[last_post_id] => 98163
[last_post_date] => 1772880454
[last_post_user_id] => 5185
[last_post_username] => Fred Chen
[last_thread_id] => 24684
[last_thread_title] => Build China’s ASML
[last_thread_prefix_id] => 0
[moderate_threads] => 0
[moderate_replies] => 0
[allow_posting] => 1
[count_messages] => 1
[auto_feature] => 0
[find_new] => 1
[allow_index] => allow
[index_criteria] =>
[field_cache] => []
[prefix_cache] => []
[prompt_cache] => []
[default_prefix_id] => 0
[default_sort_order] => last_post_date
[default_sort_direction] => desc
[list_date_limit_days] => 0
[require_prefix] => 0
[allowed_watch_notifications] => all
[min_tags] => 0
[forum_type_id] => discussion
[type_config] => {"allowed_thread_types":["poll"]}
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
[Node] => XF\Entity\Node Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 55
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\Node
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[node_id] => 2
[title] => SemiWiki Main Forum ( Ask the Experts! )
[description] => Post your questions to the experts here!
[node_name] =>
[node_type_id] => Forum
[parent_node_id] => 1
[display_order] => 1
[display_in_list] => 1
[lft] => 2
[rgt] => 3
[depth] => 1
[style_id] => 0
[effective_style_id] => 0
[breadcrumb_data] => {"1":{"node_id":1,"title":"Main Category","depth":0,"lft":1,"node_name":null,"node_type_id":"Category","display_in_list":true}}
[navigation_id] =>
[effective_navigation_id] =>
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
[24681] => ThemeHouse\XPress\XF\Entity\Thread Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 77
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\Thread
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[thread_id] => 24681
[node_id] => 2
[title] => Intel has manufacturing capacity issues. They may take years to fix.
[reply_count] => 5
[view_count] => 813
[user_id] => 5185
[username] => Fred Chen
[post_date] => 1772714721
[sticky] => 0
[discussion_state] => visible
[discussion_open] => 1
[discussion_type] => discussion
[first_post_id] => 98072
[first_post_reaction_score] => 2
[first_post_reactions] => {"1":2}
[last_post_date] => 1772832873
[last_post_id] => 98147
[last_post_user_id] => 138292
[last_post_username] => MKWVentures
[prefix_id] => 0
[tags] => []
[custom_fields] => []
[vote_score] => 0
[vote_count] => 0
[featured] => 0
[type_data] => []
[index_state] => default
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
[User] => ThemeHouse\XLink\XF\Entity\User Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 58
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\User
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[user_id] => 5185
[username] => Fred Chen
[username_date] => 0
[username_date_visible] => 0
[email] => chen.t.fred@gmail.com
[custom_title] =>
[language_id] => 1
[style_id] => 0
[style_variation] =>
[timezone] => America/Los_Angeles
[visible] => 1
[activity_visible] => 1
[user_group_id] => 4
[secondary_group_ids] =>
[display_style_group_id] => 4
[permission_combination_id] => 92
[message_count] => 2555
[question_solution_count] => 0
[conversations_unread] => 0
[register_date] => 1333032401
[last_activity] => 1772880818
[last_summary_email_date] => 1605940563
[trophy_points] => 113
[alerts_unviewed] => 0
[alerts_unread] => 1
[avatar_date] => 0
[avatar_width] => 0
[avatar_height] => 0
[avatar_highdpi] => 0
[avatar_optimized] => 0
[gravatar] =>
[user_state] => valid
[security_lock] =>
[is_moderator] => 0
[is_admin] => 0
[is_banned] => 0
[reaction_score] => 1860
[warning_points] => 0
[is_staff] => 0
[secret_key] => 5m-bZq0HRSi9VA-96QONHJeevdQas5S8
[privacy_policy_accepted] => 0
[terms_accepted] => 0
[vote_score] => 0
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
[Forum] => XF\Entity\Forum Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 56
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\Forum
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[node_id] => 2
[discussion_count] => 8388
[message_count] => 61505
[last_post_id] => 98163
[last_post_date] => 1772880454
[last_post_user_id] => 5185
[last_post_username] => Fred Chen
[last_thread_id] => 24684
[last_thread_title] => Build China’s ASML
[last_thread_prefix_id] => 0
[moderate_threads] => 0
[moderate_replies] => 0
[allow_posting] => 1
[count_messages] => 1
[auto_feature] => 0
[find_new] => 1
[allow_index] => allow
[index_criteria] =>
[field_cache] => []
[prefix_cache] => []
[prompt_cache] => []
[default_prefix_id] => 0
[default_sort_order] => last_post_date
[default_sort_direction] => desc
[list_date_limit_days] => 0
[require_prefix] => 0
[allowed_watch_notifications] => all
[min_tags] => 0
[forum_type_id] => discussion
[type_config] => {"allowed_thread_types":["poll"]}
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
[Node] => XF\Entity\Node Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 55
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\Node
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[node_id] => 2
[title] => SemiWiki Main Forum ( Ask the Experts! )
[description] => Post your questions to the experts here!
[node_name] =>
[node_type_id] => Forum
[parent_node_id] => 1
[display_order] => 1
[display_in_list] => 1
[lft] => 2
[rgt] => 3
[depth] => 1
[style_id] => 0
[effective_style_id] => 0
[breadcrumb_data] => {"1":{"node_id":1,"title":"Main Category","depth":0,"lft":1,"node_name":null,"node_type_id":"Category","display_in_list":true}}
[navigation_id] =>
[effective_navigation_id] =>
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
[24687] => ThemeHouse\XPress\XF\Entity\Thread Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 81
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\Thread
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[thread_id] => 24687
[node_id] => 2
[title] => US Considers Requiring Permits for Nvidia, AMD Global AI Chip Sales
[reply_count] => 6
[view_count] => 310
[user_id] => 5
[username] => Daniel Nenni
[post_date] => 1772813834
[sticky] => 0
[discussion_state] => visible
[discussion_open] => 1
[discussion_type] => discussion
[first_post_id] => 98138
[first_post_reaction_score] => 0
[first_post_reactions] => {"6":2}
[last_post_date] => 1772830398
[last_post_id] => 98146
[last_post_user_id] => 19450
[last_post_username] => user nl
[prefix_id] => 0
[tags] => []
[custom_fields] => []
[vote_score] => 0
[vote_count] => 0
[featured] => 0
[type_data] => []
[index_state] => default
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
[User] => ThemeHouse\XLink\XF\Entity\User Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 62
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\User
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[user_id] => 5
[username] => Daniel Nenni
[username_date] => 0
[username_date_visible] => 0
[email] => dnenni@semiwiki.com
[custom_title] => Admin
[language_id] => 1
[style_id] => 0
[style_variation] =>
[timezone] => America/Los_Angeles
[visible] => 1
[activity_visible] => 1
[user_group_id] => 3
[secondary_group_ids] => 4,5,132
[display_style_group_id] => 3
[permission_combination_id] => 88
[message_count] => 15330
[question_solution_count] => 0
[conversations_unread] => 0
[register_date] => 1280720820
[last_activity] => 1772877925
[last_summary_email_date] => 1605968657
[trophy_points] => 113
[alerts_unviewed] => 35
[alerts_unread] => 35
[avatar_date] => 1663211649
[avatar_width] => 110
[avatar_height] => 107
[avatar_highdpi] => 0
[avatar_optimized] => 0
[gravatar] =>
[user_state] => valid
[security_lock] =>
[is_moderator] => 1
[is_admin] => 1
[is_banned] => 0
[reaction_score] => 9187
[warning_points] => 0
[is_staff] => 1
[secret_key] => 0HwyUVVHCwJotUUVEpvqAclfYJdGNPpw
[privacy_policy_accepted] => 0
[terms_accepted] => 0
[vote_score] => 0
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
[Forum] => XF\Entity\Forum Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 56
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\Forum
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[node_id] => 2
[discussion_count] => 8388
[message_count] => 61505
[last_post_id] => 98163
[last_post_date] => 1772880454
[last_post_user_id] => 5185
[last_post_username] => Fred Chen
[last_thread_id] => 24684
[last_thread_title] => Build China’s ASML
[last_thread_prefix_id] => 0
[moderate_threads] => 0
[moderate_replies] => 0
[allow_posting] => 1
[count_messages] => 1
[auto_feature] => 0
[find_new] => 1
[allow_index] => allow
[index_criteria] =>
[field_cache] => []
[prefix_cache] => []
[prompt_cache] => []
[default_prefix_id] => 0
[default_sort_order] => last_post_date
[default_sort_direction] => desc
[list_date_limit_days] => 0
[require_prefix] => 0
[allowed_watch_notifications] => all
[min_tags] => 0
[forum_type_id] => discussion
[type_config] => {"allowed_thread_types":["poll"]}
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
[Node] => XF\Entity\Node Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 55
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\Node
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[node_id] => 2
[title] => SemiWiki Main Forum ( Ask the Experts! )
[description] => Post your questions to the experts here!
[node_name] =>
[node_type_id] => Forum
[parent_node_id] => 1
[display_order] => 1
[display_in_list] => 1
[lft] => 2
[rgt] => 3
[depth] => 1
[style_id] => 0
[effective_style_id] => 0
[breadcrumb_data] => {"1":{"node_id":1,"title":"Main Category","depth":0,"lft":1,"node_name":null,"node_type_id":"Category","display_in_list":true}}
[navigation_id] =>
[effective_navigation_id] =>
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
[24685] => ThemeHouse\XPress\XF\Entity\Thread Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 85
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\Thread
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[thread_id] => 24685
[node_id] => 2
[title] => Rapidus Corporation today announced that it has completed a funding round totaling $1.7 billion USD from the Japan government and private sector
[reply_count] => 0
[view_count] => 210
[user_id] => 5
[username] => Daniel Nenni
[post_date] => 1772795340
[sticky] => 0
[discussion_state] => visible
[discussion_open] => 1
[discussion_type] => discussion
[first_post_id] => 98125
[first_post_reaction_score] => 1
[first_post_reactions] => {"1":1}
[last_post_date] => 1772795340
[last_post_id] => 98125
[last_post_user_id] => 5
[last_post_username] => Daniel Nenni
[prefix_id] => 0
[tags] => []
[custom_fields] => []
[vote_score] => 0
[vote_count] => 0
[featured] => 0
[type_data] => []
[index_state] => default
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
[User] => ThemeHouse\XLink\XF\Entity\User Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 62
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\User
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[user_id] => 5
[username] => Daniel Nenni
[username_date] => 0
[username_date_visible] => 0
[email] => dnenni@semiwiki.com
[custom_title] => Admin
[language_id] => 1
[style_id] => 0
[style_variation] =>
[timezone] => America/Los_Angeles
[visible] => 1
[activity_visible] => 1
[user_group_id] => 3
[secondary_group_ids] => 4,5,132
[display_style_group_id] => 3
[permission_combination_id] => 88
[message_count] => 15330
[question_solution_count] => 0
[conversations_unread] => 0
[register_date] => 1280720820
[last_activity] => 1772877925
[last_summary_email_date] => 1605968657
[trophy_points] => 113
[alerts_unviewed] => 35
[alerts_unread] => 35
[avatar_date] => 1663211649
[avatar_width] => 110
[avatar_height] => 107
[avatar_highdpi] => 0
[avatar_optimized] => 0
[gravatar] =>
[user_state] => valid
[security_lock] =>
[is_moderator] => 1
[is_admin] => 1
[is_banned] => 0
[reaction_score] => 9187
[warning_points] => 0
[is_staff] => 1
[secret_key] => 0HwyUVVHCwJotUUVEpvqAclfYJdGNPpw
[privacy_policy_accepted] => 0
[terms_accepted] => 0
[vote_score] => 0
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
[Forum] => XF\Entity\Forum Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 56
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\Forum
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[node_id] => 2
[discussion_count] => 8388
[message_count] => 61505
[last_post_id] => 98163
[last_post_date] => 1772880454
[last_post_user_id] => 5185
[last_post_username] => Fred Chen
[last_thread_id] => 24684
[last_thread_title] => Build China’s ASML
[last_thread_prefix_id] => 0
[moderate_threads] => 0
[moderate_replies] => 0
[allow_posting] => 1
[count_messages] => 1
[auto_feature] => 0
[find_new] => 1
[allow_index] => allow
[index_criteria] =>
[field_cache] => []
[prefix_cache] => []
[prompt_cache] => []
[default_prefix_id] => 0
[default_sort_order] => last_post_date
[default_sort_direction] => desc
[list_date_limit_days] => 0
[require_prefix] => 0
[allowed_watch_notifications] => all
[min_tags] => 0
[forum_type_id] => discussion
[type_config] => {"allowed_thread_types":["poll"]}
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
[Node] => XF\Entity\Node Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 55
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\Node
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[node_id] => 2
[title] => SemiWiki Main Forum ( Ask the Experts! )
[description] => Post your questions to the experts here!
[node_name] =>
[node_type_id] => Forum
[parent_node_id] => 1
[display_order] => 1
[display_in_list] => 1
[lft] => 2
[rgt] => 3
[depth] => 1
[style_id] => 0
[effective_style_id] => 0
[breadcrumb_data] => {"1":{"node_id":1,"title":"Main Category","depth":0,"lft":1,"node_name":null,"node_type_id":"Category","display_in_list":true}}
[navigation_id] =>
[effective_navigation_id] =>
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
[24659] => ThemeHouse\XPress\XF\Entity\Thread Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 89
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\Thread
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[thread_id] => 24659
[node_id] => 2
[title] => OpenAI amends Pentagon deal as Sam Altman admits it looks ‘sloppy’
[reply_count] => 19
[view_count] => 922
[user_id] => 5
[username] => Daniel Nenni
[post_date] => 1772555708
[sticky] => 0
[discussion_state] => visible
[discussion_open] => 1
[discussion_type] => discussion
[first_post_id] => 98019
[first_post_reaction_score] => 1
[first_post_reactions] => {"1":1}
[last_post_date] => 1772747963
[last_post_id] => 98116
[last_post_user_id] => 38697
[last_post_username] => blueone
[prefix_id] => 0
[tags] => []
[custom_fields] => []
[vote_score] => 0
[vote_count] => 0
[featured] => 0
[type_data] => []
[index_state] => default
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
[User] => ThemeHouse\XLink\XF\Entity\User Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 62
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\User
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[user_id] => 5
[username] => Daniel Nenni
[username_date] => 0
[username_date_visible] => 0
[email] => dnenni@semiwiki.com
[custom_title] => Admin
[language_id] => 1
[style_id] => 0
[style_variation] =>
[timezone] => America/Los_Angeles
[visible] => 1
[activity_visible] => 1
[user_group_id] => 3
[secondary_group_ids] => 4,5,132
[display_style_group_id] => 3
[permission_combination_id] => 88
[message_count] => 15330
[question_solution_count] => 0
[conversations_unread] => 0
[register_date] => 1280720820
[last_activity] => 1772877925
[last_summary_email_date] => 1605968657
[trophy_points] => 113
[alerts_unviewed] => 35
[alerts_unread] => 35
[avatar_date] => 1663211649
[avatar_width] => 110
[avatar_height] => 107
[avatar_highdpi] => 0
[avatar_optimized] => 0
[gravatar] =>
[user_state] => valid
[security_lock] =>
[is_moderator] => 1
[is_admin] => 1
[is_banned] => 0
[reaction_score] => 9187
[warning_points] => 0
[is_staff] => 1
[secret_key] => 0HwyUVVHCwJotUUVEpvqAclfYJdGNPpw
[privacy_policy_accepted] => 0
[terms_accepted] => 0
[vote_score] => 0
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
[Forum] => XF\Entity\Forum Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 56
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\Forum
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[node_id] => 2
[discussion_count] => 8388
[message_count] => 61505
[last_post_id] => 98163
[last_post_date] => 1772880454
[last_post_user_id] => 5185
[last_post_username] => Fred Chen
[last_thread_id] => 24684
[last_thread_title] => Build China’s ASML
[last_thread_prefix_id] => 0
[moderate_threads] => 0
[moderate_replies] => 0
[allow_posting] => 1
[count_messages] => 1
[auto_feature] => 0
[find_new] => 1
[allow_index] => allow
[index_criteria] =>
[field_cache] => []
[prefix_cache] => []
[prompt_cache] => []
[default_prefix_id] => 0
[default_sort_order] => last_post_date
[default_sort_direction] => desc
[list_date_limit_days] => 0
[require_prefix] => 0
[allowed_watch_notifications] => all
[min_tags] => 0
[forum_type_id] => discussion
[type_config] => {"allowed_thread_types":["poll"]}
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
[Node] => XF\Entity\Node Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 55
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\Node
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[node_id] => 2
[title] => SemiWiki Main Forum ( Ask the Experts! )
[description] => Post your questions to the experts here!
[node_name] =>
[node_type_id] => Forum
[parent_node_id] => 1
[display_order] => 1
[display_in_list] => 1
[lft] => 2
[rgt] => 3
[depth] => 1
[style_id] => 0
[effective_style_id] => 0
[breadcrumb_data] => {"1":{"node_id":1,"title":"Main Category","depth":0,"lft":1,"node_name":null,"node_type_id":"Category","display_in_list":true}}
[navigation_id] =>
[effective_navigation_id] =>
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
[24678] => ThemeHouse\XPress\XF\Entity\Thread Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 93
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\Thread
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[thread_id] => 24678
[node_id] => 2
[title] => I'm having trouble understanding Broadcom's claimed AI revenue results and projections
[reply_count] => 17
[view_count] => 874
[user_id] => 38697
[username] => blueone
[post_date] => 1772681440
[sticky] => 0
[discussion_state] => visible
[discussion_open] => 1
[discussion_type] => discussion
[first_post_id] => 98065
[first_post_reaction_score] => 0
[first_post_reactions] => []
[last_post_date] => 1772740907
[last_post_id] => 98113
[last_post_user_id] => 6522
[last_post_username] => IanD
[prefix_id] => 0
[tags] => []
[custom_fields] => []
[vote_score] => 0
[vote_count] => 0
[featured] => 0
[type_data] => []
[index_state] => default
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
[User] => ThemeHouse\XLink\XF\Entity\User Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 70
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\User
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[user_id] => 38697
[username] => blueone
[username_date] => 0
[username_date_visible] => 0
[email] => rob8633@hotmail.com
[custom_title] =>
[language_id] => 1
[style_id] => 0
[style_variation] =>
[timezone] => America/Denver
[visible] => 0
[activity_visible] => 0
[user_group_id] => 2
[secondary_group_ids] =>
[display_style_group_id] => 2
[permission_combination_id] => 8
[message_count] => 2539
[question_solution_count] => 0
[conversations_unread] => 0
[register_date] => 1621824096
[last_activity] => 1772851357
[last_summary_email_date] =>
[trophy_points] => 113
[alerts_unviewed] => 0
[alerts_unread] => 0
[avatar_date] => 0
[avatar_width] => 0
[avatar_height] => 0
[avatar_highdpi] => 0
[avatar_optimized] => 0
[gravatar] =>
[user_state] => valid
[security_lock] =>
[is_moderator] => 0
[is_admin] => 0
[is_banned] => 0
[reaction_score] => 3368
[warning_points] => 0
[is_staff] => 0
[secret_key] => aGlUsVcP2cy-QllnjVLMCtpGT8e-_F_T
[privacy_policy_accepted] => 1621824096
[terms_accepted] => 1621824096
[vote_score] => 0
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
[Forum] => XF\Entity\Forum Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 56
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\Forum
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[node_id] => 2
[discussion_count] => 8388
[message_count] => 61505
[last_post_id] => 98163
[last_post_date] => 1772880454
[last_post_user_id] => 5185
[last_post_username] => Fred Chen
[last_thread_id] => 24684
[last_thread_title] => Build China’s ASML
[last_thread_prefix_id] => 0
[moderate_threads] => 0
[moderate_replies] => 0
[allow_posting] => 1
[count_messages] => 1
[auto_feature] => 0
[find_new] => 1
[allow_index] => allow
[index_criteria] =>
[field_cache] => []
[prefix_cache] => []
[prompt_cache] => []
[default_prefix_id] => 0
[default_sort_order] => last_post_date
[default_sort_direction] => desc
[list_date_limit_days] => 0
[require_prefix] => 0
[allowed_watch_notifications] => all
[min_tags] => 0
[forum_type_id] => discussion
[type_config] => {"allowed_thread_types":["poll"]}
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
[Node] => XF\Entity\Node Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 55
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\Node
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[node_id] => 2
[title] => SemiWiki Main Forum ( Ask the Experts! )
[description] => Post your questions to the experts here!
[node_name] =>
[node_type_id] => Forum
[parent_node_id] => 1
[display_order] => 1
[display_in_list] => 1
[lft] => 2
[rgt] => 3
[depth] => 1
[style_id] => 0
[effective_style_id] => 0
[breadcrumb_data] => {"1":{"node_id":1,"title":"Main Category","depth":0,"lft":1,"node_name":null,"node_type_id":"Category","display_in_list":true}}
[navigation_id] =>
[effective_navigation_id] =>
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
[24683] => ThemeHouse\XPress\XF\Entity\Thread Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 97
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\Thread
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[thread_id] => 24683
[node_id] => 2
[title] => How a Taiwanese VC Broke Into the Commercial Space Industry
[reply_count] => 0
[view_count] => 184
[user_id] => 398583
[username] => karin623
[post_date] => 1772732518
[sticky] => 0
[discussion_state] => visible
[discussion_open] => 1
[discussion_type] => discussion
[first_post_id] => 98109
[first_post_reaction_score] => 1
[first_post_reactions] => {"1":1}
[last_post_date] => 1772732518
[last_post_id] => 98109
[last_post_user_id] => 398583
[last_post_username] => karin623
[prefix_id] => 0
[tags] => []
[custom_fields] => []
[vote_score] => 0
[vote_count] => 0
[featured] => 0
[type_data] => []
[index_state] => default
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
[User] => ThemeHouse\XLink\XF\Entity\User Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 94
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\User
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[user_id] => 398583
[username] => karin623
[username_date] => 0
[username_date_visible] => 0
[email] => karin623@gmail.com
[custom_title] =>
[language_id] => 1
[style_id] => 0
[style_variation] =>
[timezone] => Asia/Hong_Kong
[visible] => 1
[activity_visible] => 1
[user_group_id] => 2
[secondary_group_ids] =>
[display_style_group_id] => 2
[permission_combination_id] => 8
[message_count] => 37
[question_solution_count] => 0
[conversations_unread] => 0
[register_date] => 1748753435
[last_activity] => 1772732518
[last_summary_email_date] => 1771856462
[trophy_points] => 18
[alerts_unviewed] => 6
[alerts_unread] => 6
[avatar_date] => 0
[avatar_width] => 0
[avatar_height] => 0
[avatar_highdpi] => 0
[avatar_optimized] => 0
[gravatar] =>
[user_state] => valid
[security_lock] =>
[is_moderator] => 0
[is_admin] => 0
[is_banned] => 0
[reaction_score] => 60
[warning_points] => 0
[is_staff] => 0
[secret_key] => PBnrLVmUtkEL7YUKL8Ij_6L3tfKYRzDQ
[privacy_policy_accepted] => 1748753435
[terms_accepted] => 1748753435
[vote_score] => 0
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
[Forum] => XF\Entity\Forum Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 56
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\Forum
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[node_id] => 2
[discussion_count] => 8388
[message_count] => 61505
[last_post_id] => 98163
[last_post_date] => 1772880454
[last_post_user_id] => 5185
[last_post_username] => Fred Chen
[last_thread_id] => 24684
[last_thread_title] => Build China’s ASML
[last_thread_prefix_id] => 0
[moderate_threads] => 0
[moderate_replies] => 0
[allow_posting] => 1
[count_messages] => 1
[auto_feature] => 0
[find_new] => 1
[allow_index] => allow
[index_criteria] =>
[field_cache] => []
[prefix_cache] => []
[prompt_cache] => []
[default_prefix_id] => 0
[default_sort_order] => last_post_date
[default_sort_direction] => desc
[list_date_limit_days] => 0
[require_prefix] => 0
[allowed_watch_notifications] => all
[min_tags] => 0
[forum_type_id] => discussion
[type_config] => {"allowed_thread_types":["poll"]}
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
[Node] => XF\Entity\Node Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 55
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\Node
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[node_id] => 2
[title] => SemiWiki Main Forum ( Ask the Experts! )
[description] => Post your questions to the experts here!
[node_name] =>
[node_type_id] => Forum
[parent_node_id] => 1
[display_order] => 1
[display_in_list] => 1
[lft] => 2
[rgt] => 3
[depth] => 1
[style_id] => 0
[effective_style_id] => 0
[breadcrumb_data] => {"1":{"node_id":1,"title":"Main Category","depth":0,"lft":1,"node_name":null,"node_type_id":"Category","display_in_list":true}}
[navigation_id] =>
[effective_navigation_id] =>
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
[24682] => ThemeHouse\XPress\XF\Entity\Thread Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 101
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\Thread
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[thread_id] => 24682
[node_id] => 2
[title] => US lawmakers raise concerns over Intel's testing of tools made by Chinese-linked firm
[reply_count] => 0
[view_count] => 270
[user_id] => 5
[username] => Daniel Nenni
[post_date] => 1772717696
[sticky] => 0
[discussion_state] => visible
[discussion_open] => 1
[discussion_type] => discussion
[first_post_id] => 98075
[first_post_reaction_score] => 0
[first_post_reactions] => []
[last_post_date] => 1772717696
[last_post_id] => 98075
[last_post_user_id] => 5
[last_post_username] => Daniel Nenni
[prefix_id] => 0
[tags] => []
[custom_fields] => []
[vote_score] => 0
[vote_count] => 0
[featured] => 0
[type_data] => []
[index_state] => default
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
[User] => ThemeHouse\XLink\XF\Entity\User Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 62
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\User
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[user_id] => 5
[username] => Daniel Nenni
[username_date] => 0
[username_date_visible] => 0
[email] => dnenni@semiwiki.com
[custom_title] => Admin
[language_id] => 1
[style_id] => 0
[style_variation] =>
[timezone] => America/Los_Angeles
[visible] => 1
[activity_visible] => 1
[user_group_id] => 3
[secondary_group_ids] => 4,5,132
[display_style_group_id] => 3
[permission_combination_id] => 88
[message_count] => 15330
[question_solution_count] => 0
[conversations_unread] => 0
[register_date] => 1280720820
[last_activity] => 1772877925
[last_summary_email_date] => 1605968657
[trophy_points] => 113
[alerts_unviewed] => 35
[alerts_unread] => 35
[avatar_date] => 1663211649
[avatar_width] => 110
[avatar_height] => 107
[avatar_highdpi] => 0
[avatar_optimized] => 0
[gravatar] =>
[user_state] => valid
[security_lock] =>
[is_moderator] => 1
[is_admin] => 1
[is_banned] => 0
[reaction_score] => 9187
[warning_points] => 0
[is_staff] => 1
[secret_key] => 0HwyUVVHCwJotUUVEpvqAclfYJdGNPpw
[privacy_policy_accepted] => 0
[terms_accepted] => 0
[vote_score] => 0
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
[Forum] => XF\Entity\Forum Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 56
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\Forum
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[node_id] => 2
[discussion_count] => 8388
[message_count] => 61505
[last_post_id] => 98163
[last_post_date] => 1772880454
[last_post_user_id] => 5185
[last_post_username] => Fred Chen
[last_thread_id] => 24684
[last_thread_title] => Build China’s ASML
[last_thread_prefix_id] => 0
[moderate_threads] => 0
[moderate_replies] => 0
[allow_posting] => 1
[count_messages] => 1
[auto_feature] => 0
[find_new] => 1
[allow_index] => allow
[index_criteria] =>
[field_cache] => []
[prefix_cache] => []
[prompt_cache] => []
[default_prefix_id] => 0
[default_sort_order] => last_post_date
[default_sort_direction] => desc
[list_date_limit_days] => 0
[require_prefix] => 0
[allowed_watch_notifications] => all
[min_tags] => 0
[forum_type_id] => discussion
[type_config] => {"allowed_thread_types":["poll"]}
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
[Node] => XF\Entity\Node Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 55
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\Node
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[node_id] => 2
[title] => SemiWiki Main Forum ( Ask the Experts! )
[description] => Post your questions to the experts here!
[node_name] =>
[node_type_id] => Forum
[parent_node_id] => 1
[display_order] => 1
[display_in_list] => 1
[lft] => 2
[rgt] => 3
[depth] => 1
[style_id] => 0
[effective_style_id] => 0
[breadcrumb_data] => {"1":{"node_id":1,"title":"Main Category","depth":0,"lft":1,"node_name":null,"node_type_id":"Category","display_in_list":true}}
[navigation_id] =>
[effective_navigation_id] =>
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
[24677] => ThemeHouse\XPress\XF\Entity\Thread Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 105
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\Thread
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[thread_id] => 24677
[node_id] => 2
[title] => Intel at Morgan Stanley Conference, 2026-Mar-04
[reply_count] => 1
[view_count] => 552
[user_id] => 90385
[username] => NY_Sam2
[post_date] => 1772675670
[sticky] => 0
[discussion_state] => visible
[discussion_open] => 1
[discussion_type] => discussion
[first_post_id] => 98063
[first_post_reaction_score] => 1
[first_post_reactions] => {"1":1}
[last_post_date] => 1772691071
[last_post_id] => 98068
[last_post_user_id] => 90182
[last_post_username] => siliconbruh999
[prefix_id] => 0
[tags] => []
[custom_fields] => []
[vote_score] => 0
[vote_count] => 0
[featured] => 0
[type_data] => []
[index_state] => default
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
[User] => ThemeHouse\XLink\XF\Entity\User Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 102
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\User
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[user_id] => 90385
[username] => NY_Sam2
[username_date] => 0
[username_date_visible] => 0
[email] => petekennedy1989@gmail.com
[custom_title] =>
[language_id] => 1
[style_id] => 0
[style_variation] =>
[timezone] => America/New_York
[visible] => 1
[activity_visible] => 1
[user_group_id] => 2
[secondary_group_ids] =>
[display_style_group_id] => 2
[permission_combination_id] => 8
[message_count] => 28
[question_solution_count] => 0
[conversations_unread] => 0
[register_date] => 1642621712
[last_activity] => 1772814040
[last_summary_email_date] => 1767709207
[trophy_points] => 13
[alerts_unviewed] => 19
[alerts_unread] => 19
[avatar_date] => 0
[avatar_width] => 0
[avatar_height] => 0
[avatar_highdpi] => 0
[avatar_optimized] => 0
[gravatar] =>
[user_state] => valid
[security_lock] =>
[is_moderator] => 0
[is_admin] => 0
[is_banned] => 0
[reaction_score] => 42
[warning_points] => 0
[is_staff] => 0
[secret_key] => egi-LmWHpsbQRZ7Y0Lk56hMyhUsrDhDE
[privacy_policy_accepted] => 1642621712
[terms_accepted] => 1642621712
[vote_score] => 0
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
[Forum] => XF\Entity\Forum Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 56
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\Forum
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[node_id] => 2
[discussion_count] => 8388
[message_count] => 61505
[last_post_id] => 98163
[last_post_date] => 1772880454
[last_post_user_id] => 5185
[last_post_username] => Fred Chen
[last_thread_id] => 24684
[last_thread_title] => Build China’s ASML
[last_thread_prefix_id] => 0
[moderate_threads] => 0
[moderate_replies] => 0
[allow_posting] => 1
[count_messages] => 1
[auto_feature] => 0
[find_new] => 1
[allow_index] => allow
[index_criteria] =>
[field_cache] => []
[prefix_cache] => []
[prompt_cache] => []
[default_prefix_id] => 0
[default_sort_order] => last_post_date
[default_sort_direction] => desc
[list_date_limit_days] => 0
[require_prefix] => 0
[allowed_watch_notifications] => all
[min_tags] => 0
[forum_type_id] => discussion
[type_config] => {"allowed_thread_types":["poll"]}
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
[Node] => XF\Entity\Node Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 55
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\Node
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[node_id] => 2
[title] => SemiWiki Main Forum ( Ask the Experts! )
[description] => Post your questions to the experts here!
[node_name] =>
[node_type_id] => Forum
[parent_node_id] => 1
[display_order] => 1
[display_in_list] => 1
[lft] => 2
[rgt] => 3
[depth] => 1
[style_id] => 0
[effective_style_id] => 0
[breadcrumb_data] => {"1":{"node_id":1,"title":"Main Category","depth":0,"lft":1,"node_name":null,"node_type_id":"Category","display_in_list":true}}
[navigation_id] =>
[effective_navigation_id] =>
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
[24660] => ThemeHouse\XPress\XF\Entity\Thread Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 109
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\Thread
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[thread_id] => 24660
[node_id] => 2
[title] => Intel Board Chair Frank D. Yeary to Retire Following Annual Meeting; Dr. Craig H. Barratt Elected as Chair
[reply_count] => 6
[view_count] => 920
[user_id] => 5
[username] => Daniel Nenni
[post_date] => 1772584001
[sticky] => 0
[discussion_state] => visible
[discussion_open] => 1
[discussion_type] => discussion
[first_post_id] => 98031
[first_post_reaction_score] => 3
[first_post_reactions] => {"1":3}
[last_post_date] => 1772682072
[last_post_id] => 98066
[last_post_user_id] => 38697
[last_post_username] => blueone
[prefix_id] => 0
[tags] => []
[custom_fields] => []
[vote_score] => 0
[vote_count] => 0
[featured] => 0
[type_data] => []
[index_state] => default
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
[User] => ThemeHouse\XLink\XF\Entity\User Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 62
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\User
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[user_id] => 5
[username] => Daniel Nenni
[username_date] => 0
[username_date_visible] => 0
[email] => dnenni@semiwiki.com
[custom_title] => Admin
[language_id] => 1
[style_id] => 0
[style_variation] =>
[timezone] => America/Los_Angeles
[visible] => 1
[activity_visible] => 1
[user_group_id] => 3
[secondary_group_ids] => 4,5,132
[display_style_group_id] => 3
[permission_combination_id] => 88
[message_count] => 15330
[question_solution_count] => 0
[conversations_unread] => 0
[register_date] => 1280720820
[last_activity] => 1772877925
[last_summary_email_date] => 1605968657
[trophy_points] => 113
[alerts_unviewed] => 35
[alerts_unread] => 35
[avatar_date] => 1663211649
[avatar_width] => 110
[avatar_height] => 107
[avatar_highdpi] => 0
[avatar_optimized] => 0
[gravatar] =>
[user_state] => valid
[security_lock] =>
[is_moderator] => 1
[is_admin] => 1
[is_banned] => 0
[reaction_score] => 9187
[warning_points] => 0
[is_staff] => 1
[secret_key] => 0HwyUVVHCwJotUUVEpvqAclfYJdGNPpw
[privacy_policy_accepted] => 0
[terms_accepted] => 0
[vote_score] => 0
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
[Forum] => XF\Entity\Forum Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 56
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\Forum
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[node_id] => 2
[discussion_count] => 8388
[message_count] => 61505
[last_post_id] => 98163
[last_post_date] => 1772880454
[last_post_user_id] => 5185
[last_post_username] => Fred Chen
[last_thread_id] => 24684
[last_thread_title] => Build China’s ASML
[last_thread_prefix_id] => 0
[moderate_threads] => 0
[moderate_replies] => 0
[allow_posting] => 1
[count_messages] => 1
[auto_feature] => 0
[find_new] => 1
[allow_index] => allow
[index_criteria] =>
[field_cache] => []
[prefix_cache] => []
[prompt_cache] => []
[default_prefix_id] => 0
[default_sort_order] => last_post_date
[default_sort_direction] => desc
[list_date_limit_days] => 0
[require_prefix] => 0
[allowed_watch_notifications] => all
[min_tags] => 0
[forum_type_id] => discussion
[type_config] => {"allowed_thread_types":["poll"]}
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
[Node] => XF\Entity\Node Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 55
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\Node
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[node_id] => 2
[title] => SemiWiki Main Forum ( Ask the Experts! )
[description] => Post your questions to the experts here!
[node_name] =>
[node_type_id] => Forum
[parent_node_id] => 1
[display_order] => 1
[display_in_list] => 1
[lft] => 2
[rgt] => 3
[depth] => 1
[style_id] => 0
[effective_style_id] => 0
[breadcrumb_data] => {"1":{"node_id":1,"title":"Main Category","depth":0,"lft":1,"node_name":null,"node_type_id":"Category","display_in_list":true}}
[navigation_id] =>
[effective_navigation_id] =>
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
[24676] => ThemeHouse\XPress\XF\Entity\Thread Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 113
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\Thread
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[thread_id] => 24676
[node_id] => 2
[title] => Exclusive: ASML plots future of chipmaking tools for AI beyond EUV
[reply_count] => 0
[view_count] => 223
[user_id] => 5185
[username] => Fred Chen
[post_date] => 1772675421
[sticky] => 0
[discussion_state] => visible
[discussion_open] => 1
[discussion_type] => discussion
[first_post_id] => 98062
[first_post_reaction_score] => 0
[first_post_reactions] => []
[last_post_date] => 1772675421
[last_post_id] => 98062
[last_post_user_id] => 5185
[last_post_username] => Fred Chen
[prefix_id] => 0
[tags] => []
[custom_fields] => []
[vote_score] => 0
[vote_count] => 0
[featured] => 0
[type_data] => []
[index_state] => default
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
[User] => ThemeHouse\XLink\XF\Entity\User Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 58
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\User
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[user_id] => 5185
[username] => Fred Chen
[username_date] => 0
[username_date_visible] => 0
[email] => chen.t.fred@gmail.com
[custom_title] =>
[language_id] => 1
[style_id] => 0
[style_variation] =>
[timezone] => America/Los_Angeles
[visible] => 1
[activity_visible] => 1
[user_group_id] => 4
[secondary_group_ids] =>
[display_style_group_id] => 4
[permission_combination_id] => 92
[message_count] => 2555
[question_solution_count] => 0
[conversations_unread] => 0
[register_date] => 1333032401
[last_activity] => 1772880818
[last_summary_email_date] => 1605940563
[trophy_points] => 113
[alerts_unviewed] => 0
[alerts_unread] => 1
[avatar_date] => 0
[avatar_width] => 0
[avatar_height] => 0
[avatar_highdpi] => 0
[avatar_optimized] => 0
[gravatar] =>
[user_state] => valid
[security_lock] =>
[is_moderator] => 0
[is_admin] => 0
[is_banned] => 0
[reaction_score] => 1860
[warning_points] => 0
[is_staff] => 0
[secret_key] => 5m-bZq0HRSi9VA-96QONHJeevdQas5S8
[privacy_policy_accepted] => 0
[terms_accepted] => 0
[vote_score] => 0
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
[Forum] => XF\Entity\Forum Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 56
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\Forum
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[node_id] => 2
[discussion_count] => 8388
[message_count] => 61505
[last_post_id] => 98163
[last_post_date] => 1772880454
[last_post_user_id] => 5185
[last_post_username] => Fred Chen
[last_thread_id] => 24684
[last_thread_title] => Build China’s ASML
[last_thread_prefix_id] => 0
[moderate_threads] => 0
[moderate_replies] => 0
[allow_posting] => 1
[count_messages] => 1
[auto_feature] => 0
[find_new] => 1
[allow_index] => allow
[index_criteria] =>
[field_cache] => []
[prefix_cache] => []
[prompt_cache] => []
[default_prefix_id] => 0
[default_sort_order] => last_post_date
[default_sort_direction] => desc
[list_date_limit_days] => 0
[require_prefix] => 0
[allowed_watch_notifications] => all
[min_tags] => 0
[forum_type_id] => discussion
[type_config] => {"allowed_thread_types":["poll"]}
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
[Node] => XF\Entity\Node Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 55
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\Node
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[node_id] => 2
[title] => SemiWiki Main Forum ( Ask the Experts! )
[description] => Post your questions to the experts here!
[node_name] =>
[node_type_id] => Forum
[parent_node_id] => 1
[display_order] => 1
[display_in_list] => 1
[lft] => 2
[rgt] => 3
[depth] => 1
[style_id] => 0
[effective_style_id] => 0
[breadcrumb_data] => {"1":{"node_id":1,"title":"Main Category","depth":0,"lft":1,"node_name":null,"node_type_id":"Category","display_in_list":true}}
[navigation_id] =>
[effective_navigation_id] =>
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
[24662] => ThemeHouse\XPress\XF\Entity\Thread Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 117
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\Thread
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[thread_id] => 24662
[node_id] => 2
[title] => Apple Orders More Arizona Chips As TSMC Valuation Premium Draws Focus
[reply_count] => 1
[view_count] => 304
[user_id] => 5
[username] => Daniel Nenni
[post_date] => 1772658928
[sticky] => 0
[discussion_state] => visible
[discussion_open] => 1
[discussion_type] => discussion
[first_post_id] => 98047
[first_post_reaction_score] => 0
[first_post_reactions] => []
[last_post_date] => 1772659176
[last_post_id] => 98048
[last_post_user_id] => 5
[last_post_username] => Daniel Nenni
[prefix_id] => 0
[tags] => []
[custom_fields] => []
[vote_score] => 0
[vote_count] => 0
[featured] => 0
[type_data] => []
[index_state] => default
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
[User] => ThemeHouse\XLink\XF\Entity\User Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 62
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\User
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[user_id] => 5
[username] => Daniel Nenni
[username_date] => 0
[username_date_visible] => 0
[email] => dnenni@semiwiki.com
[custom_title] => Admin
[language_id] => 1
[style_id] => 0
[style_variation] =>
[timezone] => America/Los_Angeles
[visible] => 1
[activity_visible] => 1
[user_group_id] => 3
[secondary_group_ids] => 4,5,132
[display_style_group_id] => 3
[permission_combination_id] => 88
[message_count] => 15330
[question_solution_count] => 0
[conversations_unread] => 0
[register_date] => 1280720820
[last_activity] => 1772877925
[last_summary_email_date] => 1605968657
[trophy_points] => 113
[alerts_unviewed] => 35
[alerts_unread] => 35
[avatar_date] => 1663211649
[avatar_width] => 110
[avatar_height] => 107
[avatar_highdpi] => 0
[avatar_optimized] => 0
[gravatar] =>
[user_state] => valid
[security_lock] =>
[is_moderator] => 1
[is_admin] => 1
[is_banned] => 0
[reaction_score] => 9187
[warning_points] => 0
[is_staff] => 1
[secret_key] => 0HwyUVVHCwJotUUVEpvqAclfYJdGNPpw
[privacy_policy_accepted] => 0
[terms_accepted] => 0
[vote_score] => 0
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
[Forum] => XF\Entity\Forum Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 56
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\Forum
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[node_id] => 2
[discussion_count] => 8388
[message_count] => 61505
[last_post_id] => 98163
[last_post_date] => 1772880454
[last_post_user_id] => 5185
[last_post_username] => Fred Chen
[last_thread_id] => 24684
[last_thread_title] => Build China’s ASML
[last_thread_prefix_id] => 0
[moderate_threads] => 0
[moderate_replies] => 0
[allow_posting] => 1
[count_messages] => 1
[auto_feature] => 0
[find_new] => 1
[allow_index] => allow
[index_criteria] =>
[field_cache] => []
[prefix_cache] => []
[prompt_cache] => []
[default_prefix_id] => 0
[default_sort_order] => last_post_date
[default_sort_direction] => desc
[list_date_limit_days] => 0
[require_prefix] => 0
[allowed_watch_notifications] => all
[min_tags] => 0
[forum_type_id] => discussion
[type_config] => {"allowed_thread_types":["poll"]}
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
[Node] => XF\Entity\Node Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 55
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\Node
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[node_id] => 2
[title] => SemiWiki Main Forum ( Ask the Experts! )
[description] => Post your questions to the experts here!
[node_name] =>
[node_type_id] => Forum
[parent_node_id] => 1
[display_order] => 1
[display_in_list] => 1
[lft] => 2
[rgt] => 3
[depth] => 1
[style_id] => 0
[effective_style_id] => 0
[breadcrumb_data] => {"1":{"node_id":1,"title":"Main Category","depth":0,"lft":1,"node_name":null,"node_type_id":"Category","display_in_list":true}}
[navigation_id] =>
[effective_navigation_id] =>
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
[24656] => ThemeHouse\XPress\XF\Entity\Thread Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 121
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\Thread
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[thread_id] => 24656
[node_id] => 2
[title] => Press Kit: Intel at MWC Barcelona 2026
[reply_count] => 3
[view_count] => 881
[user_id] => 5
[username] => Daniel Nenni
[post_date] => 1772506885
[sticky] => 0
[discussion_state] => visible
[discussion_open] => 1
[discussion_type] => discussion
[first_post_id] => 98009
[first_post_reaction_score] => 0
[first_post_reactions] => []
[last_post_date] => 1772598530
[last_post_id] => 98043
[last_post_user_id] => 90182
[last_post_username] => siliconbruh999
[prefix_id] => 0
[tags] => []
[custom_fields] => []
[vote_score] => 0
[vote_count] => 0
[featured] => 0
[type_data] => []
[index_state] => default
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
[User] => ThemeHouse\XLink\XF\Entity\User Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 62
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\User
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[user_id] => 5
[username] => Daniel Nenni
[username_date] => 0
[username_date_visible] => 0
[email] => dnenni@semiwiki.com
[custom_title] => Admin
[language_id] => 1
[style_id] => 0
[style_variation] =>
[timezone] => America/Los_Angeles
[visible] => 1
[activity_visible] => 1
[user_group_id] => 3
[secondary_group_ids] => 4,5,132
[display_style_group_id] => 3
[permission_combination_id] => 88
[message_count] => 15330
[question_solution_count] => 0
[conversations_unread] => 0
[register_date] => 1280720820
[last_activity] => 1772877925
[last_summary_email_date] => 1605968657
[trophy_points] => 113
[alerts_unviewed] => 35
[alerts_unread] => 35
[avatar_date] => 1663211649
[avatar_width] => 110
[avatar_height] => 107
[avatar_highdpi] => 0
[avatar_optimized] => 0
[gravatar] =>
[user_state] => valid
[security_lock] =>
[is_moderator] => 1
[is_admin] => 1
[is_banned] => 0
[reaction_score] => 9187
[warning_points] => 0
[is_staff] => 1
[secret_key] => 0HwyUVVHCwJotUUVEpvqAclfYJdGNPpw
[privacy_policy_accepted] => 0
[terms_accepted] => 0
[vote_score] => 0
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
[Forum] => XF\Entity\Forum Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 56
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\Forum
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[node_id] => 2
[discussion_count] => 8388
[message_count] => 61505
[last_post_id] => 98163
[last_post_date] => 1772880454
[last_post_user_id] => 5185
[last_post_username] => Fred Chen
[last_thread_id] => 24684
[last_thread_title] => Build China’s ASML
[last_thread_prefix_id] => 0
[moderate_threads] => 0
[moderate_replies] => 0
[allow_posting] => 1
[count_messages] => 1
[auto_feature] => 0
[find_new] => 1
[allow_index] => allow
[index_criteria] =>
[field_cache] => []
[prefix_cache] => []
[prompt_cache] => []
[default_prefix_id] => 0
[default_sort_order] => last_post_date
[default_sort_direction] => desc
[list_date_limit_days] => 0
[require_prefix] => 0
[allowed_watch_notifications] => all
[min_tags] => 0
[forum_type_id] => discussion
[type_config] => {"allowed_thread_types":["poll"]}
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
[Node] => XF\Entity\Node Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 55
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\Node
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[node_id] => 2
[title] => SemiWiki Main Forum ( Ask the Experts! )
[description] => Post your questions to the experts here!
[node_name] =>
[node_type_id] => Forum
[parent_node_id] => 1
[display_order] => 1
[display_in_list] => 1
[lft] => 2
[rgt] => 3
[depth] => 1
[style_id] => 0
[effective_style_id] => 0
[breadcrumb_data] => {"1":{"node_id":1,"title":"Main Category","depth":0,"lft":1,"node_name":null,"node_type_id":"Category","display_in_list":true}}
[navigation_id] =>
[effective_navigation_id] =>
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
[24628] => ThemeHouse\XPress\XF\Entity\Thread Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 125
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\Thread
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[thread_id] => 24628
[node_id] => 2
[title] => Chinese DDR5 RAM: Is This the Solution to Crazy Memory Prices?
[reply_count] => 7
[view_count] => 1364
[user_id] => 5185
[username] => Fred Chen
[post_date] => 1772264219
[sticky] => 0
[discussion_state] => visible
[discussion_open] => 1
[discussion_type] => discussion
[first_post_id] => 97928
[first_post_reaction_score] => 0
[first_post_reactions] => []
[last_post_date] => 1772594289
[last_post_id] => 98040
[last_post_user_id] => 5185
[last_post_username] => Fred Chen
[prefix_id] => 0
[tags] => []
[custom_fields] => []
[vote_score] => 0
[vote_count] => 0
[featured] => 0
[type_data] => []
[index_state] => default
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
[User] => ThemeHouse\XLink\XF\Entity\User Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 58
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\User
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[user_id] => 5185
[username] => Fred Chen
[username_date] => 0
[username_date_visible] => 0
[email] => chen.t.fred@gmail.com
[custom_title] =>
[language_id] => 1
[style_id] => 0
[style_variation] =>
[timezone] => America/Los_Angeles
[visible] => 1
[activity_visible] => 1
[user_group_id] => 4
[secondary_group_ids] =>
[display_style_group_id] => 4
[permission_combination_id] => 92
[message_count] => 2555
[question_solution_count] => 0
[conversations_unread] => 0
[register_date] => 1333032401
[last_activity] => 1772880818
[last_summary_email_date] => 1605940563
[trophy_points] => 113
[alerts_unviewed] => 0
[alerts_unread] => 1
[avatar_date] => 0
[avatar_width] => 0
[avatar_height] => 0
[avatar_highdpi] => 0
[avatar_optimized] => 0
[gravatar] =>
[user_state] => valid
[security_lock] =>
[is_moderator] => 0
[is_admin] => 0
[is_banned] => 0
[reaction_score] => 1860
[warning_points] => 0
[is_staff] => 0
[secret_key] => 5m-bZq0HRSi9VA-96QONHJeevdQas5S8
[privacy_policy_accepted] => 0
[terms_accepted] => 0
[vote_score] => 0
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
[Forum] => XF\Entity\Forum Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 56
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\Forum
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[node_id] => 2
[discussion_count] => 8388
[message_count] => 61505
[last_post_id] => 98163
[last_post_date] => 1772880454
[last_post_user_id] => 5185
[last_post_username] => Fred Chen
[last_thread_id] => 24684
[last_thread_title] => Build China’s ASML
[last_thread_prefix_id] => 0
[moderate_threads] => 0
[moderate_replies] => 0
[allow_posting] => 1
[count_messages] => 1
[auto_feature] => 0
[find_new] => 1
[allow_index] => allow
[index_criteria] =>
[field_cache] => []
[prefix_cache] => []
[prompt_cache] => []
[default_prefix_id] => 0
[default_sort_order] => last_post_date
[default_sort_direction] => desc
[list_date_limit_days] => 0
[require_prefix] => 0
[allowed_watch_notifications] => all
[min_tags] => 0
[forum_type_id] => discussion
[type_config] => {"allowed_thread_types":["poll"]}
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
[Node] => XF\Entity\Node Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 55
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\Node
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[node_id] => 2
[title] => SemiWiki Main Forum ( Ask the Experts! )
[description] => Post your questions to the experts here!
[node_name] =>
[node_type_id] => Forum
[parent_node_id] => 1
[display_order] => 1
[display_in_list] => 1
[lft] => 2
[rgt] => 3
[depth] => 1
[style_id] => 0
[effective_style_id] => 0
[breadcrumb_data] => {"1":{"node_id":1,"title":"Main Category","depth":0,"lft":1,"node_name":null,"node_type_id":"Category","display_in_list":true}}
[navigation_id] =>
[effective_navigation_id] =>
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
[24607] => ThemeHouse\XPress\XF\Entity\Thread Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 129
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\Thread
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[thread_id] => 24607
[node_id] => 2
[title] => The Looming Taiwan Chip Disaster That Silicon Valley Has Long Ignored
[reply_count] => 12
[view_count] => 2550
[user_id] => 5
[username] => Daniel Nenni
[post_date] => 1771919951
[sticky] => 0
[discussion_state] => visible
[discussion_open] => 1
[discussion_type] => discussion
[first_post_id] => 97767
[first_post_reaction_score] => 3
[first_post_reactions] => {"1":3}
[last_post_date] => 1772587654
[last_post_id] => 98036
[last_post_user_id] => 20231
[last_post_username] => Barnsley
[prefix_id] => 0
[tags] => []
[custom_fields] => []
[vote_score] => 0
[vote_count] => 0
[featured] => 0
[type_data] => []
[index_state] => default
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
[User] => ThemeHouse\XLink\XF\Entity\User Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 62
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\User
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[user_id] => 5
[username] => Daniel Nenni
[username_date] => 0
[username_date_visible] => 0
[email] => dnenni@semiwiki.com
[custom_title] => Admin
[language_id] => 1
[style_id] => 0
[style_variation] =>
[timezone] => America/Los_Angeles
[visible] => 1
[activity_visible] => 1
[user_group_id] => 3
[secondary_group_ids] => 4,5,132
[display_style_group_id] => 3
[permission_combination_id] => 88
[message_count] => 15330
[question_solution_count] => 0
[conversations_unread] => 0
[register_date] => 1280720820
[last_activity] => 1772877925
[last_summary_email_date] => 1605968657
[trophy_points] => 113
[alerts_unviewed] => 35
[alerts_unread] => 35
[avatar_date] => 1663211649
[avatar_width] => 110
[avatar_height] => 107
[avatar_highdpi] => 0
[avatar_optimized] => 0
[gravatar] =>
[user_state] => valid
[security_lock] =>
[is_moderator] => 1
[is_admin] => 1
[is_banned] => 0
[reaction_score] => 9187
[warning_points] => 0
[is_staff] => 1
[secret_key] => 0HwyUVVHCwJotUUVEpvqAclfYJdGNPpw
[privacy_policy_accepted] => 0
[terms_accepted] => 0
[vote_score] => 0
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
[Forum] => XF\Entity\Forum Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 56
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\Forum
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[node_id] => 2
[discussion_count] => 8388
[message_count] => 61505
[last_post_id] => 98163
[last_post_date] => 1772880454
[last_post_user_id] => 5185
[last_post_username] => Fred Chen
[last_thread_id] => 24684
[last_thread_title] => Build China’s ASML
[last_thread_prefix_id] => 0
[moderate_threads] => 0
[moderate_replies] => 0
[allow_posting] => 1
[count_messages] => 1
[auto_feature] => 0
[find_new] => 1
[allow_index] => allow
[index_criteria] =>
[field_cache] => []
[prefix_cache] => []
[prompt_cache] => []
[default_prefix_id] => 0
[default_sort_order] => last_post_date
[default_sort_direction] => desc
[list_date_limit_days] => 0
[require_prefix] => 0
[allowed_watch_notifications] => all
[min_tags] => 0
[forum_type_id] => discussion
[type_config] => {"allowed_thread_types":["poll"]}
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
[Node] => XF\Entity\Node Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 55
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\Node
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[node_id] => 2
[title] => SemiWiki Main Forum ( Ask the Experts! )
[description] => Post your questions to the experts here!
[node_name] =>
[node_type_id] => Forum
[parent_node_id] => 1
[display_order] => 1
[display_in_list] => 1
[lft] => 2
[rgt] => 3
[depth] => 1
[style_id] => 0
[effective_style_id] => 0
[breadcrumb_data] => {"1":{"node_id":1,"title":"Main Category","depth":0,"lft":1,"node_name":null,"node_type_id":"Category","display_in_list":true}}
[navigation_id] =>
[effective_navigation_id] =>
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
[24657] => ThemeHouse\XPress\XF\Entity\Thread Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 133
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\Thread
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[thread_id] => 24657
[node_id] => 2
[title] => Intel Ohio One Construction Timeline Update
[reply_count] => 10
[view_count] => 1074
[user_id] => 5
[username] => Daniel Nenni
[post_date] => 1772507358
[sticky] => 0
[discussion_state] => visible
[discussion_open] => 1
[discussion_type] => discussion
[first_post_id] => 98010
[first_post_reaction_score] => 1
[first_post_reactions] => {"1":1}
[last_post_date] => 1772587580
[last_post_id] => 98035
[last_post_user_id] => 20231
[last_post_username] => Barnsley
[prefix_id] => 0
[tags] => []
[custom_fields] => []
[vote_score] => 0
[vote_count] => 0
[featured] => 0
[type_data] => []
[index_state] => default
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
[User] => ThemeHouse\XLink\XF\Entity\User Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 62
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\User
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[user_id] => 5
[username] => Daniel Nenni
[username_date] => 0
[username_date_visible] => 0
[email] => dnenni@semiwiki.com
[custom_title] => Admin
[language_id] => 1
[style_id] => 0
[style_variation] =>
[timezone] => America/Los_Angeles
[visible] => 1
[activity_visible] => 1
[user_group_id] => 3
[secondary_group_ids] => 4,5,132
[display_style_group_id] => 3
[permission_combination_id] => 88
[message_count] => 15330
[question_solution_count] => 0
[conversations_unread] => 0
[register_date] => 1280720820
[last_activity] => 1772877925
[last_summary_email_date] => 1605968657
[trophy_points] => 113
[alerts_unviewed] => 35
[alerts_unread] => 35
[avatar_date] => 1663211649
[avatar_width] => 110
[avatar_height] => 107
[avatar_highdpi] => 0
[avatar_optimized] => 0
[gravatar] =>
[user_state] => valid
[security_lock] =>
[is_moderator] => 1
[is_admin] => 1
[is_banned] => 0
[reaction_score] => 9187
[warning_points] => 0
[is_staff] => 1
[secret_key] => 0HwyUVVHCwJotUUVEpvqAclfYJdGNPpw
[privacy_policy_accepted] => 0
[terms_accepted] => 0
[vote_score] => 0
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
[Forum] => XF\Entity\Forum Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 56
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\Forum
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[node_id] => 2
[discussion_count] => 8388
[message_count] => 61505
[last_post_id] => 98163
[last_post_date] => 1772880454
[last_post_user_id] => 5185
[last_post_username] => Fred Chen
[last_thread_id] => 24684
[last_thread_title] => Build China’s ASML
[last_thread_prefix_id] => 0
[moderate_threads] => 0
[moderate_replies] => 0
[allow_posting] => 1
[count_messages] => 1
[auto_feature] => 0
[find_new] => 1
[allow_index] => allow
[index_criteria] =>
[field_cache] => []
[prefix_cache] => []
[prompt_cache] => []
[default_prefix_id] => 0
[default_sort_order] => last_post_date
[default_sort_direction] => desc
[list_date_limit_days] => 0
[require_prefix] => 0
[allowed_watch_notifications] => all
[min_tags] => 0
[forum_type_id] => discussion
[type_config] => {"allowed_thread_types":["poll"]}
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
[Node] => XF\Entity\Node Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 55
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\Node
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[node_id] => 2
[title] => SemiWiki Main Forum ( Ask the Experts! )
[description] => Post your questions to the experts here!
[node_name] =>
[node_type_id] => Forum
[parent_node_id] => 1
[display_order] => 1
[display_in_list] => 1
[lft] => 2
[rgt] => 3
[depth] => 1
[style_id] => 0
[effective_style_id] => 0
[breadcrumb_data] => {"1":{"node_id":1,"title":"Main Category","depth":0,"lft":1,"node_name":null,"node_type_id":"Category","display_in_list":true}}
[navigation_id] =>
[effective_navigation_id] =>
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
)
[populated:protected] => 1
)
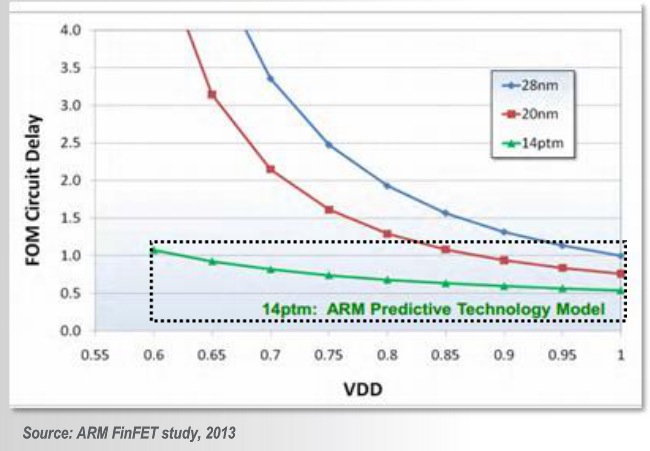
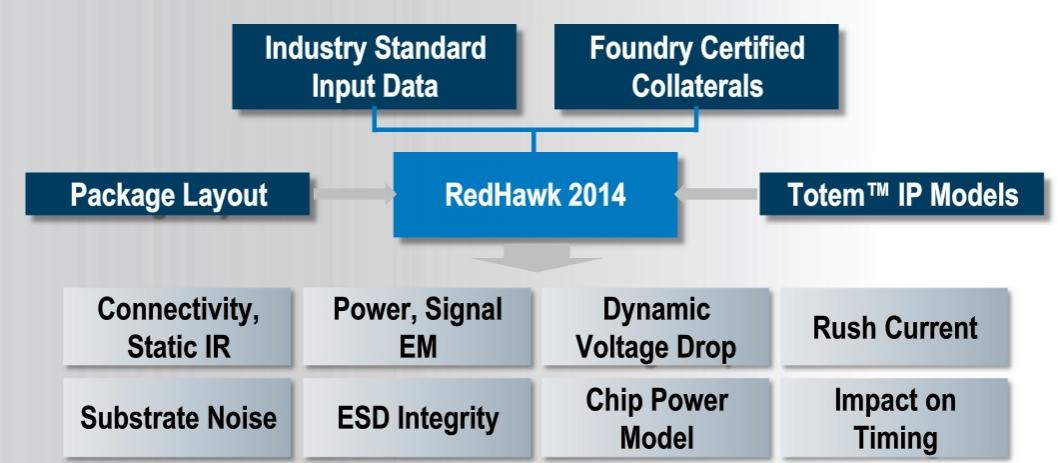
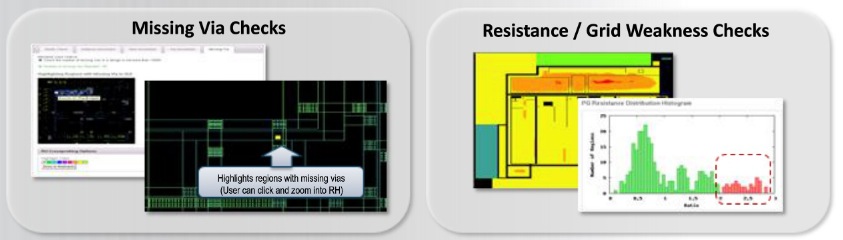




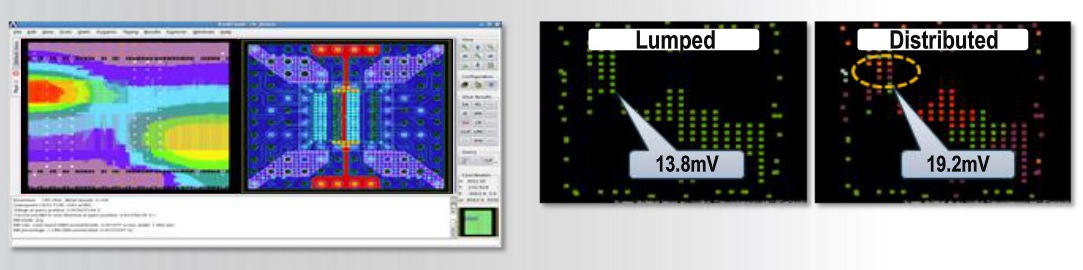




Comments
0 Replies to “FinFET Design for Power, Noise and Reliability”
You must register or log in to view/post comments.