Threads
XF\Mvc\Entity\ArrayCollection Object
(
[entities:protected] => Array
(
[23133] => ThemeHouse\XPress\XF\Entity\Thread Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 51
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\Thread
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[thread_id] => 23133
[node_id] => 2
[title] => Samsung delaying completion of US chip plant due to lack of customers
[reply_count] => 4
[view_count] => 930
[user_id] => 5
[username] => Daniel Nenni
[post_date] => 1751640597
[sticky] => 0
[discussion_state] => visible
[discussion_open] => 1
[discussion_type] => discussion
[first_post_id] => 88223
[first_post_reaction_score] => 3
[first_post_reactions] => {"1":3}
[last_post_date] => 1751824136
[last_post_id] => 88259
[last_post_user_id] => 170878
[last_post_username] => Markwrob
[prefix_id] => 0
[tags] => []
[custom_fields] => []
[vote_score] => 0
[vote_count] => 0
[type_data] => []
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
[User] => ThemeHouse\XLink\XF\Entity\User Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 48
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\User
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[user_id] => 5
[username] => Daniel Nenni
[username_date] => 0
[username_date_visible] => 0
[email] => dnenni@semiwiki.com
[custom_title] => Admin
[language_id] => 1
[style_id] => 0
[timezone] => America/Los_Angeles
[visible] => 1
[activity_visible] => 1
[user_group_id] => 3
[secondary_group_ids] => 4,5,132
[display_style_group_id] => 3
[permission_combination_id] => 88
[message_count] => 13861
[question_solution_count] => 0
[conversations_unread] => 0
[register_date] => 1280720820
[last_activity] => 1751813122
[last_summary_email_date] => 1605968657
[trophy_points] => 113
[alerts_unviewed] => 0
[alerts_unread] => 33
[avatar_date] => 1663211649
[avatar_width] => 110
[avatar_height] => 107
[avatar_highdpi] => 0
[gravatar] =>
[user_state] => valid
[security_lock] =>
[is_moderator] => 1
[is_admin] => 1
[is_banned] => 0
[reaction_score] => 6945
[warning_points] => 0
[is_staff] => 1
[secret_key] => 0HwyUVVHCwJotUUVEpvqAclfYJdGNPpw
[privacy_policy_accepted] => 0
[terms_accepted] => 0
[vote_score] => 0
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
[Forum] => XF\Entity\Forum Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 50
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\Forum
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[node_id] => 2
[discussion_count] => 7507
[message_count] => 52508
[last_post_id] => 88259
[last_post_date] => 1751824136
[last_post_user_id] => 170878
[last_post_username] => Markwrob
[last_thread_id] => 23133
[last_thread_title] => Samsung delaying completion of US chip plant due to lack of customers
[last_thread_prefix_id] => 0
[moderate_threads] => 0
[moderate_replies] => 0
[allow_posting] => 1
[count_messages] => 1
[find_new] => 1
[allow_index] => allow
[index_criteria] =>
[field_cache] => []
[prefix_cache] => []
[prompt_cache] => []
[default_prefix_id] => 0
[default_sort_order] => last_post_date
[default_sort_direction] => desc
[list_date_limit_days] => 0
[require_prefix] => 0
[allowed_watch_notifications] => all
[min_tags] => 0
[forum_type_id] => discussion
[type_config] => {"allowed_thread_types":["poll"]}
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
[Node] => XF\Entity\Node Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 49
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\Node
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[node_id] => 2
[title] => SemiWiki Main Forum ( Ask the Experts! )
[description] => Post your questions to the experts here!
[node_name] =>
[node_type_id] => Forum
[parent_node_id] => 1
[display_order] => 1
[display_in_list] => 1
[lft] => 2
[rgt] => 3
[depth] => 1
[style_id] => 0
[effective_style_id] => 0
[breadcrumb_data] => {"1":{"node_id":1,"title":"Main Category","depth":0,"lft":1,"node_name":null,"node_type_id":"Category","display_in_list":true}}
[navigation_id] =>
[effective_navigation_id] =>
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
[23122] => ThemeHouse\XPress\XF\Entity\Thread Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 55
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\Thread
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[thread_id] => 23122
[node_id] => 2
[title] => Exclusive: Intel's new CEO explores big shift in chip manufacturing business
[reply_count] => 63
[view_count] => 8116
[user_id] => 332041
[username] => XYang2023
[post_date] => 1751421336
[sticky] => 0
[discussion_state] => visible
[discussion_open] => 1
[discussion_type] => discussion
[first_post_id] => 88142
[first_post_reaction_score] => 1
[first_post_reactions] => {"1":1}
[last_post_date] => 1751804614
[last_post_id] => 88258
[last_post_user_id] => 38697
[last_post_username] => blueone
[prefix_id] => 0
[tags] => []
[custom_fields] => []
[vote_score] => 0
[vote_count] => 0
[type_data] => []
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
[User] => ThemeHouse\XLink\XF\Entity\User Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 52
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\User
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[user_id] => 332041
[username] => XYang2023
[username_date] => 0
[username_date_visible] => 0
[email] => xiao.yang17@gmail.com
[custom_title] =>
[language_id] => 1
[style_id] => 0
[timezone] => Australia/Sydney
[visible] => 1
[activity_visible] => 1
[user_group_id] => 2
[secondary_group_ids] =>
[display_style_group_id] => 2
[permission_combination_id] => 8
[message_count] => 1183
[question_solution_count] => 0
[conversations_unread] => 0
[register_date] => 1708819075
[last_activity] => 1751785017
[last_summary_email_date] => 1723213219
[trophy_points] => 113
[alerts_unviewed] => 1
[alerts_unread] => 2
[avatar_date] => 0
[avatar_width] => 0
[avatar_height] => 0
[avatar_highdpi] => 0
[gravatar] =>
[user_state] => valid
[security_lock] =>
[is_moderator] => 0
[is_admin] => 0
[is_banned] => 0
[reaction_score] => 714
[warning_points] => 0
[is_staff] => 0
[secret_key] => NBs1n4BMtljiqSmfC-EZI_MMUn9Rzevl
[privacy_policy_accepted] => 1708819075
[terms_accepted] => 1708819075
[vote_score] => 0
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
[Forum] => XF\Entity\Forum Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 50
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\Forum
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[node_id] => 2
[discussion_count] => 7507
[message_count] => 52508
[last_post_id] => 88259
[last_post_date] => 1751824136
[last_post_user_id] => 170878
[last_post_username] => Markwrob
[last_thread_id] => 23133
[last_thread_title] => Samsung delaying completion of US chip plant due to lack of customers
[last_thread_prefix_id] => 0
[moderate_threads] => 0
[moderate_replies] => 0
[allow_posting] => 1
[count_messages] => 1
[find_new] => 1
[allow_index] => allow
[index_criteria] =>
[field_cache] => []
[prefix_cache] => []
[prompt_cache] => []
[default_prefix_id] => 0
[default_sort_order] => last_post_date
[default_sort_direction] => desc
[list_date_limit_days] => 0
[require_prefix] => 0
[allowed_watch_notifications] => all
[min_tags] => 0
[forum_type_id] => discussion
[type_config] => {"allowed_thread_types":["poll"]}
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
[Node] => XF\Entity\Node Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 49
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\Node
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[node_id] => 2
[title] => SemiWiki Main Forum ( Ask the Experts! )
[description] => Post your questions to the experts here!
[node_name] =>
[node_type_id] => Forum
[parent_node_id] => 1
[display_order] => 1
[display_in_list] => 1
[lft] => 2
[rgt] => 3
[depth] => 1
[style_id] => 0
[effective_style_id] => 0
[breadcrumb_data] => {"1":{"node_id":1,"title":"Main Category","depth":0,"lft":1,"node_name":null,"node_type_id":"Category","display_in_list":true}}
[navigation_id] =>
[effective_navigation_id] =>
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
[23134] => ThemeHouse\XPress\XF\Entity\Thread Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 59
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\Thread
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[thread_id] => 23134
[node_id] => 2
[title] => Is China Catching Up in Semiconductor Talent? Can Taiwan Still Nurture the Tech Talent It Needs?
[reply_count] => 0
[view_count] => 118
[user_id] => 398583
[username] => karin623
[post_date] => 1751802440
[sticky] => 0
[discussion_state] => visible
[discussion_open] => 1
[discussion_type] => discussion
[first_post_id] => 88256
[first_post_reaction_score] => 0
[first_post_reactions] => []
[last_post_date] => 1751802440
[last_post_id] => 88256
[last_post_user_id] => 398583
[last_post_username] => karin623
[prefix_id] => 0
[tags] => []
[custom_fields] => []
[vote_score] => 0
[vote_count] => 0
[type_data] => []
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
[User] => ThemeHouse\XLink\XF\Entity\User Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 56
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\User
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[user_id] => 398583
[username] => karin623
[username_date] => 0
[username_date_visible] => 0
[email] => karin623@gmail.com
[custom_title] =>
[language_id] => 1
[style_id] => 0
[timezone] => Asia/Hong_Kong
[visible] => 1
[activity_visible] => 1
[user_group_id] => 2
[secondary_group_ids] =>
[display_style_group_id] => 2
[permission_combination_id] => 8
[message_count] => 6
[question_solution_count] => 0
[conversations_unread] => 0
[register_date] => 1748753435
[last_activity] => 1751802441
[last_summary_email_date] => 1748753435
[trophy_points] => 3
[alerts_unviewed] => 1
[alerts_unread] => 1
[avatar_date] => 0
[avatar_width] => 0
[avatar_height] => 0
[avatar_highdpi] => 0
[gravatar] =>
[user_state] => valid
[security_lock] =>
[is_moderator] => 0
[is_admin] => 0
[is_banned] => 0
[reaction_score] => 6
[warning_points] => 0
[is_staff] => 0
[secret_key] => PBnrLVmUtkEL7YUKL8Ij_6L3tfKYRzDQ
[privacy_policy_accepted] => 1748753435
[terms_accepted] => 1748753435
[vote_score] => 0
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
[Forum] => XF\Entity\Forum Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 50
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\Forum
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[node_id] => 2
[discussion_count] => 7507
[message_count] => 52508
[last_post_id] => 88259
[last_post_date] => 1751824136
[last_post_user_id] => 170878
[last_post_username] => Markwrob
[last_thread_id] => 23133
[last_thread_title] => Samsung delaying completion of US chip plant due to lack of customers
[last_thread_prefix_id] => 0
[moderate_threads] => 0
[moderate_replies] => 0
[allow_posting] => 1
[count_messages] => 1
[find_new] => 1
[allow_index] => allow
[index_criteria] =>
[field_cache] => []
[prefix_cache] => []
[prompt_cache] => []
[default_prefix_id] => 0
[default_sort_order] => last_post_date
[default_sort_direction] => desc
[list_date_limit_days] => 0
[require_prefix] => 0
[allowed_watch_notifications] => all
[min_tags] => 0
[forum_type_id] => discussion
[type_config] => {"allowed_thread_types":["poll"]}
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
[Node] => XF\Entity\Node Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 49
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\Node
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[node_id] => 2
[title] => SemiWiki Main Forum ( Ask the Experts! )
[description] => Post your questions to the experts here!
[node_name] =>
[node_type_id] => Forum
[parent_node_id] => 1
[display_order] => 1
[display_in_list] => 1
[lft] => 2
[rgt] => 3
[depth] => 1
[style_id] => 0
[effective_style_id] => 0
[breadcrumb_data] => {"1":{"node_id":1,"title":"Main Category","depth":0,"lft":1,"node_name":null,"node_type_id":"Category","display_in_list":true}}
[navigation_id] =>
[effective_navigation_id] =>
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
[23126] => ThemeHouse\XPress\XF\Entity\Thread Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 63
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\Thread
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[thread_id] => 23126
[node_id] => 2
[title] => NXP plans to close four 8-inch wafer fabs and expand production capacity to 12-inch wafers
[reply_count] => 4
[view_count] => 1015
[user_id] => 5
[username] => Daniel Nenni
[post_date] => 1751498383
[sticky] => 0
[discussion_state] => visible
[discussion_open] => 1
[discussion_type] => discussion
[first_post_id] => 88180
[first_post_reaction_score] => 1
[first_post_reactions] => {"1":1}
[last_post_date] => 1751788918
[last_post_id] => 88254
[last_post_user_id] => 19450
[last_post_username] => user nl
[prefix_id] => 0
[tags] => []
[custom_fields] => []
[vote_score] => 0
[vote_count] => 0
[type_data] => []
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
[User] => ThemeHouse\XLink\XF\Entity\User Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 48
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\User
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[user_id] => 5
[username] => Daniel Nenni
[username_date] => 0
[username_date_visible] => 0
[email] => dnenni@semiwiki.com
[custom_title] => Admin
[language_id] => 1
[style_id] => 0
[timezone] => America/Los_Angeles
[visible] => 1
[activity_visible] => 1
[user_group_id] => 3
[secondary_group_ids] => 4,5,132
[display_style_group_id] => 3
[permission_combination_id] => 88
[message_count] => 13861
[question_solution_count] => 0
[conversations_unread] => 0
[register_date] => 1280720820
[last_activity] => 1751813122
[last_summary_email_date] => 1605968657
[trophy_points] => 113
[alerts_unviewed] => 0
[alerts_unread] => 33
[avatar_date] => 1663211649
[avatar_width] => 110
[avatar_height] => 107
[avatar_highdpi] => 0
[gravatar] =>
[user_state] => valid
[security_lock] =>
[is_moderator] => 1
[is_admin] => 1
[is_banned] => 0
[reaction_score] => 6945
[warning_points] => 0
[is_staff] => 1
[secret_key] => 0HwyUVVHCwJotUUVEpvqAclfYJdGNPpw
[privacy_policy_accepted] => 0
[terms_accepted] => 0
[vote_score] => 0
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
[Forum] => XF\Entity\Forum Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 50
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\Forum
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[node_id] => 2
[discussion_count] => 7507
[message_count] => 52508
[last_post_id] => 88259
[last_post_date] => 1751824136
[last_post_user_id] => 170878
[last_post_username] => Markwrob
[last_thread_id] => 23133
[last_thread_title] => Samsung delaying completion of US chip plant due to lack of customers
[last_thread_prefix_id] => 0
[moderate_threads] => 0
[moderate_replies] => 0
[allow_posting] => 1
[count_messages] => 1
[find_new] => 1
[allow_index] => allow
[index_criteria] =>
[field_cache] => []
[prefix_cache] => []
[prompt_cache] => []
[default_prefix_id] => 0
[default_sort_order] => last_post_date
[default_sort_direction] => desc
[list_date_limit_days] => 0
[require_prefix] => 0
[allowed_watch_notifications] => all
[min_tags] => 0
[forum_type_id] => discussion
[type_config] => {"allowed_thread_types":["poll"]}
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
[Node] => XF\Entity\Node Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 49
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\Node
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[node_id] => 2
[title] => SemiWiki Main Forum ( Ask the Experts! )
[description] => Post your questions to the experts here!
[node_name] =>
[node_type_id] => Forum
[parent_node_id] => 1
[display_order] => 1
[display_in_list] => 1
[lft] => 2
[rgt] => 3
[depth] => 1
[style_id] => 0
[effective_style_id] => 0
[breadcrumb_data] => {"1":{"node_id":1,"title":"Main Category","depth":0,"lft":1,"node_name":null,"node_type_id":"Category","display_in_list":true}}
[navigation_id] =>
[effective_navigation_id] =>
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
[23123] => ThemeHouse\XPress\XF\Entity\Thread Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 67
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\Thread
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[thread_id] => 23123
[node_id] => 2
[title] => How far are perovskite solar cells?
[reply_count] => 7
[view_count] => 873
[user_id] => 10499
[username] => Arthur Hanson
[post_date] => 1751456796
[sticky] => 0
[discussion_state] => visible
[discussion_open] => 1
[discussion_type] => discussion
[first_post_id] => 88156
[first_post_reaction_score] => 1
[first_post_reactions] => {"1":1}
[last_post_date] => 1751788802
[last_post_id] => 88253
[last_post_user_id] => 30473
[last_post_username] => peter
[prefix_id] => 0
[tags] => []
[custom_fields] => []
[vote_score] => 0
[vote_count] => 0
[type_data] => []
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
[User] => ThemeHouse\XLink\XF\Entity\User Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 64
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\User
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[user_id] => 10499
[username] => Arthur Hanson
[username_date] => 0
[username_date_visible] => 0
[email] => a-j-hanson@att.net
[custom_title] =>
[language_id] => 1
[style_id] => 1
[timezone] => America/Los_Angeles
[visible] => 1
[activity_visible] => 1
[user_group_id] => 2
[secondary_group_ids] =>
[display_style_group_id] => 2
[permission_combination_id] => 8
[message_count] => 3256
[question_solution_count] => 0
[conversations_unread] => 0
[register_date] => 1366028460
[last_activity] => 1751760746
[last_summary_email_date] => 1606051785
[trophy_points] => 83
[alerts_unviewed] => 7
[alerts_unread] => 7
[avatar_date] => 0
[avatar_width] => 0
[avatar_height] => 0
[avatar_highdpi] => 0
[gravatar] =>
[user_state] => valid
[security_lock] =>
[is_moderator] => 0
[is_admin] => 0
[is_banned] => 0
[reaction_score] => 432
[warning_points] => 0
[is_staff] => 0
[secret_key] => ta_8_Pj20m6PDO6RnrGK-VnSP_vyhP_m
[privacy_policy_accepted] => 0
[terms_accepted] => 0
[vote_score] => 0
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
[Forum] => XF\Entity\Forum Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 50
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\Forum
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[node_id] => 2
[discussion_count] => 7507
[message_count] => 52508
[last_post_id] => 88259
[last_post_date] => 1751824136
[last_post_user_id] => 170878
[last_post_username] => Markwrob
[last_thread_id] => 23133
[last_thread_title] => Samsung delaying completion of US chip plant due to lack of customers
[last_thread_prefix_id] => 0
[moderate_threads] => 0
[moderate_replies] => 0
[allow_posting] => 1
[count_messages] => 1
[find_new] => 1
[allow_index] => allow
[index_criteria] =>
[field_cache] => []
[prefix_cache] => []
[prompt_cache] => []
[default_prefix_id] => 0
[default_sort_order] => last_post_date
[default_sort_direction] => desc
[list_date_limit_days] => 0
[require_prefix] => 0
[allowed_watch_notifications] => all
[min_tags] => 0
[forum_type_id] => discussion
[type_config] => {"allowed_thread_types":["poll"]}
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
[Node] => XF\Entity\Node Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 49
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\Node
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[node_id] => 2
[title] => SemiWiki Main Forum ( Ask the Experts! )
[description] => Post your questions to the experts here!
[node_name] =>
[node_type_id] => Forum
[parent_node_id] => 1
[display_order] => 1
[display_in_list] => 1
[lft] => 2
[rgt] => 3
[depth] => 1
[style_id] => 0
[effective_style_id] => 0
[breadcrumb_data] => {"1":{"node_id":1,"title":"Main Category","depth":0,"lft":1,"node_name":null,"node_type_id":"Category","display_in_list":true}}
[navigation_id] =>
[effective_navigation_id] =>
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
[23131] => ThemeHouse\XPress\XF\Entity\Thread Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 71
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\Thread
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[thread_id] => 23131
[node_id] => 2
[title] => TSMC to Delay Japan Chip Plant and Prioritize U.S. to Avoid Trump Tariffs
[reply_count] => 5
[view_count] => 733
[user_id] => 332041
[username] => XYang2023
[post_date] => 1751620259
[sticky] => 0
[discussion_state] => visible
[discussion_open] => 1
[discussion_type] => discussion
[first_post_id] => 88212
[first_post_reaction_score] => 1
[first_post_reactions] => {"4":1,"1":1}
[last_post_date] => 1751648918
[last_post_id] => 88231
[last_post_user_id] => 90182
[last_post_username] => siliconbruh999
[prefix_id] => 0
[tags] => []
[custom_fields] => []
[vote_score] => 0
[vote_count] => 0
[type_data] => []
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
[User] => ThemeHouse\XLink\XF\Entity\User Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 52
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\User
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[user_id] => 332041
[username] => XYang2023
[username_date] => 0
[username_date_visible] => 0
[email] => xiao.yang17@gmail.com
[custom_title] =>
[language_id] => 1
[style_id] => 0
[timezone] => Australia/Sydney
[visible] => 1
[activity_visible] => 1
[user_group_id] => 2
[secondary_group_ids] =>
[display_style_group_id] => 2
[permission_combination_id] => 8
[message_count] => 1183
[question_solution_count] => 0
[conversations_unread] => 0
[register_date] => 1708819075
[last_activity] => 1751785017
[last_summary_email_date] => 1723213219
[trophy_points] => 113
[alerts_unviewed] => 1
[alerts_unread] => 2
[avatar_date] => 0
[avatar_width] => 0
[avatar_height] => 0
[avatar_highdpi] => 0
[gravatar] =>
[user_state] => valid
[security_lock] =>
[is_moderator] => 0
[is_admin] => 0
[is_banned] => 0
[reaction_score] => 714
[warning_points] => 0
[is_staff] => 0
[secret_key] => NBs1n4BMtljiqSmfC-EZI_MMUn9Rzevl
[privacy_policy_accepted] => 1708819075
[terms_accepted] => 1708819075
[vote_score] => 0
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
[Forum] => XF\Entity\Forum Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 50
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\Forum
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[node_id] => 2
[discussion_count] => 7507
[message_count] => 52508
[last_post_id] => 88259
[last_post_date] => 1751824136
[last_post_user_id] => 170878
[last_post_username] => Markwrob
[last_thread_id] => 23133
[last_thread_title] => Samsung delaying completion of US chip plant due to lack of customers
[last_thread_prefix_id] => 0
[moderate_threads] => 0
[moderate_replies] => 0
[allow_posting] => 1
[count_messages] => 1
[find_new] => 1
[allow_index] => allow
[index_criteria] =>
[field_cache] => []
[prefix_cache] => []
[prompt_cache] => []
[default_prefix_id] => 0
[default_sort_order] => last_post_date
[default_sort_direction] => desc
[list_date_limit_days] => 0
[require_prefix] => 0
[allowed_watch_notifications] => all
[min_tags] => 0
[forum_type_id] => discussion
[type_config] => {"allowed_thread_types":["poll"]}
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
[Node] => XF\Entity\Node Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 49
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\Node
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[node_id] => 2
[title] => SemiWiki Main Forum ( Ask the Experts! )
[description] => Post your questions to the experts here!
[node_name] =>
[node_type_id] => Forum
[parent_node_id] => 1
[display_order] => 1
[display_in_list] => 1
[lft] => 2
[rgt] => 3
[depth] => 1
[style_id] => 0
[effective_style_id] => 0
[breadcrumb_data] => {"1":{"node_id":1,"title":"Main Category","depth":0,"lft":1,"node_name":null,"node_type_id":"Category","display_in_list":true}}
[navigation_id] =>
[effective_navigation_id] =>
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
[23132] => ThemeHouse\XPress\XF\Entity\Thread Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 75
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\Thread
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[thread_id] => 23132
[node_id] => 2
[title] => UMC Reports Sales for June 2025
[reply_count] => 2
[view_count] => 511
[user_id] => 5
[username] => Daniel Nenni
[post_date] => 1751639772
[sticky] => 0
[discussion_state] => visible
[discussion_open] => 1
[discussion_type] => discussion
[first_post_id] => 88219
[first_post_reaction_score] => 1
[first_post_reactions] => {"1":1}
[last_post_date] => 1751640404
[last_post_id] => 88222
[last_post_user_id] => 5
[last_post_username] => Daniel Nenni
[prefix_id] => 0
[tags] => []
[custom_fields] => []
[vote_score] => 0
[vote_count] => 0
[type_data] => []
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
[User] => ThemeHouse\XLink\XF\Entity\User Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 48
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\User
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[user_id] => 5
[username] => Daniel Nenni
[username_date] => 0
[username_date_visible] => 0
[email] => dnenni@semiwiki.com
[custom_title] => Admin
[language_id] => 1
[style_id] => 0
[timezone] => America/Los_Angeles
[visible] => 1
[activity_visible] => 1
[user_group_id] => 3
[secondary_group_ids] => 4,5,132
[display_style_group_id] => 3
[permission_combination_id] => 88
[message_count] => 13861
[question_solution_count] => 0
[conversations_unread] => 0
[register_date] => 1280720820
[last_activity] => 1751813122
[last_summary_email_date] => 1605968657
[trophy_points] => 113
[alerts_unviewed] => 0
[alerts_unread] => 33
[avatar_date] => 1663211649
[avatar_width] => 110
[avatar_height] => 107
[avatar_highdpi] => 0
[gravatar] =>
[user_state] => valid
[security_lock] =>
[is_moderator] => 1
[is_admin] => 1
[is_banned] => 0
[reaction_score] => 6945
[warning_points] => 0
[is_staff] => 1
[secret_key] => 0HwyUVVHCwJotUUVEpvqAclfYJdGNPpw
[privacy_policy_accepted] => 0
[terms_accepted] => 0
[vote_score] => 0
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
[Forum] => XF\Entity\Forum Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 50
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\Forum
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[node_id] => 2
[discussion_count] => 7507
[message_count] => 52508
[last_post_id] => 88259
[last_post_date] => 1751824136
[last_post_user_id] => 170878
[last_post_username] => Markwrob
[last_thread_id] => 23133
[last_thread_title] => Samsung delaying completion of US chip plant due to lack of customers
[last_thread_prefix_id] => 0
[moderate_threads] => 0
[moderate_replies] => 0
[allow_posting] => 1
[count_messages] => 1
[find_new] => 1
[allow_index] => allow
[index_criteria] =>
[field_cache] => []
[prefix_cache] => []
[prompt_cache] => []
[default_prefix_id] => 0
[default_sort_order] => last_post_date
[default_sort_direction] => desc
[list_date_limit_days] => 0
[require_prefix] => 0
[allowed_watch_notifications] => all
[min_tags] => 0
[forum_type_id] => discussion
[type_config] => {"allowed_thread_types":["poll"]}
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
[Node] => XF\Entity\Node Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 49
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\Node
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[node_id] => 2
[title] => SemiWiki Main Forum ( Ask the Experts! )
[description] => Post your questions to the experts here!
[node_name] =>
[node_type_id] => Forum
[parent_node_id] => 1
[display_order] => 1
[display_in_list] => 1
[lft] => 2
[rgt] => 3
[depth] => 1
[style_id] => 0
[effective_style_id] => 0
[breadcrumb_data] => {"1":{"node_id":1,"title":"Main Category","depth":0,"lft":1,"node_name":null,"node_type_id":"Category","display_in_list":true}}
[navigation_id] =>
[effective_navigation_id] =>
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
[23068] => ThemeHouse\XPress\XF\Entity\Thread Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 79
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\Thread
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[thread_id] => 23068
[node_id] => 2
[title] => SoftBank's Son pitches $1 trillion Arizona AI hub, Bloomberg News reports
[reply_count] => 8
[view_count] => 2173
[user_id] => 14042
[username] => hist78
[post_date] => 1750440912
[sticky] => 0
[discussion_state] => visible
[discussion_open] => 1
[discussion_type] => discussion
[first_post_id] => 87772
[first_post_reaction_score] => 0
[first_post_reactions] => {"4":1}
[last_post_date] => 1751632080
[last_post_id] => 88216
[last_post_user_id] => 20231
[last_post_username] => Barnsley
[prefix_id] => 0
[tags] => []
[custom_fields] => []
[vote_score] => 0
[vote_count] => 0
[type_data] => []
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
[User] => ThemeHouse\XLink\XF\Entity\User Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 76
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\User
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[user_id] => 14042
[username] => hist78
[username_date] => 0
[username_date_visible] => 0
[email] => ckckhcdc@gmail.com
[custom_title] =>
[language_id] => 1
[style_id] => 0
[timezone] => America/Los_Angeles
[visible] => 0
[activity_visible] => 0
[user_group_id] => 2
[secondary_group_ids] =>
[display_style_group_id] => 2
[permission_combination_id] => 8
[message_count] => 3590
[question_solution_count] => 0
[conversations_unread] => 0
[register_date] => 1389969050
[last_activity] => 1751827159
[last_summary_email_date] => 1605978520
[trophy_points] => 113
[alerts_unviewed] => 0
[alerts_unread] => 0
[avatar_date] => 1604959511
[avatar_width] => 807
[avatar_height] => 384
[avatar_highdpi] => 1
[gravatar] =>
[user_state] => valid
[security_lock] =>
[is_moderator] => 0
[is_admin] => 0
[is_banned] => 0
[reaction_score] => 3098
[warning_points] => 0
[is_staff] => 0
[secret_key] => 2YRSnPrl4fVQSdv3R6uqHxqi6BDQOXve
[privacy_policy_accepted] => 0
[terms_accepted] => 0
[vote_score] => 0
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
[Forum] => XF\Entity\Forum Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 50
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\Forum
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[node_id] => 2
[discussion_count] => 7507
[message_count] => 52508
[last_post_id] => 88259
[last_post_date] => 1751824136
[last_post_user_id] => 170878
[last_post_username] => Markwrob
[last_thread_id] => 23133
[last_thread_title] => Samsung delaying completion of US chip plant due to lack of customers
[last_thread_prefix_id] => 0
[moderate_threads] => 0
[moderate_replies] => 0
[allow_posting] => 1
[count_messages] => 1
[find_new] => 1
[allow_index] => allow
[index_criteria] =>
[field_cache] => []
[prefix_cache] => []
[prompt_cache] => []
[default_prefix_id] => 0
[default_sort_order] => last_post_date
[default_sort_direction] => desc
[list_date_limit_days] => 0
[require_prefix] => 0
[allowed_watch_notifications] => all
[min_tags] => 0
[forum_type_id] => discussion
[type_config] => {"allowed_thread_types":["poll"]}
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
[Node] => XF\Entity\Node Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 49
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\Node
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[node_id] => 2
[title] => SemiWiki Main Forum ( Ask the Experts! )
[description] => Post your questions to the experts here!
[node_name] =>
[node_type_id] => Forum
[parent_node_id] => 1
[display_order] => 1
[display_in_list] => 1
[lft] => 2
[rgt] => 3
[depth] => 1
[style_id] => 0
[effective_style_id] => 0
[breadcrumb_data] => {"1":{"node_id":1,"title":"Main Category","depth":0,"lft":1,"node_name":null,"node_type_id":"Category","display_in_list":true}}
[navigation_id] =>
[effective_navigation_id] =>
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
[23085] => ThemeHouse\XPress\XF\Entity\Thread Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 83
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\Thread
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[thread_id] => 23085
[node_id] => 2
[title] => Taiwan has upped the ante in the cold war over chips
[reply_count] => 11
[view_count] => 2470
[user_id] => 14042
[username] => hist78
[post_date] => 1750904215
[sticky] => 0
[discussion_state] => visible
[discussion_open] => 1
[discussion_type] => discussion
[first_post_id] => 87928
[first_post_reaction_score] => 3
[first_post_reactions] => {"1":3}
[last_post_date] => 1751584986
[last_post_id] => 88205
[last_post_user_id] => 36448
[last_post_username] => Paul2
[prefix_id] => 0
[tags] => []
[custom_fields] => []
[vote_score] => 0
[vote_count] => 0
[type_data] => []
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
[User] => ThemeHouse\XLink\XF\Entity\User Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 76
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\User
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[user_id] => 14042
[username] => hist78
[username_date] => 0
[username_date_visible] => 0
[email] => ckckhcdc@gmail.com
[custom_title] =>
[language_id] => 1
[style_id] => 0
[timezone] => America/Los_Angeles
[visible] => 0
[activity_visible] => 0
[user_group_id] => 2
[secondary_group_ids] =>
[display_style_group_id] => 2
[permission_combination_id] => 8
[message_count] => 3590
[question_solution_count] => 0
[conversations_unread] => 0
[register_date] => 1389969050
[last_activity] => 1751827159
[last_summary_email_date] => 1605978520
[trophy_points] => 113
[alerts_unviewed] => 0
[alerts_unread] => 0
[avatar_date] => 1604959511
[avatar_width] => 807
[avatar_height] => 384
[avatar_highdpi] => 1
[gravatar] =>
[user_state] => valid
[security_lock] =>
[is_moderator] => 0
[is_admin] => 0
[is_banned] => 0
[reaction_score] => 3098
[warning_points] => 0
[is_staff] => 0
[secret_key] => 2YRSnPrl4fVQSdv3R6uqHxqi6BDQOXve
[privacy_policy_accepted] => 0
[terms_accepted] => 0
[vote_score] => 0
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
[Forum] => XF\Entity\Forum Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 50
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\Forum
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[node_id] => 2
[discussion_count] => 7507
[message_count] => 52508
[last_post_id] => 88259
[last_post_date] => 1751824136
[last_post_user_id] => 170878
[last_post_username] => Markwrob
[last_thread_id] => 23133
[last_thread_title] => Samsung delaying completion of US chip plant due to lack of customers
[last_thread_prefix_id] => 0
[moderate_threads] => 0
[moderate_replies] => 0
[allow_posting] => 1
[count_messages] => 1
[find_new] => 1
[allow_index] => allow
[index_criteria] =>
[field_cache] => []
[prefix_cache] => []
[prompt_cache] => []
[default_prefix_id] => 0
[default_sort_order] => last_post_date
[default_sort_direction] => desc
[list_date_limit_days] => 0
[require_prefix] => 0
[allowed_watch_notifications] => all
[min_tags] => 0
[forum_type_id] => discussion
[type_config] => {"allowed_thread_types":["poll"]}
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
[Node] => XF\Entity\Node Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 49
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\Node
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[node_id] => 2
[title] => SemiWiki Main Forum ( Ask the Experts! )
[description] => Post your questions to the experts here!
[node_name] =>
[node_type_id] => Forum
[parent_node_id] => 1
[display_order] => 1
[display_in_list] => 1
[lft] => 2
[rgt] => 3
[depth] => 1
[style_id] => 0
[effective_style_id] => 0
[breadcrumb_data] => {"1":{"node_id":1,"title":"Main Category","depth":0,"lft":1,"node_name":null,"node_type_id":"Category","display_in_list":true}}
[navigation_id] =>
[effective_navigation_id] =>
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
[23128] => ThemeHouse\XPress\XF\Entity\Thread Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 87
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\Thread
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[thread_id] => 23128
[node_id] => 2
[title] => US lifts chip design software curbs against China following London trade talks
[reply_count] => 6
[view_count] => 912
[user_id] => 36640
[username] => soAsian
[post_date] => 1751531429
[sticky] => 0
[discussion_state] => visible
[discussion_open] => 1
[discussion_type] => discussion
[first_post_id] => 88189
[first_post_reaction_score] => 3
[first_post_reactions] => {"3":3}
[last_post_date] => 1751563600
[last_post_id] => 88200
[last_post_user_id] => 396
[last_post_username] => swka
[prefix_id] => 0
[tags] => []
[custom_fields] => []
[vote_score] => 0
[vote_count] => 0
[type_data] => []
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
[User] => ThemeHouse\XLink\XF\Entity\User Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 84
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\User
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[user_id] => 36640
[username] => soAsian
[username_date] => 0
[username_date_visible] => 0
[email] => jackmtsai@gmail.com
[custom_title] =>
[language_id] => 1
[style_id] => 0
[timezone] => America/Chicago
[visible] => 1
[activity_visible] => 1
[user_group_id] => 2
[secondary_group_ids] =>
[display_style_group_id] => 2
[permission_combination_id] => 8
[message_count] => 308
[question_solution_count] => 0
[conversations_unread] => 0
[register_date] => 1608139716
[last_activity] => 1751683011
[last_summary_email_date] => 1719670845
[trophy_points] => 43
[alerts_unviewed] => 0
[alerts_unread] => 0
[avatar_date] => 0
[avatar_width] => 0
[avatar_height] => 0
[avatar_highdpi] => 0
[gravatar] =>
[user_state] => valid
[security_lock] =>
[is_moderator] => 0
[is_admin] => 0
[is_banned] => 0
[reaction_score] => 234
[warning_points] => 0
[is_staff] => 0
[secret_key] => 2oKeCTFkGUpMro5tcmj7WaY9HksB13Kw
[privacy_policy_accepted] => 1608139716
[terms_accepted] => 1608139716
[vote_score] => 0
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
[Forum] => XF\Entity\Forum Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 50
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\Forum
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[node_id] => 2
[discussion_count] => 7507
[message_count] => 52508
[last_post_id] => 88259
[last_post_date] => 1751824136
[last_post_user_id] => 170878
[last_post_username] => Markwrob
[last_thread_id] => 23133
[last_thread_title] => Samsung delaying completion of US chip plant due to lack of customers
[last_thread_prefix_id] => 0
[moderate_threads] => 0
[moderate_replies] => 0
[allow_posting] => 1
[count_messages] => 1
[find_new] => 1
[allow_index] => allow
[index_criteria] =>
[field_cache] => []
[prefix_cache] => []
[prompt_cache] => []
[default_prefix_id] => 0
[default_sort_order] => last_post_date
[default_sort_direction] => desc
[list_date_limit_days] => 0
[require_prefix] => 0
[allowed_watch_notifications] => all
[min_tags] => 0
[forum_type_id] => discussion
[type_config] => {"allowed_thread_types":["poll"]}
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
[Node] => XF\Entity\Node Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 49
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\Node
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[node_id] => 2
[title] => SemiWiki Main Forum ( Ask the Experts! )
[description] => Post your questions to the experts here!
[node_name] =>
[node_type_id] => Forum
[parent_node_id] => 1
[display_order] => 1
[display_in_list] => 1
[lft] => 2
[rgt] => 3
[depth] => 1
[style_id] => 0
[effective_style_id] => 0
[breadcrumb_data] => {"1":{"node_id":1,"title":"Main Category","depth":0,"lft":1,"node_name":null,"node_type_id":"Category","display_in_list":true}}
[navigation_id] =>
[effective_navigation_id] =>
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
[23127] => ThemeHouse\XPress\XF\Entity\Thread Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 91
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\Thread
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[thread_id] => 23127
[node_id] => 2
[title] => TSMC ending GaN on Si manufacturing by 2027
[reply_count] => 0
[view_count] => 712
[user_id] => 332012
[username] => osnium
[post_date] => 1751515588
[sticky] => 0
[discussion_state] => visible
[discussion_open] => 1
[discussion_type] => discussion
[first_post_id] => 88186
[first_post_reaction_score] => 2
[first_post_reactions] => {"1":2}
[last_post_date] => 1751515588
[last_post_id] => 88186
[last_post_user_id] => 332012
[last_post_username] => osnium
[prefix_id] => 0
[tags] => []
[custom_fields] => []
[vote_score] => 0
[vote_count] => 0
[type_data] => []
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
[User] => ThemeHouse\XLink\XF\Entity\User Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 88
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\User
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[user_id] => 332012
[username] => osnium
[username_date] => 0
[username_date_visible] => 0
[email] => prelim_upturn_0p@icloud.com
[custom_title] =>
[language_id] => 1
[style_id] => 0
[timezone] => America/Los_Angeles
[visible] => 1
[activity_visible] => 1
[user_group_id] => 2
[secondary_group_ids] =>
[display_style_group_id] => 2
[permission_combination_id] => 8
[message_count] => 293
[question_solution_count] => 0
[conversations_unread] => 4
[register_date] => 1708476721
[last_activity] => 1751827033
[last_summary_email_date] => 1708476721
[trophy_points] => 43
[alerts_unviewed] => 13
[alerts_unread] => 13
[avatar_date] => 0
[avatar_width] => 0
[avatar_height] => 0
[avatar_highdpi] => 0
[gravatar] =>
[user_state] => valid
[security_lock] =>
[is_moderator] => 0
[is_admin] => 0
[is_banned] => 0
[reaction_score] => 229
[warning_points] => 0
[is_staff] => 0
[secret_key] => LslDOzdhXWoAXmgbm-AZIYJy2n9ao8Yy
[privacy_policy_accepted] => 1708476721
[terms_accepted] => 1708476721
[vote_score] => 0
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
[Forum] => XF\Entity\Forum Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 50
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\Forum
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[node_id] => 2
[discussion_count] => 7507
[message_count] => 52508
[last_post_id] => 88259
[last_post_date] => 1751824136
[last_post_user_id] => 170878
[last_post_username] => Markwrob
[last_thread_id] => 23133
[last_thread_title] => Samsung delaying completion of US chip plant due to lack of customers
[last_thread_prefix_id] => 0
[moderate_threads] => 0
[moderate_replies] => 0
[allow_posting] => 1
[count_messages] => 1
[find_new] => 1
[allow_index] => allow
[index_criteria] =>
[field_cache] => []
[prefix_cache] => []
[prompt_cache] => []
[default_prefix_id] => 0
[default_sort_order] => last_post_date
[default_sort_direction] => desc
[list_date_limit_days] => 0
[require_prefix] => 0
[allowed_watch_notifications] => all
[min_tags] => 0
[forum_type_id] => discussion
[type_config] => {"allowed_thread_types":["poll"]}
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
[Node] => XF\Entity\Node Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 49
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\Node
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[node_id] => 2
[title] => SemiWiki Main Forum ( Ask the Experts! )
[description] => Post your questions to the experts here!
[node_name] =>
[node_type_id] => Forum
[parent_node_id] => 1
[display_order] => 1
[display_in_list] => 1
[lft] => 2
[rgt] => 3
[depth] => 1
[style_id] => 0
[effective_style_id] => 0
[breadcrumb_data] => {"1":{"node_id":1,"title":"Main Category","depth":0,"lft":1,"node_name":null,"node_type_id":"Category","display_in_list":true}}
[navigation_id] =>
[effective_navigation_id] =>
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
[23107] => ThemeHouse\XPress\XF\Entity\Thread Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 95
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\Thread
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[thread_id] => 23107
[node_id] => 2
[title] => Taiwan's No. 2 chipmaker UMC eyes entering cutting-edge race
[reply_count] => 29
[view_count] => 3293
[user_id] => 332041
[username] => XYang2023
[post_date] => 1751275417
[sticky] => 0
[discussion_state] => visible
[discussion_open] => 1
[discussion_type] => discussion
[first_post_id] => 88055
[first_post_reaction_score] => 1
[first_post_reactions] => {"1":1}
[last_post_date] => 1751513582
[last_post_id] => 88185
[last_post_user_id] => 90182
[last_post_username] => siliconbruh999
[prefix_id] => 0
[tags] => []
[custom_fields] => []
[vote_score] => 0
[vote_count] => 0
[type_data] => []
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
[User] => ThemeHouse\XLink\XF\Entity\User Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 52
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\User
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[user_id] => 332041
[username] => XYang2023
[username_date] => 0
[username_date_visible] => 0
[email] => xiao.yang17@gmail.com
[custom_title] =>
[language_id] => 1
[style_id] => 0
[timezone] => Australia/Sydney
[visible] => 1
[activity_visible] => 1
[user_group_id] => 2
[secondary_group_ids] =>
[display_style_group_id] => 2
[permission_combination_id] => 8
[message_count] => 1183
[question_solution_count] => 0
[conversations_unread] => 0
[register_date] => 1708819075
[last_activity] => 1751785017
[last_summary_email_date] => 1723213219
[trophy_points] => 113
[alerts_unviewed] => 1
[alerts_unread] => 2
[avatar_date] => 0
[avatar_width] => 0
[avatar_height] => 0
[avatar_highdpi] => 0
[gravatar] =>
[user_state] => valid
[security_lock] =>
[is_moderator] => 0
[is_admin] => 0
[is_banned] => 0
[reaction_score] => 714
[warning_points] => 0
[is_staff] => 0
[secret_key] => NBs1n4BMtljiqSmfC-EZI_MMUn9Rzevl
[privacy_policy_accepted] => 1708819075
[terms_accepted] => 1708819075
[vote_score] => 0
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
[Forum] => XF\Entity\Forum Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 50
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\Forum
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[node_id] => 2
[discussion_count] => 7507
[message_count] => 52508
[last_post_id] => 88259
[last_post_date] => 1751824136
[last_post_user_id] => 170878
[last_post_username] => Markwrob
[last_thread_id] => 23133
[last_thread_title] => Samsung delaying completion of US chip plant due to lack of customers
[last_thread_prefix_id] => 0
[moderate_threads] => 0
[moderate_replies] => 0
[allow_posting] => 1
[count_messages] => 1
[find_new] => 1
[allow_index] => allow
[index_criteria] =>
[field_cache] => []
[prefix_cache] => []
[prompt_cache] => []
[default_prefix_id] => 0
[default_sort_order] => last_post_date
[default_sort_direction] => desc
[list_date_limit_days] => 0
[require_prefix] => 0
[allowed_watch_notifications] => all
[min_tags] => 0
[forum_type_id] => discussion
[type_config] => {"allowed_thread_types":["poll"]}
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
[Node] => XF\Entity\Node Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 49
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\Node
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[node_id] => 2
[title] => SemiWiki Main Forum ( Ask the Experts! )
[description] => Post your questions to the experts here!
[node_name] =>
[node_type_id] => Forum
[parent_node_id] => 1
[display_order] => 1
[display_in_list] => 1
[lft] => 2
[rgt] => 3
[depth] => 1
[style_id] => 0
[effective_style_id] => 0
[breadcrumb_data] => {"1":{"node_id":1,"title":"Main Category","depth":0,"lft":1,"node_name":null,"node_type_id":"Category","display_in_list":true}}
[navigation_id] =>
[effective_navigation_id] =>
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
[23125] => ThemeHouse\XPress\XF\Entity\Thread Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 99
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\Thread
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[thread_id] => 23125
[node_id] => 2
[title] => Chipmakers get larger tax credits in Trump’s latest ‘big beautiful bill’
[reply_count] => 2
[view_count] => 818
[user_id] => 5
[username] => Daniel Nenni
[post_date] => 1751471724
[sticky] => 0
[discussion_state] => visible
[discussion_open] => 1
[discussion_type] => discussion
[first_post_id] => 88168
[first_post_reaction_score] => 0
[first_post_reactions] => []
[last_post_date] => 1751497661
[last_post_id] => 88179
[last_post_user_id] => 38088
[last_post_username] => Brady
[prefix_id] => 0
[tags] => []
[custom_fields] => []
[vote_score] => 0
[vote_count] => 0
[type_data] => []
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
[User] => ThemeHouse\XLink\XF\Entity\User Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 48
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\User
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[user_id] => 5
[username] => Daniel Nenni
[username_date] => 0
[username_date_visible] => 0
[email] => dnenni@semiwiki.com
[custom_title] => Admin
[language_id] => 1
[style_id] => 0
[timezone] => America/Los_Angeles
[visible] => 1
[activity_visible] => 1
[user_group_id] => 3
[secondary_group_ids] => 4,5,132
[display_style_group_id] => 3
[permission_combination_id] => 88
[message_count] => 13861
[question_solution_count] => 0
[conversations_unread] => 0
[register_date] => 1280720820
[last_activity] => 1751813122
[last_summary_email_date] => 1605968657
[trophy_points] => 113
[alerts_unviewed] => 0
[alerts_unread] => 33
[avatar_date] => 1663211649
[avatar_width] => 110
[avatar_height] => 107
[avatar_highdpi] => 0
[gravatar] =>
[user_state] => valid
[security_lock] =>
[is_moderator] => 1
[is_admin] => 1
[is_banned] => 0
[reaction_score] => 6945
[warning_points] => 0
[is_staff] => 1
[secret_key] => 0HwyUVVHCwJotUUVEpvqAclfYJdGNPpw
[privacy_policy_accepted] => 0
[terms_accepted] => 0
[vote_score] => 0
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
[Forum] => XF\Entity\Forum Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 50
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\Forum
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[node_id] => 2
[discussion_count] => 7507
[message_count] => 52508
[last_post_id] => 88259
[last_post_date] => 1751824136
[last_post_user_id] => 170878
[last_post_username] => Markwrob
[last_thread_id] => 23133
[last_thread_title] => Samsung delaying completion of US chip plant due to lack of customers
[last_thread_prefix_id] => 0
[moderate_threads] => 0
[moderate_replies] => 0
[allow_posting] => 1
[count_messages] => 1
[find_new] => 1
[allow_index] => allow
[index_criteria] =>
[field_cache] => []
[prefix_cache] => []
[prompt_cache] => []
[default_prefix_id] => 0
[default_sort_order] => last_post_date
[default_sort_direction] => desc
[list_date_limit_days] => 0
[require_prefix] => 0
[allowed_watch_notifications] => all
[min_tags] => 0
[forum_type_id] => discussion
[type_config] => {"allowed_thread_types":["poll"]}
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
[Node] => XF\Entity\Node Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 49
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\Node
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[node_id] => 2
[title] => SemiWiki Main Forum ( Ask the Experts! )
[description] => Post your questions to the experts here!
[node_name] =>
[node_type_id] => Forum
[parent_node_id] => 1
[display_order] => 1
[display_in_list] => 1
[lft] => 2
[rgt] => 3
[depth] => 1
[style_id] => 0
[effective_style_id] => 0
[breadcrumb_data] => {"1":{"node_id":1,"title":"Main Category","depth":0,"lft":1,"node_name":null,"node_type_id":"Category","display_in_list":true}}
[navigation_id] =>
[effective_navigation_id] =>
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
[23087] => ThemeHouse\XPress\XF\Entity\Thread Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 103
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\Thread
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[thread_id] => 23087
[node_id] => 2
[title] => Just finished "Only the Paranoid Survive", and have a few thoughts about current day Intel
[reply_count] => 41
[view_count] => 5403
[user_id] => 35301
[username] => Xebec
[post_date] => 1750974235
[sticky] => 0
[discussion_state] => visible
[discussion_open] => 1
[discussion_type] => discussion
[first_post_id] => 87942
[first_post_reaction_score] => 6
[first_post_reactions] => {"1":3,"3":3}
[last_post_date] => 1751443496
[last_post_id] => 88153
[last_post_user_id] => 29779
[last_post_username] => tooLongInEDA
[prefix_id] => 0
[tags] => []
[custom_fields] => []
[vote_score] => 0
[vote_count] => 0
[type_data] => []
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
[User] => ThemeHouse\XLink\XF\Entity\User Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 100
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\User
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[user_id] => 35301
[username] => Xebec
[username_date] => 0
[username_date_visible] => 0
[email] => john.heritage@gmail.com
[custom_title] =>
[language_id] => 1
[style_id] => 0
[timezone] => America/New_York
[visible] => 1
[activity_visible] => 1
[user_group_id] => 2
[secondary_group_ids] =>
[display_style_group_id] => 2
[permission_combination_id] => 8
[message_count] => 1069
[question_solution_count] => 0
[conversations_unread] => 0
[register_date] => 1598710106
[last_activity] => 1751828115
[last_summary_email_date] => 1631629203
[trophy_points] => 113
[alerts_unviewed] => 0
[alerts_unread] => 3
[avatar_date] => 0
[avatar_width] => 0
[avatar_height] => 0
[avatar_highdpi] => 0
[gravatar] =>
[user_state] => valid
[security_lock] =>
[is_moderator] => 0
[is_admin] => 0
[is_banned] => 0
[reaction_score] => 1151
[warning_points] => 0
[is_staff] => 0
[secret_key] => Y7XyJgQMBi7ZiDtuAyqNGDrBQQsi8JB4
[privacy_policy_accepted] => 1598710106
[terms_accepted] => 1598710106
[vote_score] => 0
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
[Forum] => XF\Entity\Forum Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 50
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\Forum
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[node_id] => 2
[discussion_count] => 7507
[message_count] => 52508
[last_post_id] => 88259
[last_post_date] => 1751824136
[last_post_user_id] => 170878
[last_post_username] => Markwrob
[last_thread_id] => 23133
[last_thread_title] => Samsung delaying completion of US chip plant due to lack of customers
[last_thread_prefix_id] => 0
[moderate_threads] => 0
[moderate_replies] => 0
[allow_posting] => 1
[count_messages] => 1
[find_new] => 1
[allow_index] => allow
[index_criteria] =>
[field_cache] => []
[prefix_cache] => []
[prompt_cache] => []
[default_prefix_id] => 0
[default_sort_order] => last_post_date
[default_sort_direction] => desc
[list_date_limit_days] => 0
[require_prefix] => 0
[allowed_watch_notifications] => all
[min_tags] => 0
[forum_type_id] => discussion
[type_config] => {"allowed_thread_types":["poll"]}
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
[Node] => XF\Entity\Node Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 49
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\Node
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[node_id] => 2
[title] => SemiWiki Main Forum ( Ask the Experts! )
[description] => Post your questions to the experts here!
[node_name] =>
[node_type_id] => Forum
[parent_node_id] => 1
[display_order] => 1
[display_in_list] => 1
[lft] => 2
[rgt] => 3
[depth] => 1
[style_id] => 0
[effective_style_id] => 0
[breadcrumb_data] => {"1":{"node_id":1,"title":"Main Category","depth":0,"lft":1,"node_name":null,"node_type_id":"Category","display_in_list":true}}
[navigation_id] =>
[effective_navigation_id] =>
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
[23118] => ThemeHouse\XPress\XF\Entity\Thread Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 107
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\Thread
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[thread_id] => 23118
[node_id] => 2
[title] => Samsung Foundry to mass produce 1.4㎚ in 2029… Focus on ‘recovery of operating rate’
[reply_count] => 6
[view_count] => 1801
[user_id] => 5
[username] => Daniel Nenni
[post_date] => 1751384151
[sticky] => 0
[discussion_state] => visible
[discussion_open] => 1
[discussion_type] => discussion
[first_post_id] => 88124
[first_post_reaction_score] => 1
[first_post_reactions] => {"1":1}
[last_post_date] => 1751421390
[last_post_id] => 88143
[last_post_user_id] => 16950
[last_post_username] => benb
[prefix_id] => 0
[tags] => []
[custom_fields] => []
[vote_score] => 0
[vote_count] => 0
[type_data] => []
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
[User] => ThemeHouse\XLink\XF\Entity\User Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 48
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\User
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[user_id] => 5
[username] => Daniel Nenni
[username_date] => 0
[username_date_visible] => 0
[email] => dnenni@semiwiki.com
[custom_title] => Admin
[language_id] => 1
[style_id] => 0
[timezone] => America/Los_Angeles
[visible] => 1
[activity_visible] => 1
[user_group_id] => 3
[secondary_group_ids] => 4,5,132
[display_style_group_id] => 3
[permission_combination_id] => 88
[message_count] => 13861
[question_solution_count] => 0
[conversations_unread] => 0
[register_date] => 1280720820
[last_activity] => 1751813122
[last_summary_email_date] => 1605968657
[trophy_points] => 113
[alerts_unviewed] => 0
[alerts_unread] => 33
[avatar_date] => 1663211649
[avatar_width] => 110
[avatar_height] => 107
[avatar_highdpi] => 0
[gravatar] =>
[user_state] => valid
[security_lock] =>
[is_moderator] => 1
[is_admin] => 1
[is_banned] => 0
[reaction_score] => 6945
[warning_points] => 0
[is_staff] => 1
[secret_key] => 0HwyUVVHCwJotUUVEpvqAclfYJdGNPpw
[privacy_policy_accepted] => 0
[terms_accepted] => 0
[vote_score] => 0
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
[Forum] => XF\Entity\Forum Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 50
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\Forum
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[node_id] => 2
[discussion_count] => 7507
[message_count] => 52508
[last_post_id] => 88259
[last_post_date] => 1751824136
[last_post_user_id] => 170878
[last_post_username] => Markwrob
[last_thread_id] => 23133
[last_thread_title] => Samsung delaying completion of US chip plant due to lack of customers
[last_thread_prefix_id] => 0
[moderate_threads] => 0
[moderate_replies] => 0
[allow_posting] => 1
[count_messages] => 1
[find_new] => 1
[allow_index] => allow
[index_criteria] =>
[field_cache] => []
[prefix_cache] => []
[prompt_cache] => []
[default_prefix_id] => 0
[default_sort_order] => last_post_date
[default_sort_direction] => desc
[list_date_limit_days] => 0
[require_prefix] => 0
[allowed_watch_notifications] => all
[min_tags] => 0
[forum_type_id] => discussion
[type_config] => {"allowed_thread_types":["poll"]}
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
[Node] => XF\Entity\Node Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 49
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\Node
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[node_id] => 2
[title] => SemiWiki Main Forum ( Ask the Experts! )
[description] => Post your questions to the experts here!
[node_name] =>
[node_type_id] => Forum
[parent_node_id] => 1
[display_order] => 1
[display_in_list] => 1
[lft] => 2
[rgt] => 3
[depth] => 1
[style_id] => 0
[effective_style_id] => 0
[breadcrumb_data] => {"1":{"node_id":1,"title":"Main Category","depth":0,"lft":1,"node_name":null,"node_type_id":"Category","display_in_list":true}}
[navigation_id] =>
[effective_navigation_id] =>
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
[23121] => ThemeHouse\XPress\XF\Entity\Thread Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 111
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\Thread
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[thread_id] => 23121
[node_id] => 2
[title] => TSMC's AI Breakthrough: Path to a $90 Billion Windfall
[reply_count] => 1
[view_count] => 1361
[user_id] => 5
[username] => Daniel Nenni
[post_date] => 1751407355
[sticky] => 0
[discussion_state] => visible
[discussion_open] => 1
[discussion_type] => discussion
[first_post_id] => 88137
[first_post_reaction_score] => 1
[first_post_reactions] => {"1":1}
[last_post_date] => 1751407480
[last_post_id] => 88138
[last_post_user_id] => 5
[last_post_username] => Daniel Nenni
[prefix_id] => 0
[tags] => []
[custom_fields] => []
[vote_score] => 0
[vote_count] => 0
[type_data] => []
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
[User] => ThemeHouse\XLink\XF\Entity\User Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 48
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\User
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[user_id] => 5
[username] => Daniel Nenni
[username_date] => 0
[username_date_visible] => 0
[email] => dnenni@semiwiki.com
[custom_title] => Admin
[language_id] => 1
[style_id] => 0
[timezone] => America/Los_Angeles
[visible] => 1
[activity_visible] => 1
[user_group_id] => 3
[secondary_group_ids] => 4,5,132
[display_style_group_id] => 3
[permission_combination_id] => 88
[message_count] => 13861
[question_solution_count] => 0
[conversations_unread] => 0
[register_date] => 1280720820
[last_activity] => 1751813122
[last_summary_email_date] => 1605968657
[trophy_points] => 113
[alerts_unviewed] => 0
[alerts_unread] => 33
[avatar_date] => 1663211649
[avatar_width] => 110
[avatar_height] => 107
[avatar_highdpi] => 0
[gravatar] =>
[user_state] => valid
[security_lock] =>
[is_moderator] => 1
[is_admin] => 1
[is_banned] => 0
[reaction_score] => 6945
[warning_points] => 0
[is_staff] => 1
[secret_key] => 0HwyUVVHCwJotUUVEpvqAclfYJdGNPpw
[privacy_policy_accepted] => 0
[terms_accepted] => 0
[vote_score] => 0
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
[Forum] => XF\Entity\Forum Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 50
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\Forum
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[node_id] => 2
[discussion_count] => 7507
[message_count] => 52508
[last_post_id] => 88259
[last_post_date] => 1751824136
[last_post_user_id] => 170878
[last_post_username] => Markwrob
[last_thread_id] => 23133
[last_thread_title] => Samsung delaying completion of US chip plant due to lack of customers
[last_thread_prefix_id] => 0
[moderate_threads] => 0
[moderate_replies] => 0
[allow_posting] => 1
[count_messages] => 1
[find_new] => 1
[allow_index] => allow
[index_criteria] =>
[field_cache] => []
[prefix_cache] => []
[prompt_cache] => []
[default_prefix_id] => 0
[default_sort_order] => last_post_date
[default_sort_direction] => desc
[list_date_limit_days] => 0
[require_prefix] => 0
[allowed_watch_notifications] => all
[min_tags] => 0
[forum_type_id] => discussion
[type_config] => {"allowed_thread_types":["poll"]}
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
[Node] => XF\Entity\Node Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 49
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\Node
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[node_id] => 2
[title] => SemiWiki Main Forum ( Ask the Experts! )
[description] => Post your questions to the experts here!
[node_name] =>
[node_type_id] => Forum
[parent_node_id] => 1
[display_order] => 1
[display_in_list] => 1
[lft] => 2
[rgt] => 3
[depth] => 1
[style_id] => 0
[effective_style_id] => 0
[breadcrumb_data] => {"1":{"node_id":1,"title":"Main Category","depth":0,"lft":1,"node_name":null,"node_type_id":"Category","display_in_list":true}}
[navigation_id] =>
[effective_navigation_id] =>
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
[23119] => ThemeHouse\XPress\XF\Entity\Thread Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 115
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\Thread
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[thread_id] => 23119
[node_id] => 2
[title] => Wolfspeed files for bankruptcy protection
[reply_count] => 1
[view_count] => 364
[user_id] => 14042
[username] => hist78
[post_date] => 1751385588
[sticky] => 0
[discussion_state] => visible
[discussion_open] => 1
[discussion_type] => discussion
[first_post_id] => 88127
[first_post_reaction_score] => 0
[first_post_reactions] => []
[last_post_date] => 1751392903
[last_post_id] => 88134
[last_post_user_id] => 36448
[last_post_username] => Paul2
[prefix_id] => 0
[tags] => []
[custom_fields] => []
[vote_score] => 0
[vote_count] => 0
[type_data] => []
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
[User] => ThemeHouse\XLink\XF\Entity\User Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 76
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\User
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[user_id] => 14042
[username] => hist78
[username_date] => 0
[username_date_visible] => 0
[email] => ckckhcdc@gmail.com
[custom_title] =>
[language_id] => 1
[style_id] => 0
[timezone] => America/Los_Angeles
[visible] => 0
[activity_visible] => 0
[user_group_id] => 2
[secondary_group_ids] =>
[display_style_group_id] => 2
[permission_combination_id] => 8
[message_count] => 3590
[question_solution_count] => 0
[conversations_unread] => 0
[register_date] => 1389969050
[last_activity] => 1751827159
[last_summary_email_date] => 1605978520
[trophy_points] => 113
[alerts_unviewed] => 0
[alerts_unread] => 0
[avatar_date] => 1604959511
[avatar_width] => 807
[avatar_height] => 384
[avatar_highdpi] => 1
[gravatar] =>
[user_state] => valid
[security_lock] =>
[is_moderator] => 0
[is_admin] => 0
[is_banned] => 0
[reaction_score] => 3098
[warning_points] => 0
[is_staff] => 0
[secret_key] => 2YRSnPrl4fVQSdv3R6uqHxqi6BDQOXve
[privacy_policy_accepted] => 0
[terms_accepted] => 0
[vote_score] => 0
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
[Forum] => XF\Entity\Forum Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 50
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\Forum
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[node_id] => 2
[discussion_count] => 7507
[message_count] => 52508
[last_post_id] => 88259
[last_post_date] => 1751824136
[last_post_user_id] => 170878
[last_post_username] => Markwrob
[last_thread_id] => 23133
[last_thread_title] => Samsung delaying completion of US chip plant due to lack of customers
[last_thread_prefix_id] => 0
[moderate_threads] => 0
[moderate_replies] => 0
[allow_posting] => 1
[count_messages] => 1
[find_new] => 1
[allow_index] => allow
[index_criteria] =>
[field_cache] => []
[prefix_cache] => []
[prompt_cache] => []
[default_prefix_id] => 0
[default_sort_order] => last_post_date
[default_sort_direction] => desc
[list_date_limit_days] => 0
[require_prefix] => 0
[allowed_watch_notifications] => all
[min_tags] => 0
[forum_type_id] => discussion
[type_config] => {"allowed_thread_types":["poll"]}
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
[Node] => XF\Entity\Node Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 49
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\Node
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[node_id] => 2
[title] => SemiWiki Main Forum ( Ask the Experts! )
[description] => Post your questions to the experts here!
[node_name] =>
[node_type_id] => Forum
[parent_node_id] => 1
[display_order] => 1
[display_in_list] => 1
[lft] => 2
[rgt] => 3
[depth] => 1
[style_id] => 0
[effective_style_id] => 0
[breadcrumb_data] => {"1":{"node_id":1,"title":"Main Category","depth":0,"lft":1,"node_name":null,"node_type_id":"Category","display_in_list":true}}
[navigation_id] =>
[effective_navigation_id] =>
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
[23116] => ThemeHouse\XPress\XF\Entity\Thread Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 119
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\Thread
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[thread_id] => 23116
[node_id] => 2
[title] => new ERA of car business
[reply_count] => 2
[view_count] => 413
[user_id] => 326464
[username] => Stan Chen
[post_date] => 1751357468
[sticky] => 0
[discussion_state] => visible
[discussion_open] => 1
[discussion_type] => discussion
[first_post_id] => 88117
[first_post_reaction_score] => 2
[first_post_reactions] => {"1":2,"4":1}
[last_post_date] => 1751385454
[last_post_id] => 88126
[last_post_user_id] => 10499
[last_post_username] => Arthur Hanson
[prefix_id] => 0
[tags] => []
[custom_fields] => []
[vote_score] => 0
[vote_count] => 0
[type_data] => []
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
[User] => ThemeHouse\XLink\XF\Entity\User Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 116
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\User
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[user_id] => 326464
[username] => Stan Chen
[username_date] => 0
[username_date_visible] => 0
[email] => csmr1204@gmail.com
[custom_title] =>
[language_id] => 1
[style_id] => 0
[timezone] => Asia/Hong_Kong
[visible] => 1
[activity_visible] => 1
[user_group_id] => 2
[secondary_group_ids] =>
[display_style_group_id] => 2
[permission_combination_id] => 8
[message_count] => 12
[question_solution_count] => 0
[conversations_unread] => 0
[register_date] => 1689648840
[last_activity] => 1751723395
[last_summary_email_date] => 1739629203
[trophy_points] => 3
[alerts_unviewed] => 3
[alerts_unread] => 3
[avatar_date] => 0
[avatar_width] => 0
[avatar_height] => 0
[avatar_highdpi] => 0
[gravatar] =>
[user_state] => valid
[security_lock] =>
[is_moderator] => 0
[is_admin] => 0
[is_banned] => 0
[reaction_score] => 8
[warning_points] => 0
[is_staff] => 0
[secret_key] => lmpiOi9Ryc9Zhzedbuxzr_i_NeeebNFX
[privacy_policy_accepted] => 1689648840
[terms_accepted] => 1689648840
[vote_score] => 0
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
[Forum] => XF\Entity\Forum Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 50
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\Forum
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[node_id] => 2
[discussion_count] => 7507
[message_count] => 52508
[last_post_id] => 88259
[last_post_date] => 1751824136
[last_post_user_id] => 170878
[last_post_username] => Markwrob
[last_thread_id] => 23133
[last_thread_title] => Samsung delaying completion of US chip plant due to lack of customers
[last_thread_prefix_id] => 0
[moderate_threads] => 0
[moderate_replies] => 0
[allow_posting] => 1
[count_messages] => 1
[find_new] => 1
[allow_index] => allow
[index_criteria] =>
[field_cache] => []
[prefix_cache] => []
[prompt_cache] => []
[default_prefix_id] => 0
[default_sort_order] => last_post_date
[default_sort_direction] => desc
[list_date_limit_days] => 0
[require_prefix] => 0
[allowed_watch_notifications] => all
[min_tags] => 0
[forum_type_id] => discussion
[type_config] => {"allowed_thread_types":["poll"]}
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
[Node] => XF\Entity\Node Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 49
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\Node
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[node_id] => 2
[title] => SemiWiki Main Forum ( Ask the Experts! )
[description] => Post your questions to the experts here!
[node_name] =>
[node_type_id] => Forum
[parent_node_id] => 1
[display_order] => 1
[display_in_list] => 1
[lft] => 2
[rgt] => 3
[depth] => 1
[style_id] => 0
[effective_style_id] => 0
[breadcrumb_data] => {"1":{"node_id":1,"title":"Main Category","depth":0,"lft":1,"node_name":null,"node_type_id":"Category","display_in_list":true}}
[navigation_id] =>
[effective_navigation_id] =>
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
[23117] => ThemeHouse\XPress\XF\Entity\Thread Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 123
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\Thread
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[thread_id] => 23117
[node_id] => 2
[title] => HongKong’s First 8-Inch SiC Wafer Plant Got Approval
[reply_count] => 1
[view_count] => 330
[user_id] => 20231
[username] => Barnsley
[post_date] => 1751365166
[sticky] => 0
[discussion_state] => visible
[discussion_open] => 1
[discussion_type] => discussion
[first_post_id] => 88118
[first_post_reaction_score] => 1
[first_post_reactions] => {"1":1}
[last_post_date] => 1751365194
[last_post_id] => 88119
[last_post_user_id] => 20231
[last_post_username] => Barnsley
[prefix_id] => 0
[tags] => []
[custom_fields] => []
[vote_score] => 0
[vote_count] => 0
[type_data] => []
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
[User] => ThemeHouse\XLink\XF\Entity\User Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 120
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\User
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[user_id] => 20231
[username] => Barnsley
[username_date] => 0
[username_date_visible] => 0
[email] => apickering72@gmail.com
[custom_title] =>
[language_id] => 1
[style_id] => 0
[timezone] => Asia/Irkutsk
[visible] => 1
[activity_visible] => 1
[user_group_id] => 2
[secondary_group_ids] =>
[display_style_group_id] => 2
[permission_combination_id] => 8
[message_count] => 1059
[question_solution_count] => 0
[conversations_unread] => 0
[register_date] => 1429440429
[last_activity] => 1751781720
[last_summary_email_date] => 1653315673
[trophy_points] => 83
[alerts_unviewed] => 24
[alerts_unread] => 24
[avatar_date] => 0
[avatar_width] => 0
[avatar_height] => 0
[avatar_highdpi] => 0
[gravatar] =>
[user_state] => valid
[security_lock] =>
[is_moderator] => 0
[is_admin] => 0
[is_banned] => 0
[reaction_score] => 496
[warning_points] => 0
[is_staff] => 0
[secret_key] => iAnkz9GTDfivRmH1BOp6OTrgESJR57G8
[privacy_policy_accepted] => 0
[terms_accepted] => 0
[vote_score] => 0
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
[Forum] => XF\Entity\Forum Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 50
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\Forum
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[node_id] => 2
[discussion_count] => 7507
[message_count] => 52508
[last_post_id] => 88259
[last_post_date] => 1751824136
[last_post_user_id] => 170878
[last_post_username] => Markwrob
[last_thread_id] => 23133
[last_thread_title] => Samsung delaying completion of US chip plant due to lack of customers
[last_thread_prefix_id] => 0
[moderate_threads] => 0
[moderate_replies] => 0
[allow_posting] => 1
[count_messages] => 1
[find_new] => 1
[allow_index] => allow
[index_criteria] =>
[field_cache] => []
[prefix_cache] => []
[prompt_cache] => []
[default_prefix_id] => 0
[default_sort_order] => last_post_date
[default_sort_direction] => desc
[list_date_limit_days] => 0
[require_prefix] => 0
[allowed_watch_notifications] => all
[min_tags] => 0
[forum_type_id] => discussion
[type_config] => {"allowed_thread_types":["poll"]}
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
[Node] => XF\Entity\Node Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 49
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\Node
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[node_id] => 2
[title] => SemiWiki Main Forum ( Ask the Experts! )
[description] => Post your questions to the experts here!
[node_name] =>
[node_type_id] => Forum
[parent_node_id] => 1
[display_order] => 1
[display_in_list] => 1
[lft] => 2
[rgt] => 3
[depth] => 1
[style_id] => 0
[effective_style_id] => 0
[breadcrumb_data] => {"1":{"node_id":1,"title":"Main Category","depth":0,"lft":1,"node_name":null,"node_type_id":"Category","display_in_list":true}}
[navigation_id] =>
[effective_navigation_id] =>
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
[23088] => ThemeHouse\XPress\XF\Entity\Thread Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 127
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\Thread
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[thread_id] => 23088
[node_id] => 2
[title] => Semiconductor foundry landscape to transform by 2030
[reply_count] => 5
[view_count] => 7495
[user_id] => 5
[username] => Daniel Nenni
[post_date] => 1750976263
[sticky] => 0
[discussion_state] => visible
[discussion_open] => 1
[discussion_type] => discussion
[first_post_id] => 87943
[first_post_reaction_score] => 3
[first_post_reactions] => {"1":3}
[last_post_date] => 1751356255
[last_post_id] => 88116
[last_post_user_id] => 326464
[last_post_username] => Stan Chen
[prefix_id] => 0
[tags] => []
[custom_fields] => []
[vote_score] => 0
[vote_count] => 0
[type_data] => []
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
[User] => ThemeHouse\XLink\XF\Entity\User Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 48
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\User
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[user_id] => 5
[username] => Daniel Nenni
[username_date] => 0
[username_date_visible] => 0
[email] => dnenni@semiwiki.com
[custom_title] => Admin
[language_id] => 1
[style_id] => 0
[timezone] => America/Los_Angeles
[visible] => 1
[activity_visible] => 1
[user_group_id] => 3
[secondary_group_ids] => 4,5,132
[display_style_group_id] => 3
[permission_combination_id] => 88
[message_count] => 13861
[question_solution_count] => 0
[conversations_unread] => 0
[register_date] => 1280720820
[last_activity] => 1751813122
[last_summary_email_date] => 1605968657
[trophy_points] => 113
[alerts_unviewed] => 0
[alerts_unread] => 33
[avatar_date] => 1663211649
[avatar_width] => 110
[avatar_height] => 107
[avatar_highdpi] => 0
[gravatar] =>
[user_state] => valid
[security_lock] =>
[is_moderator] => 1
[is_admin] => 1
[is_banned] => 0
[reaction_score] => 6945
[warning_points] => 0
[is_staff] => 1
[secret_key] => 0HwyUVVHCwJotUUVEpvqAclfYJdGNPpw
[privacy_policy_accepted] => 0
[terms_accepted] => 0
[vote_score] => 0
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
[Forum] => XF\Entity\Forum Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 50
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\Forum
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[node_id] => 2
[discussion_count] => 7507
[message_count] => 52508
[last_post_id] => 88259
[last_post_date] => 1751824136
[last_post_user_id] => 170878
[last_post_username] => Markwrob
[last_thread_id] => 23133
[last_thread_title] => Samsung delaying completion of US chip plant due to lack of customers
[last_thread_prefix_id] => 0
[moderate_threads] => 0
[moderate_replies] => 0
[allow_posting] => 1
[count_messages] => 1
[find_new] => 1
[allow_index] => allow
[index_criteria] =>
[field_cache] => []
[prefix_cache] => []
[prompt_cache] => []
[default_prefix_id] => 0
[default_sort_order] => last_post_date
[default_sort_direction] => desc
[list_date_limit_days] => 0
[require_prefix] => 0
[allowed_watch_notifications] => all
[min_tags] => 0
[forum_type_id] => discussion
[type_config] => {"allowed_thread_types":["poll"]}
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
[Node] => XF\Entity\Node Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 49
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\Node
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[node_id] => 2
[title] => SemiWiki Main Forum ( Ask the Experts! )
[description] => Post your questions to the experts here!
[node_name] =>
[node_type_id] => Forum
[parent_node_id] => 1
[display_order] => 1
[display_in_list] => 1
[lft] => 2
[rgt] => 3
[depth] => 1
[style_id] => 0
[effective_style_id] => 0
[breadcrumb_data] => {"1":{"node_id":1,"title":"Main Category","depth":0,"lft":1,"node_name":null,"node_type_id":"Category","display_in_list":true}}
[navigation_id] =>
[effective_navigation_id] =>
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
)
[populated:protected] => 1
)
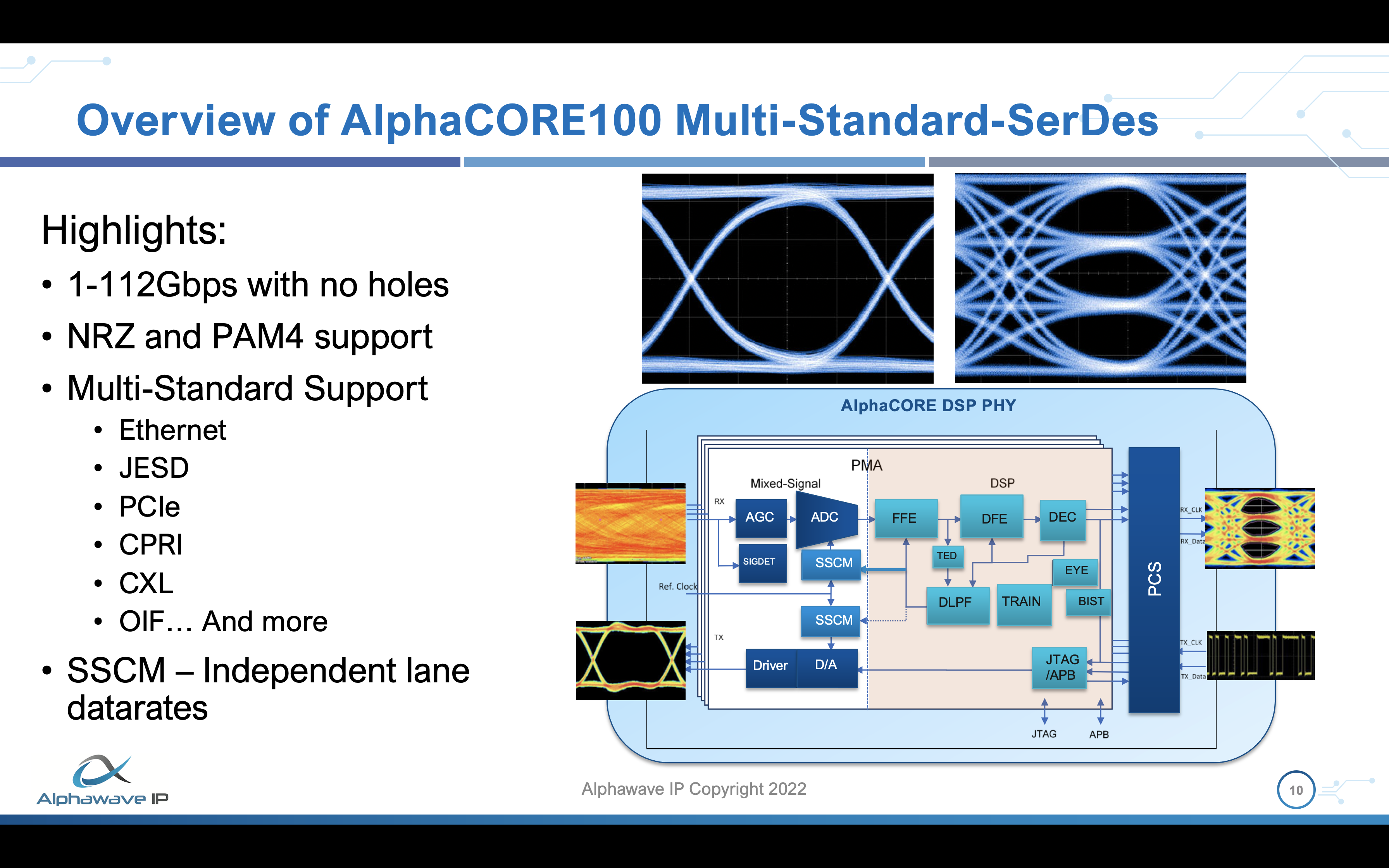
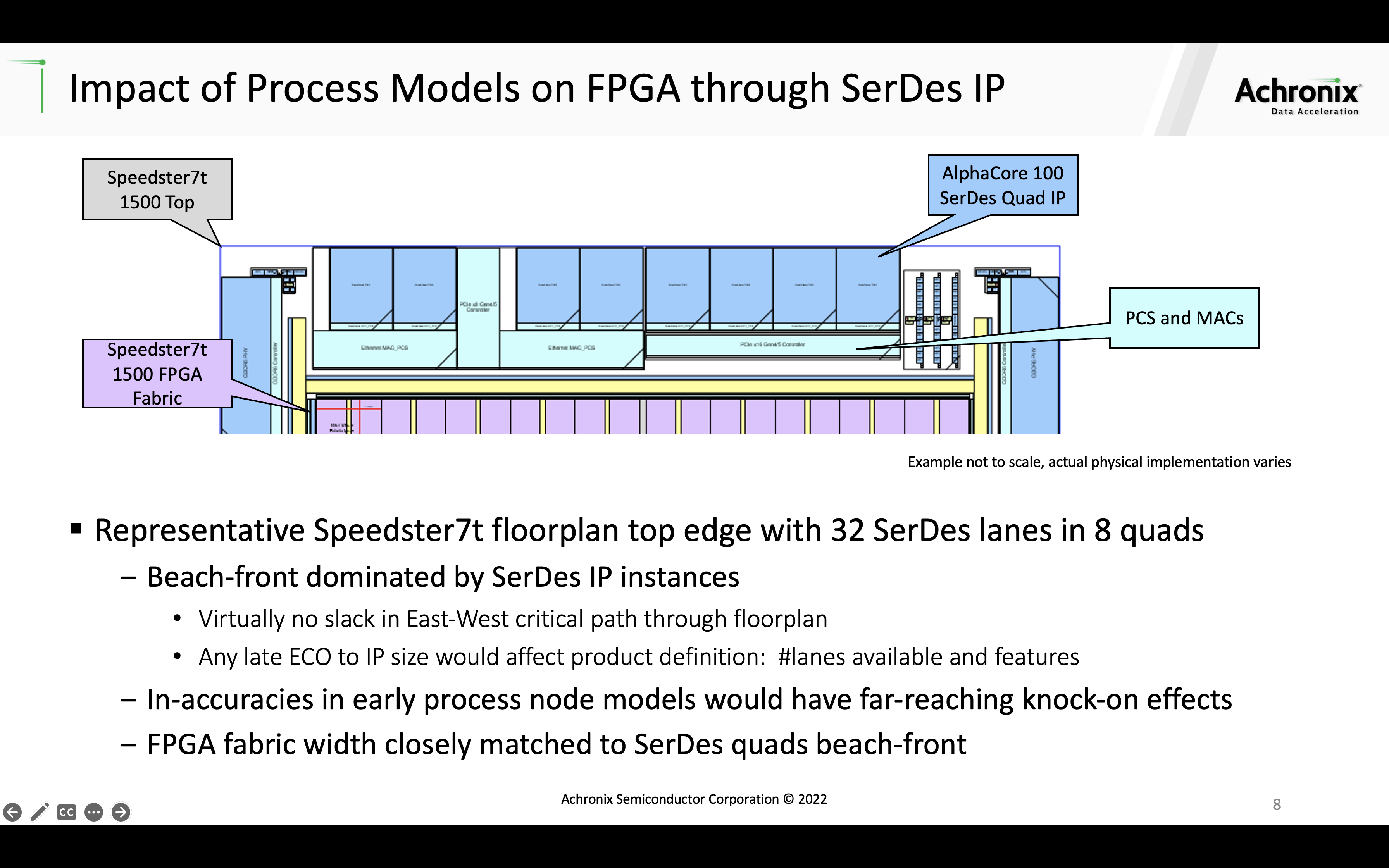
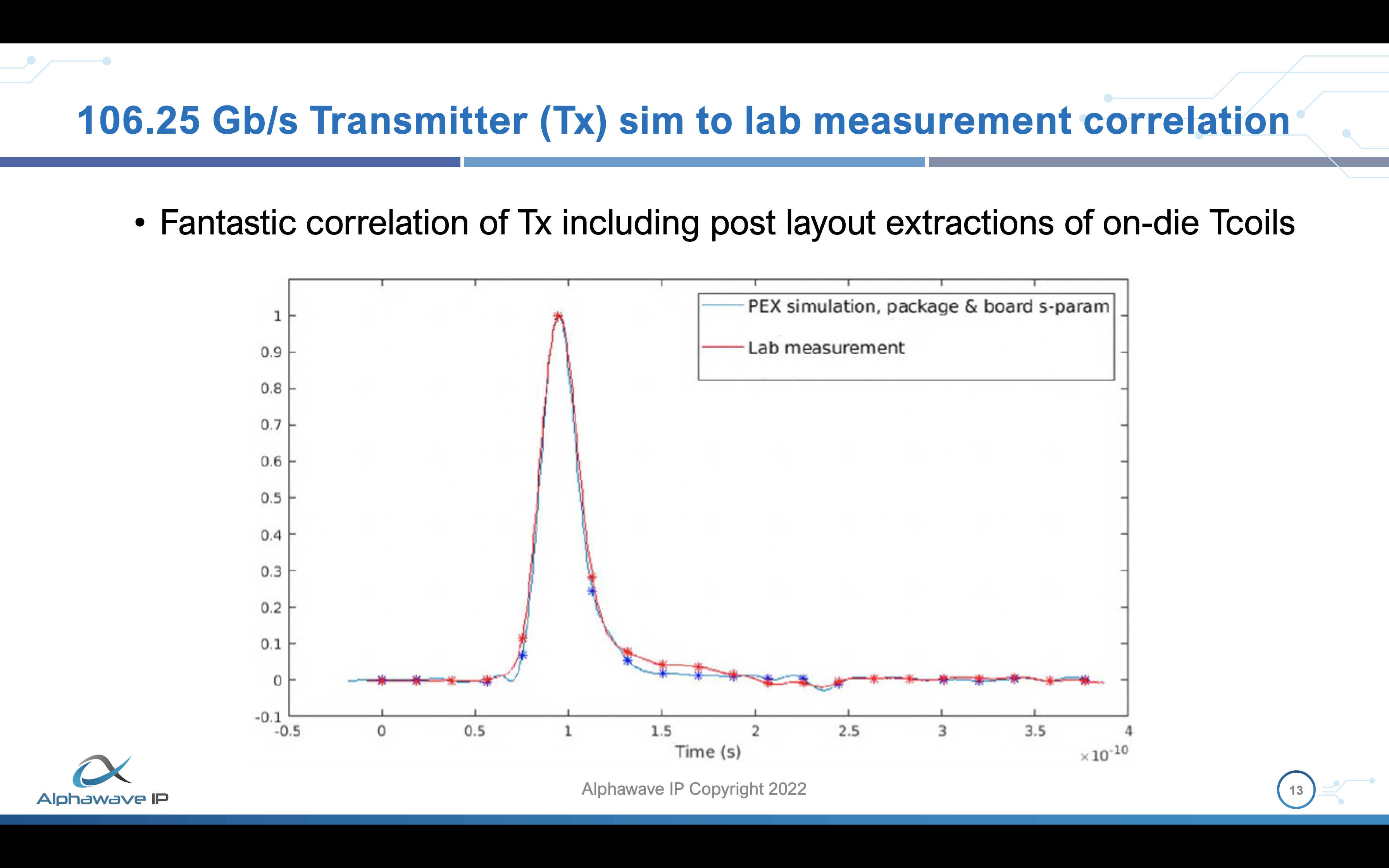
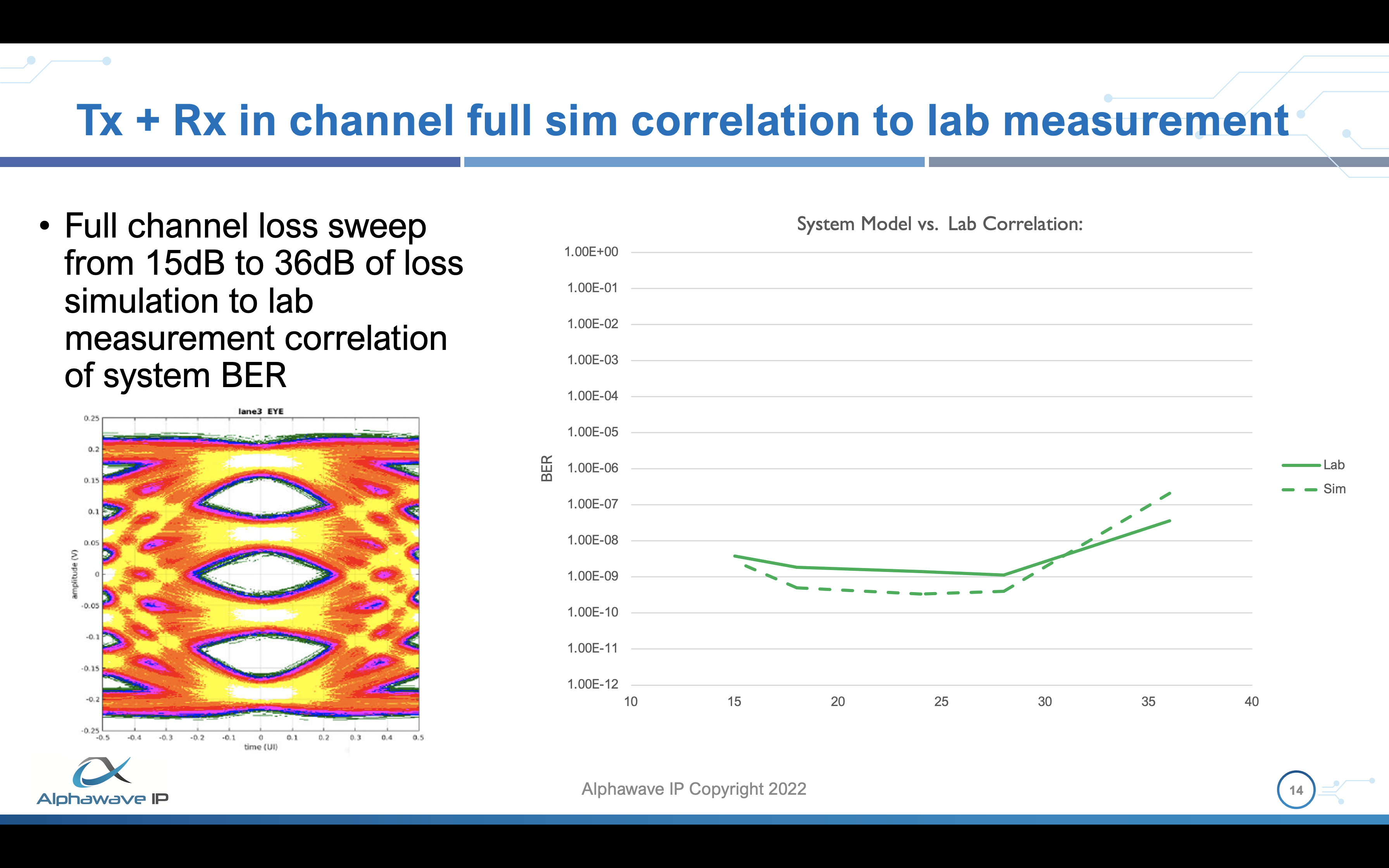

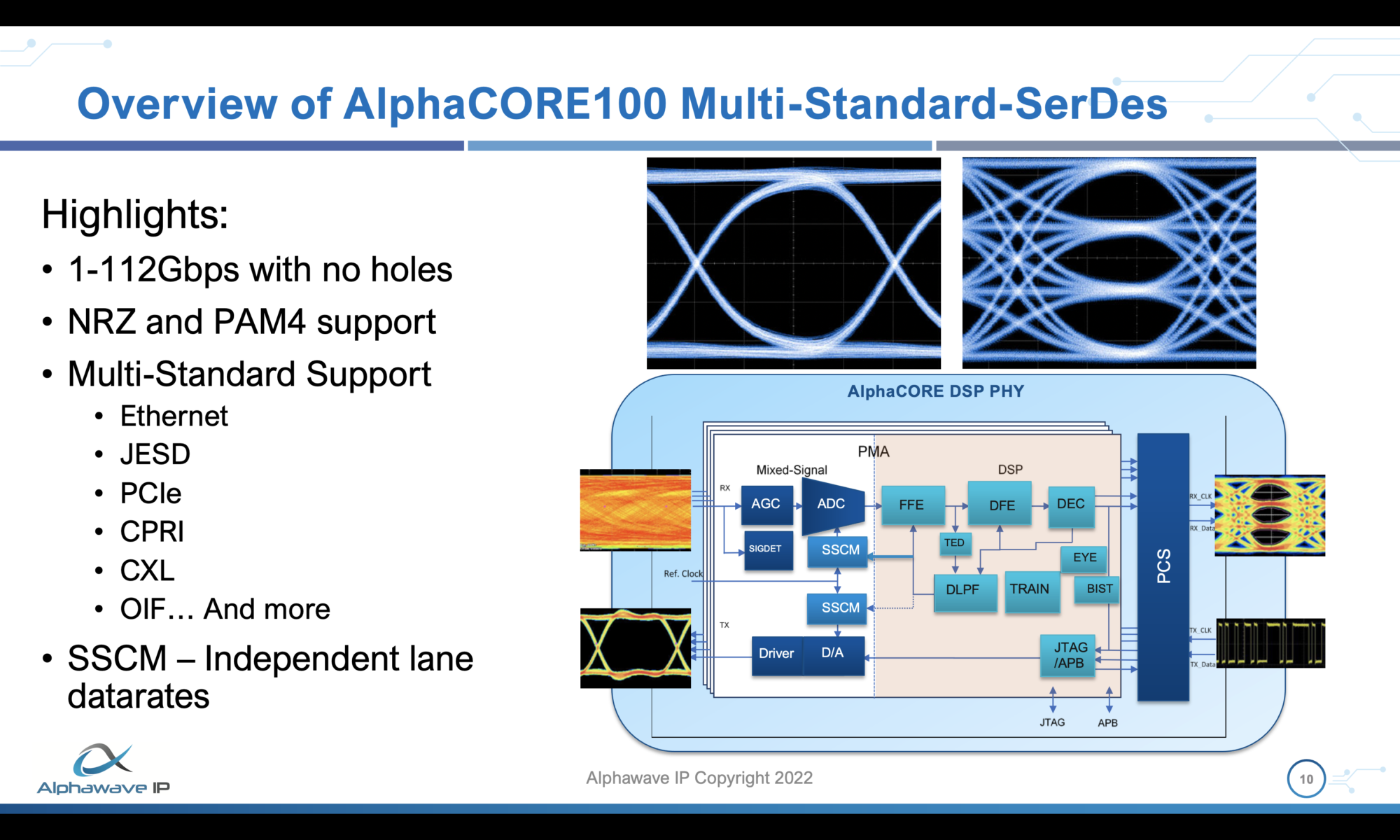





Comments
There are no comments yet.
You must register or log in to view/post comments.