Threads
XF\Mvc\Entity\ArrayCollection Object
(
[entities:protected] => Array
(
[24737] => ThemeHouse\XPress\XF\Entity\Thread Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 57
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\Thread
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[thread_id] => 24737
[node_id] => 2
[title] => The Great AI Silicon Shortage
[reply_count] => 0
[view_count] => 45
[user_id] => 19450
[username] => user nl
[post_date] => 1773398181
[sticky] => 0
[discussion_state] => visible
[discussion_open] => 1
[discussion_type] => discussion
[first_post_id] => 98305
[first_post_reaction_score] => 0
[first_post_reactions] => []
[last_post_date] => 1773398181
[last_post_id] => 98305
[last_post_user_id] => 19450
[last_post_username] => user nl
[prefix_id] => 0
[tags] => []
[custom_fields] => []
[vote_score] => 0
[vote_count] => 0
[featured] => 0
[type_data] => []
[index_state] => default
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
[User] => ThemeHouse\XLink\XF\Entity\User Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 54
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\User
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[user_id] => 19450
[username] => user nl
[username_date] => 0
[username_date_visible] => 0
[email] => mauricehmjanssen@gmail.com
[custom_title] =>
[language_id] => 1
[style_id] => 0
[style_variation] =>
[timezone] => Europe/Amsterdam
[visible] => 1
[activity_visible] => 1
[user_group_id] => 2
[secondary_group_ids] =>
[display_style_group_id] => 2
[permission_combination_id] => 8
[message_count] => 462
[question_solution_count] => 0
[conversations_unread] => 0
[register_date] => 1424291496
[last_activity] => 1773399233
[last_summary_email_date] =>
[trophy_points] => 63
[alerts_unviewed] => 0
[alerts_unread] => 0
[avatar_date] => 1726169369
[avatar_width] => 384
[avatar_height] => 384
[avatar_highdpi] => 1
[avatar_optimized] => 0
[gravatar] =>
[user_state] => valid
[security_lock] =>
[is_moderator] => 0
[is_admin] => 0
[is_banned] => 0
[reaction_score] => 345
[warning_points] => 0
[is_staff] => 0
[secret_key] => V-1lb5_AW69yhzqA5ok9b64U0fMjJiqf
[privacy_policy_accepted] => 0
[terms_accepted] => 0
[vote_score] => 0
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
[Forum] => XF\Entity\Forum Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 56
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\Forum
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[node_id] => 2
[discussion_count] => 8402
[message_count] => 61611
[last_post_id] => 98305
[last_post_date] => 1773398181
[last_post_user_id] => 19450
[last_post_username] => user nl
[last_thread_id] => 24737
[last_thread_title] => The Great AI Silicon Shortage
[last_thread_prefix_id] => 0
[moderate_threads] => 0
[moderate_replies] => 0
[allow_posting] => 1
[count_messages] => 1
[auto_feature] => 0
[find_new] => 1
[allow_index] => allow
[index_criteria] =>
[field_cache] => []
[prefix_cache] => []
[prompt_cache] => []
[default_prefix_id] => 0
[default_sort_order] => last_post_date
[default_sort_direction] => desc
[list_date_limit_days] => 0
[require_prefix] => 0
[allowed_watch_notifications] => all
[min_tags] => 0
[forum_type_id] => discussion
[type_config] => {"allowed_thread_types":["poll"]}
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
[Node] => XF\Entity\Node Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 55
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\Node
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[node_id] => 2
[title] => SemiWiki Main Forum ( Ask the Experts! )
[description] => Post your questions to the experts here!
[node_name] =>
[node_type_id] => Forum
[parent_node_id] => 1
[display_order] => 1
[display_in_list] => 1
[lft] => 2
[rgt] => 3
[depth] => 1
[style_id] => 0
[effective_style_id] => 0
[breadcrumb_data] => {"1":{"node_id":1,"title":"Main Category","depth":0,"lft":1,"node_name":null,"node_type_id":"Category","display_in_list":true}}
[navigation_id] =>
[effective_navigation_id] =>
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
[24722] => ThemeHouse\XPress\XF\Entity\Thread Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 61
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\Thread
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[thread_id] => 24722
[node_id] => 2
[title] => Nvidia halts China-bound H200 production, shifts TSMC capacity to Vera Rubin
[reply_count] => 8
[view_count] => 671
[user_id] => 5
[username] => Daniel Nenni
[post_date] => 1773211172
[sticky] => 0
[discussion_state] => visible
[discussion_open] => 1
[discussion_type] => discussion
[first_post_id] => 98245
[first_post_reaction_score] => 1
[first_post_reactions] => {"1":1}
[last_post_date] => 1773396790
[last_post_id] => 98304
[last_post_user_id] => 19450
[last_post_username] => user nl
[prefix_id] => 0
[tags] => []
[custom_fields] => []
[vote_score] => 0
[vote_count] => 0
[featured] => 0
[type_data] => []
[index_state] => default
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
[User] => ThemeHouse\XLink\XF\Entity\User Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 58
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\User
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[user_id] => 5
[username] => Daniel Nenni
[username_date] => 0
[username_date_visible] => 0
[email] => dnenni@semiwiki.com
[custom_title] => Admin
[language_id] => 1
[style_id] => 0
[style_variation] =>
[timezone] => America/Los_Angeles
[visible] => 1
[activity_visible] => 1
[user_group_id] => 3
[secondary_group_ids] => 4,5,132
[display_style_group_id] => 3
[permission_combination_id] => 88
[message_count] => 15351
[question_solution_count] => 0
[conversations_unread] => 0
[register_date] => 1280720820
[last_activity] => 1773398127
[last_summary_email_date] => 1605968657
[trophy_points] => 113
[alerts_unviewed] => 47
[alerts_unread] => 47
[avatar_date] => 1663211649
[avatar_width] => 110
[avatar_height] => 107
[avatar_highdpi] => 0
[avatar_optimized] => 0
[gravatar] =>
[user_state] => valid
[security_lock] =>
[is_moderator] => 1
[is_admin] => 1
[is_banned] => 0
[reaction_score] => 9203
[warning_points] => 0
[is_staff] => 1
[secret_key] => 0HwyUVVHCwJotUUVEpvqAclfYJdGNPpw
[privacy_policy_accepted] => 0
[terms_accepted] => 0
[vote_score] => 0
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
[Forum] => XF\Entity\Forum Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 56
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\Forum
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[node_id] => 2
[discussion_count] => 8402
[message_count] => 61611
[last_post_id] => 98305
[last_post_date] => 1773398181
[last_post_user_id] => 19450
[last_post_username] => user nl
[last_thread_id] => 24737
[last_thread_title] => The Great AI Silicon Shortage
[last_thread_prefix_id] => 0
[moderate_threads] => 0
[moderate_replies] => 0
[allow_posting] => 1
[count_messages] => 1
[auto_feature] => 0
[find_new] => 1
[allow_index] => allow
[index_criteria] =>
[field_cache] => []
[prefix_cache] => []
[prompt_cache] => []
[default_prefix_id] => 0
[default_sort_order] => last_post_date
[default_sort_direction] => desc
[list_date_limit_days] => 0
[require_prefix] => 0
[allowed_watch_notifications] => all
[min_tags] => 0
[forum_type_id] => discussion
[type_config] => {"allowed_thread_types":["poll"]}
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
[Node] => XF\Entity\Node Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 55
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\Node
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[node_id] => 2
[title] => SemiWiki Main Forum ( Ask the Experts! )
[description] => Post your questions to the experts here!
[node_name] =>
[node_type_id] => Forum
[parent_node_id] => 1
[display_order] => 1
[display_in_list] => 1
[lft] => 2
[rgt] => 3
[depth] => 1
[style_id] => 0
[effective_style_id] => 0
[breadcrumb_data] => {"1":{"node_id":1,"title":"Main Category","depth":0,"lft":1,"node_name":null,"node_type_id":"Category","display_in_list":true}}
[navigation_id] =>
[effective_navigation_id] =>
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
[24724] => ThemeHouse\XPress\XF\Entity\Thread Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 65
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\Thread
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[thread_id] => 24724
[node_id] => 2
[title] => Meta announces 4 new AI chips, raising competitive stakes with Nvidia, AMD
[reply_count] => 6
[view_count] => 614
[user_id] => 5
[username] => Daniel Nenni
[post_date] => 1773260988
[sticky] => 0
[discussion_state] => visible
[discussion_open] => 1
[discussion_type] => discussion
[first_post_id] => 98268
[first_post_reaction_score] => 2
[first_post_reactions] => {"1":2}
[last_post_date] => 1773392180
[last_post_id] => 98303
[last_post_user_id] => 5
[last_post_username] => Daniel Nenni
[prefix_id] => 0
[tags] => []
[custom_fields] => []
[vote_score] => 0
[vote_count] => 0
[featured] => 0
[type_data] => []
[index_state] => default
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
[User] => ThemeHouse\XLink\XF\Entity\User Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 58
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\User
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[user_id] => 5
[username] => Daniel Nenni
[username_date] => 0
[username_date_visible] => 0
[email] => dnenni@semiwiki.com
[custom_title] => Admin
[language_id] => 1
[style_id] => 0
[style_variation] =>
[timezone] => America/Los_Angeles
[visible] => 1
[activity_visible] => 1
[user_group_id] => 3
[secondary_group_ids] => 4,5,132
[display_style_group_id] => 3
[permission_combination_id] => 88
[message_count] => 15351
[question_solution_count] => 0
[conversations_unread] => 0
[register_date] => 1280720820
[last_activity] => 1773398127
[last_summary_email_date] => 1605968657
[trophy_points] => 113
[alerts_unviewed] => 47
[alerts_unread] => 47
[avatar_date] => 1663211649
[avatar_width] => 110
[avatar_height] => 107
[avatar_highdpi] => 0
[avatar_optimized] => 0
[gravatar] =>
[user_state] => valid
[security_lock] =>
[is_moderator] => 1
[is_admin] => 1
[is_banned] => 0
[reaction_score] => 9203
[warning_points] => 0
[is_staff] => 1
[secret_key] => 0HwyUVVHCwJotUUVEpvqAclfYJdGNPpw
[privacy_policy_accepted] => 0
[terms_accepted] => 0
[vote_score] => 0
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
[Forum] => XF\Entity\Forum Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 56
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\Forum
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[node_id] => 2
[discussion_count] => 8402
[message_count] => 61611
[last_post_id] => 98305
[last_post_date] => 1773398181
[last_post_user_id] => 19450
[last_post_username] => user nl
[last_thread_id] => 24737
[last_thread_title] => The Great AI Silicon Shortage
[last_thread_prefix_id] => 0
[moderate_threads] => 0
[moderate_replies] => 0
[allow_posting] => 1
[count_messages] => 1
[auto_feature] => 0
[find_new] => 1
[allow_index] => allow
[index_criteria] =>
[field_cache] => []
[prefix_cache] => []
[prompt_cache] => []
[default_prefix_id] => 0
[default_sort_order] => last_post_date
[default_sort_direction] => desc
[list_date_limit_days] => 0
[require_prefix] => 0
[allowed_watch_notifications] => all
[min_tags] => 0
[forum_type_id] => discussion
[type_config] => {"allowed_thread_types":["poll"]}
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
[Node] => XF\Entity\Node Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 55
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\Node
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[node_id] => 2
[title] => SemiWiki Main Forum ( Ask the Experts! )
[description] => Post your questions to the experts here!
[node_name] =>
[node_type_id] => Forum
[parent_node_id] => 1
[display_order] => 1
[display_in_list] => 1
[lft] => 2
[rgt] => 3
[depth] => 1
[style_id] => 0
[effective_style_id] => 0
[breadcrumb_data] => {"1":{"node_id":1,"title":"Main Category","depth":0,"lft":1,"node_name":null,"node_type_id":"Category","display_in_list":true}}
[navigation_id] =>
[effective_navigation_id] =>
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
[24721] => ThemeHouse\XPress\XF\Entity\Thread Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 69
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\Thread
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[thread_id] => 24721
[node_id] => 2
[title] => China to promote use of AI in creating new jobs, empowering traditional ones: minister of human resources and social security
[reply_count] => 4
[view_count] => 358
[user_id] => 5
[username] => Daniel Nenni
[post_date] => 1773173761
[sticky] => 0
[discussion_state] => visible
[discussion_open] => 1
[discussion_type] => discussion
[first_post_id] => 98238
[first_post_reaction_score] => 0
[first_post_reactions] => []
[last_post_date] => 1773363918
[last_post_id] => 98301
[last_post_user_id] => 712
[last_post_username] => yanfeng
[prefix_id] => 0
[tags] => []
[custom_fields] => []
[vote_score] => 0
[vote_count] => 0
[featured] => 0
[type_data] => []
[index_state] => default
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
[User] => ThemeHouse\XLink\XF\Entity\User Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 58
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\User
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[user_id] => 5
[username] => Daniel Nenni
[username_date] => 0
[username_date_visible] => 0
[email] => dnenni@semiwiki.com
[custom_title] => Admin
[language_id] => 1
[style_id] => 0
[style_variation] =>
[timezone] => America/Los_Angeles
[visible] => 1
[activity_visible] => 1
[user_group_id] => 3
[secondary_group_ids] => 4,5,132
[display_style_group_id] => 3
[permission_combination_id] => 88
[message_count] => 15351
[question_solution_count] => 0
[conversations_unread] => 0
[register_date] => 1280720820
[last_activity] => 1773398127
[last_summary_email_date] => 1605968657
[trophy_points] => 113
[alerts_unviewed] => 47
[alerts_unread] => 47
[avatar_date] => 1663211649
[avatar_width] => 110
[avatar_height] => 107
[avatar_highdpi] => 0
[avatar_optimized] => 0
[gravatar] =>
[user_state] => valid
[security_lock] =>
[is_moderator] => 1
[is_admin] => 1
[is_banned] => 0
[reaction_score] => 9203
[warning_points] => 0
[is_staff] => 1
[secret_key] => 0HwyUVVHCwJotUUVEpvqAclfYJdGNPpw
[privacy_policy_accepted] => 0
[terms_accepted] => 0
[vote_score] => 0
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
[Forum] => XF\Entity\Forum Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 56
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\Forum
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[node_id] => 2
[discussion_count] => 8402
[message_count] => 61611
[last_post_id] => 98305
[last_post_date] => 1773398181
[last_post_user_id] => 19450
[last_post_username] => user nl
[last_thread_id] => 24737
[last_thread_title] => The Great AI Silicon Shortage
[last_thread_prefix_id] => 0
[moderate_threads] => 0
[moderate_replies] => 0
[allow_posting] => 1
[count_messages] => 1
[auto_feature] => 0
[find_new] => 1
[allow_index] => allow
[index_criteria] =>
[field_cache] => []
[prefix_cache] => []
[prompt_cache] => []
[default_prefix_id] => 0
[default_sort_order] => last_post_date
[default_sort_direction] => desc
[list_date_limit_days] => 0
[require_prefix] => 0
[allowed_watch_notifications] => all
[min_tags] => 0
[forum_type_id] => discussion
[type_config] => {"allowed_thread_types":["poll"]}
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
[Node] => XF\Entity\Node Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 55
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\Node
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[node_id] => 2
[title] => SemiWiki Main Forum ( Ask the Experts! )
[description] => Post your questions to the experts here!
[node_name] =>
[node_type_id] => Forum
[parent_node_id] => 1
[display_order] => 1
[display_in_list] => 1
[lft] => 2
[rgt] => 3
[depth] => 1
[style_id] => 0
[effective_style_id] => 0
[breadcrumb_data] => {"1":{"node_id":1,"title":"Main Category","depth":0,"lft":1,"node_name":null,"node_type_id":"Category","display_in_list":true}}
[navigation_id] =>
[effective_navigation_id] =>
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
[24678] => ThemeHouse\XPress\XF\Entity\Thread Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 73
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\Thread
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[thread_id] => 24678
[node_id] => 2
[title] => I'm having trouble understanding Broadcom's claimed AI revenue results and projections
[reply_count] => 23
[view_count] => 1881
[user_id] => 38697
[username] => blueone
[post_date] => 1772681440
[sticky] => 0
[discussion_state] => visible
[discussion_open] => 1
[discussion_type] => discussion
[first_post_id] => 98065
[first_post_reaction_score] => 0
[first_post_reactions] => []
[last_post_date] => 1773355953
[last_post_id] => 98299
[last_post_user_id] => 38697
[last_post_username] => blueone
[prefix_id] => 0
[tags] => []
[custom_fields] => []
[vote_score] => 0
[vote_count] => 0
[featured] => 0
[type_data] => []
[index_state] => default
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
[User] => ThemeHouse\XLink\XF\Entity\User Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 70
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\User
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[user_id] => 38697
[username] => blueone
[username_date] => 0
[username_date_visible] => 0
[email] => rob8633@hotmail.com
[custom_title] =>
[language_id] => 1
[style_id] => 0
[style_variation] =>
[timezone] => America/Denver
[visible] => 0
[activity_visible] => 0
[user_group_id] => 2
[secondary_group_ids] =>
[display_style_group_id] => 2
[permission_combination_id] => 8
[message_count] => 2545
[question_solution_count] => 0
[conversations_unread] => 0
[register_date] => 1621824096
[last_activity] => 1773367079
[last_summary_email_date] =>
[trophy_points] => 113
[alerts_unviewed] => 0
[alerts_unread] => 1
[avatar_date] => 0
[avatar_width] => 0
[avatar_height] => 0
[avatar_highdpi] => 0
[avatar_optimized] => 0
[gravatar] =>
[user_state] => valid
[security_lock] =>
[is_moderator] => 0
[is_admin] => 0
[is_banned] => 0
[reaction_score] => 3370
[warning_points] => 0
[is_staff] => 0
[secret_key] => aGlUsVcP2cy-QllnjVLMCtpGT8e-_F_T
[privacy_policy_accepted] => 1621824096
[terms_accepted] => 1621824096
[vote_score] => 0
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
[Forum] => XF\Entity\Forum Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 56
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\Forum
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[node_id] => 2
[discussion_count] => 8402
[message_count] => 61611
[last_post_id] => 98305
[last_post_date] => 1773398181
[last_post_user_id] => 19450
[last_post_username] => user nl
[last_thread_id] => 24737
[last_thread_title] => The Great AI Silicon Shortage
[last_thread_prefix_id] => 0
[moderate_threads] => 0
[moderate_replies] => 0
[allow_posting] => 1
[count_messages] => 1
[auto_feature] => 0
[find_new] => 1
[allow_index] => allow
[index_criteria] =>
[field_cache] => []
[prefix_cache] => []
[prompt_cache] => []
[default_prefix_id] => 0
[default_sort_order] => last_post_date
[default_sort_direction] => desc
[list_date_limit_days] => 0
[require_prefix] => 0
[allowed_watch_notifications] => all
[min_tags] => 0
[forum_type_id] => discussion
[type_config] => {"allowed_thread_types":["poll"]}
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
[Node] => XF\Entity\Node Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 55
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\Node
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[node_id] => 2
[title] => SemiWiki Main Forum ( Ask the Experts! )
[description] => Post your questions to the experts here!
[node_name] =>
[node_type_id] => Forum
[parent_node_id] => 1
[display_order] => 1
[display_in_list] => 1
[lft] => 2
[rgt] => 3
[depth] => 1
[style_id] => 0
[effective_style_id] => 0
[breadcrumb_data] => {"1":{"node_id":1,"title":"Main Category","depth":0,"lft":1,"node_name":null,"node_type_id":"Category","display_in_list":true}}
[navigation_id] =>
[effective_navigation_id] =>
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
[24736] => ThemeHouse\XPress\XF\Entity\Thread Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 77
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\Thread
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[thread_id] => 24736
[node_id] => 2
[title] => A New Wave of Silicon Valley Returnees? Qualcomm and Apple Veterans Launch AI Chip Startup in Taiwan
[reply_count] => 2
[view_count] => 251
[user_id] => 398583
[username] => karin623
[post_date] => 1773329645
[sticky] => 0
[discussion_state] => visible
[discussion_open] => 1
[discussion_type] => discussion
[first_post_id] => 98293
[first_post_reaction_score] => 0
[first_post_reactions] => []
[last_post_date] => 1773355473
[last_post_id] => 98298
[last_post_user_id] => 396
[last_post_username] => swka
[prefix_id] => 0
[tags] => []
[custom_fields] => []
[vote_score] => 0
[vote_count] => 0
[featured] => 0
[type_data] => []
[index_state] => default
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
[User] => ThemeHouse\XLink\XF\Entity\User Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 74
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\User
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[user_id] => 398583
[username] => karin623
[username_date] => 0
[username_date_visible] => 0
[email] => karin623@gmail.com
[custom_title] =>
[language_id] => 1
[style_id] => 0
[style_variation] =>
[timezone] => Asia/Hong_Kong
[visible] => 1
[activity_visible] => 1
[user_group_id] => 2
[secondary_group_ids] =>
[display_style_group_id] => 2
[permission_combination_id] => 8
[message_count] => 38
[question_solution_count] => 0
[conversations_unread] => 0
[register_date] => 1748753435
[last_activity] => 1773329645
[last_summary_email_date] => 1771856462
[trophy_points] => 18
[alerts_unviewed] => 4
[alerts_unread] => 4
[avatar_date] => 0
[avatar_width] => 0
[avatar_height] => 0
[avatar_highdpi] => 0
[avatar_optimized] => 0
[gravatar] =>
[user_state] => valid
[security_lock] =>
[is_moderator] => 0
[is_admin] => 0
[is_banned] => 0
[reaction_score] => 60
[warning_points] => 0
[is_staff] => 0
[secret_key] => PBnrLVmUtkEL7YUKL8Ij_6L3tfKYRzDQ
[privacy_policy_accepted] => 1748753435
[terms_accepted] => 1748753435
[vote_score] => 0
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
[Forum] => XF\Entity\Forum Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 56
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\Forum
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[node_id] => 2
[discussion_count] => 8402
[message_count] => 61611
[last_post_id] => 98305
[last_post_date] => 1773398181
[last_post_user_id] => 19450
[last_post_username] => user nl
[last_thread_id] => 24737
[last_thread_title] => The Great AI Silicon Shortage
[last_thread_prefix_id] => 0
[moderate_threads] => 0
[moderate_replies] => 0
[allow_posting] => 1
[count_messages] => 1
[auto_feature] => 0
[find_new] => 1
[allow_index] => allow
[index_criteria] =>
[field_cache] => []
[prefix_cache] => []
[prompt_cache] => []
[default_prefix_id] => 0
[default_sort_order] => last_post_date
[default_sort_direction] => desc
[list_date_limit_days] => 0
[require_prefix] => 0
[allowed_watch_notifications] => all
[min_tags] => 0
[forum_type_id] => discussion
[type_config] => {"allowed_thread_types":["poll"]}
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
[Node] => XF\Entity\Node Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 55
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\Node
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[node_id] => 2
[title] => SemiWiki Main Forum ( Ask the Experts! )
[description] => Post your questions to the experts here!
[node_name] =>
[node_type_id] => Forum
[parent_node_id] => 1
[display_order] => 1
[display_in_list] => 1
[lft] => 2
[rgt] => 3
[depth] => 1
[style_id] => 0
[effective_style_id] => 0
[breadcrumb_data] => {"1":{"node_id":1,"title":"Main Category","depth":0,"lft":1,"node_name":null,"node_type_id":"Category","display_in_list":true}}
[navigation_id] =>
[effective_navigation_id] =>
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
[24702] => ThemeHouse\XPress\XF\Entity\Thread Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 81
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\Thread
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[thread_id] => 24702
[node_id] => 2
[title] => TSMC February 2026 Revenue Report
[reply_count] => 7
[view_count] => 1234
[user_id] => 5
[username] => Daniel Nenni
[post_date] => 1773122825
[sticky] => 0
[discussion_state] => visible
[discussion_open] => 1
[discussion_type] => discussion
[first_post_id] => 98216
[first_post_reaction_score] => 0
[first_post_reactions] => []
[last_post_date] => 1773329249
[last_post_id] => 98292
[last_post_user_id] => 138292
[last_post_username] => MKWVentures
[prefix_id] => 0
[tags] => []
[custom_fields] => []
[vote_score] => 0
[vote_count] => 0
[featured] => 0
[type_data] => []
[index_state] => default
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
[User] => ThemeHouse\XLink\XF\Entity\User Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 58
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\User
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[user_id] => 5
[username] => Daniel Nenni
[username_date] => 0
[username_date_visible] => 0
[email] => dnenni@semiwiki.com
[custom_title] => Admin
[language_id] => 1
[style_id] => 0
[style_variation] =>
[timezone] => America/Los_Angeles
[visible] => 1
[activity_visible] => 1
[user_group_id] => 3
[secondary_group_ids] => 4,5,132
[display_style_group_id] => 3
[permission_combination_id] => 88
[message_count] => 15351
[question_solution_count] => 0
[conversations_unread] => 0
[register_date] => 1280720820
[last_activity] => 1773398127
[last_summary_email_date] => 1605968657
[trophy_points] => 113
[alerts_unviewed] => 47
[alerts_unread] => 47
[avatar_date] => 1663211649
[avatar_width] => 110
[avatar_height] => 107
[avatar_highdpi] => 0
[avatar_optimized] => 0
[gravatar] =>
[user_state] => valid
[security_lock] =>
[is_moderator] => 1
[is_admin] => 1
[is_banned] => 0
[reaction_score] => 9203
[warning_points] => 0
[is_staff] => 1
[secret_key] => 0HwyUVVHCwJotUUVEpvqAclfYJdGNPpw
[privacy_policy_accepted] => 0
[terms_accepted] => 0
[vote_score] => 0
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
[Forum] => XF\Entity\Forum Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 56
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\Forum
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[node_id] => 2
[discussion_count] => 8402
[message_count] => 61611
[last_post_id] => 98305
[last_post_date] => 1773398181
[last_post_user_id] => 19450
[last_post_username] => user nl
[last_thread_id] => 24737
[last_thread_title] => The Great AI Silicon Shortage
[last_thread_prefix_id] => 0
[moderate_threads] => 0
[moderate_replies] => 0
[allow_posting] => 1
[count_messages] => 1
[auto_feature] => 0
[find_new] => 1
[allow_index] => allow
[index_criteria] =>
[field_cache] => []
[prefix_cache] => []
[prompt_cache] => []
[default_prefix_id] => 0
[default_sort_order] => last_post_date
[default_sort_direction] => desc
[list_date_limit_days] => 0
[require_prefix] => 0
[allowed_watch_notifications] => all
[min_tags] => 0
[forum_type_id] => discussion
[type_config] => {"allowed_thread_types":["poll"]}
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
[Node] => XF\Entity\Node Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 55
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\Node
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[node_id] => 2
[title] => SemiWiki Main Forum ( Ask the Experts! )
[description] => Post your questions to the experts here!
[node_name] =>
[node_type_id] => Forum
[parent_node_id] => 1
[display_order] => 1
[display_in_list] => 1
[lft] => 2
[rgt] => 3
[depth] => 1
[style_id] => 0
[effective_style_id] => 0
[breadcrumb_data] => {"1":{"node_id":1,"title":"Main Category","depth":0,"lft":1,"node_name":null,"node_type_id":"Category","display_in_list":true}}
[navigation_id] =>
[effective_navigation_id] =>
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
[24681] => ThemeHouse\XPress\XF\Entity\Thread Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 85
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\Thread
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[thread_id] => 24681
[node_id] => 2
[title] => Intel has manufacturing capacity issues. They may take years to fix.
[reply_count] => 24
[view_count] => 3374
[user_id] => 5185
[username] => Fred Chen
[post_date] => 1772714721
[sticky] => 0
[discussion_state] => visible
[discussion_open] => 1
[discussion_type] => discussion
[first_post_id] => 98072
[first_post_reaction_score] => 3
[first_post_reactions] => {"1":3}
[last_post_date] => 1773329081
[last_post_id] => 98291
[last_post_user_id] => 138292
[last_post_username] => MKWVentures
[prefix_id] => 0
[tags] => []
[custom_fields] => []
[vote_score] => 0
[vote_count] => 0
[featured] => 0
[type_data] => []
[index_state] => default
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
[User] => ThemeHouse\XLink\XF\Entity\User Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 82
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\User
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[user_id] => 5185
[username] => Fred Chen
[username_date] => 0
[username_date_visible] => 0
[email] => chen.t.fred@gmail.com
[custom_title] =>
[language_id] => 1
[style_id] => 0
[style_variation] =>
[timezone] => America/Los_Angeles
[visible] => 1
[activity_visible] => 1
[user_group_id] => 4
[secondary_group_ids] =>
[display_style_group_id] => 4
[permission_combination_id] => 92
[message_count] => 2560
[question_solution_count] => 0
[conversations_unread] => 0
[register_date] => 1333032401
[last_activity] => 1773377504
[last_summary_email_date] => 1605940563
[trophy_points] => 113
[alerts_unviewed] => 0
[alerts_unread] => 1
[avatar_date] => 0
[avatar_width] => 0
[avatar_height] => 0
[avatar_highdpi] => 0
[avatar_optimized] => 0
[gravatar] =>
[user_state] => valid
[security_lock] =>
[is_moderator] => 0
[is_admin] => 0
[is_banned] => 0
[reaction_score] => 1863
[warning_points] => 0
[is_staff] => 0
[secret_key] => 5m-bZq0HRSi9VA-96QONHJeevdQas5S8
[privacy_policy_accepted] => 0
[terms_accepted] => 0
[vote_score] => 0
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
[Forum] => XF\Entity\Forum Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 56
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\Forum
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[node_id] => 2
[discussion_count] => 8402
[message_count] => 61611
[last_post_id] => 98305
[last_post_date] => 1773398181
[last_post_user_id] => 19450
[last_post_username] => user nl
[last_thread_id] => 24737
[last_thread_title] => The Great AI Silicon Shortage
[last_thread_prefix_id] => 0
[moderate_threads] => 0
[moderate_replies] => 0
[allow_posting] => 1
[count_messages] => 1
[auto_feature] => 0
[find_new] => 1
[allow_index] => allow
[index_criteria] =>
[field_cache] => []
[prefix_cache] => []
[prompt_cache] => []
[default_prefix_id] => 0
[default_sort_order] => last_post_date
[default_sort_direction] => desc
[list_date_limit_days] => 0
[require_prefix] => 0
[allowed_watch_notifications] => all
[min_tags] => 0
[forum_type_id] => discussion
[type_config] => {"allowed_thread_types":["poll"]}
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
[Node] => XF\Entity\Node Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 55
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\Node
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[node_id] => 2
[title] => SemiWiki Main Forum ( Ask the Experts! )
[description] => Post your questions to the experts here!
[node_name] =>
[node_type_id] => Forum
[parent_node_id] => 1
[display_order] => 1
[display_in_list] => 1
[lft] => 2
[rgt] => 3
[depth] => 1
[style_id] => 0
[effective_style_id] => 0
[breadcrumb_data] => {"1":{"node_id":1,"title":"Main Category","depth":0,"lft":1,"node_name":null,"node_type_id":"Category","display_in_list":true}}
[navigation_id] =>
[effective_navigation_id] =>
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
[24680] => ThemeHouse\XPress\XF\Entity\Thread Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 89
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\Thread
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[thread_id] => 24680
[node_id] => 2
[title] => Intel CEO Tan reconsidering fate of chipmaker's new manufacturing tech, CFO says
[reply_count] => 29
[view_count] => 4444
[user_id] => 5
[username] => Daniel Nenni
[post_date] => 1772695350
[sticky] => 0
[discussion_state] => visible
[discussion_open] => 1
[discussion_type] => discussion
[first_post_id] => 98070
[first_post_reaction_score] => 0
[first_post_reactions] => []
[last_post_date] => 1773312437
[last_post_id] => 98289
[last_post_user_id] => 90182
[last_post_username] => siliconbruh999
[prefix_id] => 0
[tags] => []
[custom_fields] => []
[vote_score] => 0
[vote_count] => 0
[featured] => 0
[type_data] => []
[index_state] => default
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
[User] => ThemeHouse\XLink\XF\Entity\User Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 58
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\User
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[user_id] => 5
[username] => Daniel Nenni
[username_date] => 0
[username_date_visible] => 0
[email] => dnenni@semiwiki.com
[custom_title] => Admin
[language_id] => 1
[style_id] => 0
[style_variation] =>
[timezone] => America/Los_Angeles
[visible] => 1
[activity_visible] => 1
[user_group_id] => 3
[secondary_group_ids] => 4,5,132
[display_style_group_id] => 3
[permission_combination_id] => 88
[message_count] => 15351
[question_solution_count] => 0
[conversations_unread] => 0
[register_date] => 1280720820
[last_activity] => 1773398127
[last_summary_email_date] => 1605968657
[trophy_points] => 113
[alerts_unviewed] => 47
[alerts_unread] => 47
[avatar_date] => 1663211649
[avatar_width] => 110
[avatar_height] => 107
[avatar_highdpi] => 0
[avatar_optimized] => 0
[gravatar] =>
[user_state] => valid
[security_lock] =>
[is_moderator] => 1
[is_admin] => 1
[is_banned] => 0
[reaction_score] => 9203
[warning_points] => 0
[is_staff] => 1
[secret_key] => 0HwyUVVHCwJotUUVEpvqAclfYJdGNPpw
[privacy_policy_accepted] => 0
[terms_accepted] => 0
[vote_score] => 0
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
[Forum] => XF\Entity\Forum Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 56
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\Forum
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[node_id] => 2
[discussion_count] => 8402
[message_count] => 61611
[last_post_id] => 98305
[last_post_date] => 1773398181
[last_post_user_id] => 19450
[last_post_username] => user nl
[last_thread_id] => 24737
[last_thread_title] => The Great AI Silicon Shortage
[last_thread_prefix_id] => 0
[moderate_threads] => 0
[moderate_replies] => 0
[allow_posting] => 1
[count_messages] => 1
[auto_feature] => 0
[find_new] => 1
[allow_index] => allow
[index_criteria] =>
[field_cache] => []
[prefix_cache] => []
[prompt_cache] => []
[default_prefix_id] => 0
[default_sort_order] => last_post_date
[default_sort_direction] => desc
[list_date_limit_days] => 0
[require_prefix] => 0
[allowed_watch_notifications] => all
[min_tags] => 0
[forum_type_id] => discussion
[type_config] => {"allowed_thread_types":["poll"]}
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
[Node] => XF\Entity\Node Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 55
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\Node
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[node_id] => 2
[title] => SemiWiki Main Forum ( Ask the Experts! )
[description] => Post your questions to the experts here!
[node_name] =>
[node_type_id] => Forum
[parent_node_id] => 1
[display_order] => 1
[display_in_list] => 1
[lft] => 2
[rgt] => 3
[depth] => 1
[style_id] => 0
[effective_style_id] => 0
[breadcrumb_data] => {"1":{"node_id":1,"title":"Main Category","depth":0,"lft":1,"node_name":null,"node_type_id":"Category","display_in_list":true}}
[navigation_id] =>
[effective_navigation_id] =>
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
[24732] => ThemeHouse\XPress\XF\Entity\Thread Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 93
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\Thread
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[thread_id] => 24732
[node_id] => 2
[title] => Taiwan Semiconductor Just Put 8,000 New Jobs On The Table
[reply_count] => 1
[view_count] => 315
[user_id] => 5
[username] => Daniel Nenni
[post_date] => 1773294237
[sticky] => 0
[discussion_state] => visible
[discussion_open] => 1
[discussion_type] => discussion
[first_post_id] => 98283
[first_post_reaction_score] => 0
[first_post_reactions] => []
[last_post_date] => 1773312400
[last_post_id] => 98288
[last_post_user_id] => 398760
[last_post_username] => essiah
[prefix_id] => 0
[tags] => []
[custom_fields] => []
[vote_score] => 0
[vote_count] => 0
[featured] => 0
[type_data] => []
[index_state] => default
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
[User] => ThemeHouse\XLink\XF\Entity\User Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 58
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\User
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[user_id] => 5
[username] => Daniel Nenni
[username_date] => 0
[username_date_visible] => 0
[email] => dnenni@semiwiki.com
[custom_title] => Admin
[language_id] => 1
[style_id] => 0
[style_variation] =>
[timezone] => America/Los_Angeles
[visible] => 1
[activity_visible] => 1
[user_group_id] => 3
[secondary_group_ids] => 4,5,132
[display_style_group_id] => 3
[permission_combination_id] => 88
[message_count] => 15351
[question_solution_count] => 0
[conversations_unread] => 0
[register_date] => 1280720820
[last_activity] => 1773398127
[last_summary_email_date] => 1605968657
[trophy_points] => 113
[alerts_unviewed] => 47
[alerts_unread] => 47
[avatar_date] => 1663211649
[avatar_width] => 110
[avatar_height] => 107
[avatar_highdpi] => 0
[avatar_optimized] => 0
[gravatar] =>
[user_state] => valid
[security_lock] =>
[is_moderator] => 1
[is_admin] => 1
[is_banned] => 0
[reaction_score] => 9203
[warning_points] => 0
[is_staff] => 1
[secret_key] => 0HwyUVVHCwJotUUVEpvqAclfYJdGNPpw
[privacy_policy_accepted] => 0
[terms_accepted] => 0
[vote_score] => 0
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
[Forum] => XF\Entity\Forum Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 56
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\Forum
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[node_id] => 2
[discussion_count] => 8402
[message_count] => 61611
[last_post_id] => 98305
[last_post_date] => 1773398181
[last_post_user_id] => 19450
[last_post_username] => user nl
[last_thread_id] => 24737
[last_thread_title] => The Great AI Silicon Shortage
[last_thread_prefix_id] => 0
[moderate_threads] => 0
[moderate_replies] => 0
[allow_posting] => 1
[count_messages] => 1
[auto_feature] => 0
[find_new] => 1
[allow_index] => allow
[index_criteria] =>
[field_cache] => []
[prefix_cache] => []
[prompt_cache] => []
[default_prefix_id] => 0
[default_sort_order] => last_post_date
[default_sort_direction] => desc
[list_date_limit_days] => 0
[require_prefix] => 0
[allowed_watch_notifications] => all
[min_tags] => 0
[forum_type_id] => discussion
[type_config] => {"allowed_thread_types":["poll"]}
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
[Node] => XF\Entity\Node Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 55
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\Node
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[node_id] => 2
[title] => SemiWiki Main Forum ( Ask the Experts! )
[description] => Post your questions to the experts here!
[node_name] =>
[node_type_id] => Forum
[parent_node_id] => 1
[display_order] => 1
[display_in_list] => 1
[lft] => 2
[rgt] => 3
[depth] => 1
[style_id] => 0
[effective_style_id] => 0
[breadcrumb_data] => {"1":{"node_id":1,"title":"Main Category","depth":0,"lft":1,"node_name":null,"node_type_id":"Category","display_in_list":true}}
[navigation_id] =>
[effective_navigation_id] =>
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
[24731] => ThemeHouse\XPress\XF\Entity\Thread Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 97
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\Thread
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[thread_id] => 24731
[node_id] => 2
[title] => BEOL M0 32nm with EUV Low NA0.33 Single Exposure, Nvidia cuLitho helps but not easy for HVM
[reply_count] => 2
[view_count] => 343
[user_id] => 90385
[username] => NY_Sam2
[post_date] => 1773275139
[sticky] => 0
[discussion_state] => visible
[discussion_open] => 1
[discussion_type] => discussion
[first_post_id] => 98280
[first_post_reaction_score] => 2
[first_post_reactions] => {"1":2}
[last_post_date] => 1773286710
[last_post_id] => 98282
[last_post_user_id] => 5185
[last_post_username] => Fred Chen
[prefix_id] => 0
[tags] => []
[custom_fields] => []
[vote_score] => 0
[vote_count] => 0
[featured] => 0
[type_data] => []
[index_state] => default
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
[User] => ThemeHouse\XLink\XF\Entity\User Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 94
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\User
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[user_id] => 90385
[username] => NY_Sam2
[username_date] => 0
[username_date_visible] => 0
[email] => petekennedy1989@gmail.com
[custom_title] =>
[language_id] => 1
[style_id] => 0
[style_variation] =>
[timezone] => America/New_York
[visible] => 1
[activity_visible] => 1
[user_group_id] => 2
[secondary_group_ids] =>
[display_style_group_id] => 2
[permission_combination_id] => 8
[message_count] => 29
[question_solution_count] => 0
[conversations_unread] => 0
[register_date] => 1642621712
[last_activity] => 1773275282
[last_summary_email_date] => 1767709207
[trophy_points] => 13
[alerts_unviewed] => 13
[alerts_unread] => 13
[avatar_date] => 0
[avatar_width] => 0
[avatar_height] => 0
[avatar_highdpi] => 0
[avatar_optimized] => 0
[gravatar] =>
[user_state] => valid
[security_lock] =>
[is_moderator] => 0
[is_admin] => 0
[is_banned] => 0
[reaction_score] => 45
[warning_points] => 0
[is_staff] => 0
[secret_key] => egi-LmWHpsbQRZ7Y0Lk56hMyhUsrDhDE
[privacy_policy_accepted] => 1642621712
[terms_accepted] => 1642621712
[vote_score] => 0
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
[Forum] => XF\Entity\Forum Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 56
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\Forum
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[node_id] => 2
[discussion_count] => 8402
[message_count] => 61611
[last_post_id] => 98305
[last_post_date] => 1773398181
[last_post_user_id] => 19450
[last_post_username] => user nl
[last_thread_id] => 24737
[last_thread_title] => The Great AI Silicon Shortage
[last_thread_prefix_id] => 0
[moderate_threads] => 0
[moderate_replies] => 0
[allow_posting] => 1
[count_messages] => 1
[auto_feature] => 0
[find_new] => 1
[allow_index] => allow
[index_criteria] =>
[field_cache] => []
[prefix_cache] => []
[prompt_cache] => []
[default_prefix_id] => 0
[default_sort_order] => last_post_date
[default_sort_direction] => desc
[list_date_limit_days] => 0
[require_prefix] => 0
[allowed_watch_notifications] => all
[min_tags] => 0
[forum_type_id] => discussion
[type_config] => {"allowed_thread_types":["poll"]}
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
[Node] => XF\Entity\Node Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 55
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\Node
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[node_id] => 2
[title] => SemiWiki Main Forum ( Ask the Experts! )
[description] => Post your questions to the experts here!
[node_name] =>
[node_type_id] => Forum
[parent_node_id] => 1
[display_order] => 1
[display_in_list] => 1
[lft] => 2
[rgt] => 3
[depth] => 1
[style_id] => 0
[effective_style_id] => 0
[breadcrumb_data] => {"1":{"node_id":1,"title":"Main Category","depth":0,"lft":1,"node_name":null,"node_type_id":"Category","display_in_list":true}}
[navigation_id] =>
[effective_navigation_id] =>
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
[24723] => ThemeHouse\XPress\XF\Entity\Thread Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 101
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\Thread
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[thread_id] => 24723
[node_id] => 2
[title] => ASUS boss calls the MacBook Neo a "shock to the entire industry" — but still downplays it as a "content consumption" slab, like iPad
[reply_count] => 1
[view_count] => 219
[user_id] => 36640
[username] => soAsian
[post_date] => 1773251461
[sticky] => 0
[discussion_state] => visible
[discussion_open] => 1
[discussion_type] => discussion
[first_post_id] => 98259
[first_post_reaction_score] => 1
[first_post_reactions] => {"1":1}
[last_post_date] => 1773251923
[last_post_id] => 98261
[last_post_user_id] => 35301
[last_post_username] => Xebec
[prefix_id] => 0
[tags] => []
[custom_fields] => []
[vote_score] => 0
[vote_count] => 0
[featured] => 0
[type_data] => []
[index_state] => default
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
[User] => ThemeHouse\XLink\XF\Entity\User Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 98
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\User
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[user_id] => 36640
[username] => soAsian
[username_date] => 0
[username_date_visible] => 0
[email] => jackmtsai@gmail.com
[custom_title] =>
[language_id] => 1
[style_id] => 0
[style_variation] =>
[timezone] => America/Chicago
[visible] => 1
[activity_visible] => 1
[user_group_id] => 2
[secondary_group_ids] =>
[display_style_group_id] => 2
[permission_combination_id] => 8
[message_count] => 404
[question_solution_count] => 0
[conversations_unread] => 0
[register_date] => 1608139716
[last_activity] => 1773354169
[last_summary_email_date] => 1719670845
[trophy_points] => 63
[alerts_unviewed] => 1
[alerts_unread] => 1
[avatar_date] => 0
[avatar_width] => 0
[avatar_height] => 0
[avatar_highdpi] => 0
[avatar_optimized] => 0
[gravatar] =>
[user_state] => valid
[security_lock] =>
[is_moderator] => 0
[is_admin] => 0
[is_banned] => 0
[reaction_score] => 366
[warning_points] => 0
[is_staff] => 0
[secret_key] => 2oKeCTFkGUpMro5tcmj7WaY9HksB13Kw
[privacy_policy_accepted] => 1608139716
[terms_accepted] => 1608139716
[vote_score] => 0
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
[Forum] => XF\Entity\Forum Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 56
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\Forum
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[node_id] => 2
[discussion_count] => 8402
[message_count] => 61611
[last_post_id] => 98305
[last_post_date] => 1773398181
[last_post_user_id] => 19450
[last_post_username] => user nl
[last_thread_id] => 24737
[last_thread_title] => The Great AI Silicon Shortage
[last_thread_prefix_id] => 0
[moderate_threads] => 0
[moderate_replies] => 0
[allow_posting] => 1
[count_messages] => 1
[auto_feature] => 0
[find_new] => 1
[allow_index] => allow
[index_criteria] =>
[field_cache] => []
[prefix_cache] => []
[prompt_cache] => []
[default_prefix_id] => 0
[default_sort_order] => last_post_date
[default_sort_direction] => desc
[list_date_limit_days] => 0
[require_prefix] => 0
[allowed_watch_notifications] => all
[min_tags] => 0
[forum_type_id] => discussion
[type_config] => {"allowed_thread_types":["poll"]}
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
[Node] => XF\Entity\Node Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 55
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\Node
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[node_id] => 2
[title] => SemiWiki Main Forum ( Ask the Experts! )
[description] => Post your questions to the experts here!
[node_name] =>
[node_type_id] => Forum
[parent_node_id] => 1
[display_order] => 1
[display_in_list] => 1
[lft] => 2
[rgt] => 3
[depth] => 1
[style_id] => 0
[effective_style_id] => 0
[breadcrumb_data] => {"1":{"node_id":1,"title":"Main Category","depth":0,"lft":1,"node_name":null,"node_type_id":"Category","display_in_list":true}}
[navigation_id] =>
[effective_navigation_id] =>
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
[24686] => ThemeHouse\XPress\XF\Entity\Thread Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 105
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\Thread
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[thread_id] => 24686
[node_id] => 2
[title] => Intel Foundry’s Advanced Packaging Innovations Lead the Industry in Scaling Past Reticle Limits
[reply_count] => 7
[view_count] => 1637
[user_id] => 5
[username] => Daniel Nenni
[post_date] => 1772813055
[sticky] => 0
[discussion_state] => visible
[discussion_open] => 1
[discussion_type] => discussion
[first_post_id] => 98137
[first_post_reaction_score] => 1
[first_post_reactions] => {"1":1}
[last_post_date] => 1773250794
[last_post_id] => 98258
[last_post_user_id] => 138292
[last_post_username] => MKWVentures
[prefix_id] => 0
[tags] => []
[custom_fields] => []
[vote_score] => 0
[vote_count] => 0
[featured] => 0
[type_data] => []
[index_state] => default
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
[User] => ThemeHouse\XLink\XF\Entity\User Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 58
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\User
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[user_id] => 5
[username] => Daniel Nenni
[username_date] => 0
[username_date_visible] => 0
[email] => dnenni@semiwiki.com
[custom_title] => Admin
[language_id] => 1
[style_id] => 0
[style_variation] =>
[timezone] => America/Los_Angeles
[visible] => 1
[activity_visible] => 1
[user_group_id] => 3
[secondary_group_ids] => 4,5,132
[display_style_group_id] => 3
[permission_combination_id] => 88
[message_count] => 15351
[question_solution_count] => 0
[conversations_unread] => 0
[register_date] => 1280720820
[last_activity] => 1773398127
[last_summary_email_date] => 1605968657
[trophy_points] => 113
[alerts_unviewed] => 47
[alerts_unread] => 47
[avatar_date] => 1663211649
[avatar_width] => 110
[avatar_height] => 107
[avatar_highdpi] => 0
[avatar_optimized] => 0
[gravatar] =>
[user_state] => valid
[security_lock] =>
[is_moderator] => 1
[is_admin] => 1
[is_banned] => 0
[reaction_score] => 9203
[warning_points] => 0
[is_staff] => 1
[secret_key] => 0HwyUVVHCwJotUUVEpvqAclfYJdGNPpw
[privacy_policy_accepted] => 0
[terms_accepted] => 0
[vote_score] => 0
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
[Forum] => XF\Entity\Forum Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 56
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\Forum
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[node_id] => 2
[discussion_count] => 8402
[message_count] => 61611
[last_post_id] => 98305
[last_post_date] => 1773398181
[last_post_user_id] => 19450
[last_post_username] => user nl
[last_thread_id] => 24737
[last_thread_title] => The Great AI Silicon Shortage
[last_thread_prefix_id] => 0
[moderate_threads] => 0
[moderate_replies] => 0
[allow_posting] => 1
[count_messages] => 1
[auto_feature] => 0
[find_new] => 1
[allow_index] => allow
[index_criteria] =>
[field_cache] => []
[prefix_cache] => []
[prompt_cache] => []
[default_prefix_id] => 0
[default_sort_order] => last_post_date
[default_sort_direction] => desc
[list_date_limit_days] => 0
[require_prefix] => 0
[allowed_watch_notifications] => all
[min_tags] => 0
[forum_type_id] => discussion
[type_config] => {"allowed_thread_types":["poll"]}
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
[Node] => XF\Entity\Node Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 55
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\Node
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[node_id] => 2
[title] => SemiWiki Main Forum ( Ask the Experts! )
[description] => Post your questions to the experts here!
[node_name] =>
[node_type_id] => Forum
[parent_node_id] => 1
[display_order] => 1
[display_in_list] => 1
[lft] => 2
[rgt] => 3
[depth] => 1
[style_id] => 0
[effective_style_id] => 0
[breadcrumb_data] => {"1":{"node_id":1,"title":"Main Category","depth":0,"lft":1,"node_name":null,"node_type_id":"Category","display_in_list":true}}
[navigation_id] =>
[effective_navigation_id] =>
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
[24687] => ThemeHouse\XPress\XF\Entity\Thread Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 109
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\Thread
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[thread_id] => 24687
[node_id] => 2
[title] => US Considers Requiring Permits for Nvidia, AMD Global AI Chip Sales
[reply_count] => 11
[view_count] => 1570
[user_id] => 5
[username] => Daniel Nenni
[post_date] => 1772813834
[sticky] => 0
[discussion_state] => visible
[discussion_open] => 1
[discussion_type] => discussion
[first_post_id] => 98138
[first_post_reaction_score] => 0
[first_post_reactions] => {"6":2}
[last_post_date] => 1773174595
[last_post_id] => 98240
[last_post_user_id] => 138292
[last_post_username] => MKWVentures
[prefix_id] => 0
[tags] => []
[custom_fields] => []
[vote_score] => 0
[vote_count] => 0
[featured] => 0
[type_data] => []
[index_state] => default
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
[User] => ThemeHouse\XLink\XF\Entity\User Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 58
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\User
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[user_id] => 5
[username] => Daniel Nenni
[username_date] => 0
[username_date_visible] => 0
[email] => dnenni@semiwiki.com
[custom_title] => Admin
[language_id] => 1
[style_id] => 0
[style_variation] =>
[timezone] => America/Los_Angeles
[visible] => 1
[activity_visible] => 1
[user_group_id] => 3
[secondary_group_ids] => 4,5,132
[display_style_group_id] => 3
[permission_combination_id] => 88
[message_count] => 15351
[question_solution_count] => 0
[conversations_unread] => 0
[register_date] => 1280720820
[last_activity] => 1773398127
[last_summary_email_date] => 1605968657
[trophy_points] => 113
[alerts_unviewed] => 47
[alerts_unread] => 47
[avatar_date] => 1663211649
[avatar_width] => 110
[avatar_height] => 107
[avatar_highdpi] => 0
[avatar_optimized] => 0
[gravatar] =>
[user_state] => valid
[security_lock] =>
[is_moderator] => 1
[is_admin] => 1
[is_banned] => 0
[reaction_score] => 9203
[warning_points] => 0
[is_staff] => 1
[secret_key] => 0HwyUVVHCwJotUUVEpvqAclfYJdGNPpw
[privacy_policy_accepted] => 0
[terms_accepted] => 0
[vote_score] => 0
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
[Forum] => XF\Entity\Forum Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 56
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\Forum
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[node_id] => 2
[discussion_count] => 8402
[message_count] => 61611
[last_post_id] => 98305
[last_post_date] => 1773398181
[last_post_user_id] => 19450
[last_post_username] => user nl
[last_thread_id] => 24737
[last_thread_title] => The Great AI Silicon Shortage
[last_thread_prefix_id] => 0
[moderate_threads] => 0
[moderate_replies] => 0
[allow_posting] => 1
[count_messages] => 1
[auto_feature] => 0
[find_new] => 1
[allow_index] => allow
[index_criteria] =>
[field_cache] => []
[prefix_cache] => []
[prompt_cache] => []
[default_prefix_id] => 0
[default_sort_order] => last_post_date
[default_sort_direction] => desc
[list_date_limit_days] => 0
[require_prefix] => 0
[allowed_watch_notifications] => all
[min_tags] => 0
[forum_type_id] => discussion
[type_config] => {"allowed_thread_types":["poll"]}
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
[Node] => XF\Entity\Node Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 55
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\Node
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[node_id] => 2
[title] => SemiWiki Main Forum ( Ask the Experts! )
[description] => Post your questions to the experts here!
[node_name] =>
[node_type_id] => Forum
[parent_node_id] => 1
[display_order] => 1
[display_in_list] => 1
[lft] => 2
[rgt] => 3
[depth] => 1
[style_id] => 0
[effective_style_id] => 0
[breadcrumb_data] => {"1":{"node_id":1,"title":"Main Category","depth":0,"lft":1,"node_name":null,"node_type_id":"Category","display_in_list":true}}
[navigation_id] =>
[effective_navigation_id] =>
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
[24536] => ThemeHouse\XPress\XF\Entity\Thread Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 113
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\Thread
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[thread_id] => 24536
[node_id] => 2
[title] => Applied Materials Unveils Transistor and Wiring Innovations for Faster AI Chips
[reply_count] => 5
[view_count] => 1826
[user_id] => 5
[username] => Daniel Nenni
[post_date] => 1770859112
[sticky] => 0
[discussion_state] => visible
[discussion_open] => 1
[discussion_type] => discussion
[first_post_id] => 97414
[first_post_reaction_score] => 2
[first_post_reactions] => {"1":2}
[last_post_date] => 1773096868
[last_post_id] => 98211
[last_post_user_id] => 14269
[last_post_username] => BillUdd
[prefix_id] => 0
[tags] => []
[custom_fields] => []
[vote_score] => 0
[vote_count] => 0
[featured] => 0
[type_data] => []
[index_state] => default
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
[User] => ThemeHouse\XLink\XF\Entity\User Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 58
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\User
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[user_id] => 5
[username] => Daniel Nenni
[username_date] => 0
[username_date_visible] => 0
[email] => dnenni@semiwiki.com
[custom_title] => Admin
[language_id] => 1
[style_id] => 0
[style_variation] =>
[timezone] => America/Los_Angeles
[visible] => 1
[activity_visible] => 1
[user_group_id] => 3
[secondary_group_ids] => 4,5,132
[display_style_group_id] => 3
[permission_combination_id] => 88
[message_count] => 15351
[question_solution_count] => 0
[conversations_unread] => 0
[register_date] => 1280720820
[last_activity] => 1773398127
[last_summary_email_date] => 1605968657
[trophy_points] => 113
[alerts_unviewed] => 47
[alerts_unread] => 47
[avatar_date] => 1663211649
[avatar_width] => 110
[avatar_height] => 107
[avatar_highdpi] => 0
[avatar_optimized] => 0
[gravatar] =>
[user_state] => valid
[security_lock] =>
[is_moderator] => 1
[is_admin] => 1
[is_banned] => 0
[reaction_score] => 9203
[warning_points] => 0
[is_staff] => 1
[secret_key] => 0HwyUVVHCwJotUUVEpvqAclfYJdGNPpw
[privacy_policy_accepted] => 0
[terms_accepted] => 0
[vote_score] => 0
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
[Forum] => XF\Entity\Forum Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 56
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\Forum
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[node_id] => 2
[discussion_count] => 8402
[message_count] => 61611
[last_post_id] => 98305
[last_post_date] => 1773398181
[last_post_user_id] => 19450
[last_post_username] => user nl
[last_thread_id] => 24737
[last_thread_title] => The Great AI Silicon Shortage
[last_thread_prefix_id] => 0
[moderate_threads] => 0
[moderate_replies] => 0
[allow_posting] => 1
[count_messages] => 1
[auto_feature] => 0
[find_new] => 1
[allow_index] => allow
[index_criteria] =>
[field_cache] => []
[prefix_cache] => []
[prompt_cache] => []
[default_prefix_id] => 0
[default_sort_order] => last_post_date
[default_sort_direction] => desc
[list_date_limit_days] => 0
[require_prefix] => 0
[allowed_watch_notifications] => all
[min_tags] => 0
[forum_type_id] => discussion
[type_config] => {"allowed_thread_types":["poll"]}
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
[Node] => XF\Entity\Node Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 55
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\Node
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[node_id] => 2
[title] => SemiWiki Main Forum ( Ask the Experts! )
[description] => Post your questions to the experts here!
[node_name] =>
[node_type_id] => Forum
[parent_node_id] => 1
[display_order] => 1
[display_in_list] => 1
[lft] => 2
[rgt] => 3
[depth] => 1
[style_id] => 0
[effective_style_id] => 0
[breadcrumb_data] => {"1":{"node_id":1,"title":"Main Category","depth":0,"lft":1,"node_name":null,"node_type_id":"Category","display_in_list":true}}
[navigation_id] =>
[effective_navigation_id] =>
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
[24660] => ThemeHouse\XPress\XF\Entity\Thread Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 117
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\Thread
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[thread_id] => 24660
[node_id] => 2
[title] => Intel Board Chair Frank D. Yeary to Retire Following Annual Meeting; Dr. Craig H. Barratt Elected as Chair
[reply_count] => 8
[view_count] => 1312
[user_id] => 5
[username] => Daniel Nenni
[post_date] => 1772584001
[sticky] => 0
[discussion_state] => visible
[discussion_open] => 1
[discussion_type] => discussion
[first_post_id] => 98031
[first_post_reaction_score] => 3
[first_post_reactions] => {"1":3}
[last_post_date] => 1773081684
[last_post_id] => 98201
[last_post_user_id] => 33967
[last_post_username] => Jert
[prefix_id] => 0
[tags] => []
[custom_fields] => []
[vote_score] => 0
[vote_count] => 0
[featured] => 0
[type_data] => []
[index_state] => default
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
[User] => ThemeHouse\XLink\XF\Entity\User Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 58
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\User
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[user_id] => 5
[username] => Daniel Nenni
[username_date] => 0
[username_date_visible] => 0
[email] => dnenni@semiwiki.com
[custom_title] => Admin
[language_id] => 1
[style_id] => 0
[style_variation] =>
[timezone] => America/Los_Angeles
[visible] => 1
[activity_visible] => 1
[user_group_id] => 3
[secondary_group_ids] => 4,5,132
[display_style_group_id] => 3
[permission_combination_id] => 88
[message_count] => 15351
[question_solution_count] => 0
[conversations_unread] => 0
[register_date] => 1280720820
[last_activity] => 1773398127
[last_summary_email_date] => 1605968657
[trophy_points] => 113
[alerts_unviewed] => 47
[alerts_unread] => 47
[avatar_date] => 1663211649
[avatar_width] => 110
[avatar_height] => 107
[avatar_highdpi] => 0
[avatar_optimized] => 0
[gravatar] =>
[user_state] => valid
[security_lock] =>
[is_moderator] => 1
[is_admin] => 1
[is_banned] => 0
[reaction_score] => 9203
[warning_points] => 0
[is_staff] => 1
[secret_key] => 0HwyUVVHCwJotUUVEpvqAclfYJdGNPpw
[privacy_policy_accepted] => 0
[terms_accepted] => 0
[vote_score] => 0
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
[Forum] => XF\Entity\Forum Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 56
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\Forum
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[node_id] => 2
[discussion_count] => 8402
[message_count] => 61611
[last_post_id] => 98305
[last_post_date] => 1773398181
[last_post_user_id] => 19450
[last_post_username] => user nl
[last_thread_id] => 24737
[last_thread_title] => The Great AI Silicon Shortage
[last_thread_prefix_id] => 0
[moderate_threads] => 0
[moderate_replies] => 0
[allow_posting] => 1
[count_messages] => 1
[auto_feature] => 0
[find_new] => 1
[allow_index] => allow
[index_criteria] =>
[field_cache] => []
[prefix_cache] => []
[prompt_cache] => []
[default_prefix_id] => 0
[default_sort_order] => last_post_date
[default_sort_direction] => desc
[list_date_limit_days] => 0
[require_prefix] => 0
[allowed_watch_notifications] => all
[min_tags] => 0
[forum_type_id] => discussion
[type_config] => {"allowed_thread_types":["poll"]}
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
[Node] => XF\Entity\Node Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 55
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\Node
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[node_id] => 2
[title] => SemiWiki Main Forum ( Ask the Experts! )
[description] => Post your questions to the experts here!
[node_name] =>
[node_type_id] => Forum
[parent_node_id] => 1
[display_order] => 1
[display_in_list] => 1
[lft] => 2
[rgt] => 3
[depth] => 1
[style_id] => 0
[effective_style_id] => 0
[breadcrumb_data] => {"1":{"node_id":1,"title":"Main Category","depth":0,"lft":1,"node_name":null,"node_type_id":"Category","display_in_list":true}}
[navigation_id] =>
[effective_navigation_id] =>
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
[24692] => ThemeHouse\XPress\XF\Entity\Thread Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 121
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\Thread
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[thread_id] => 24692
[node_id] => 2
[title] => PC processors entered the Gigahertz era today in the year 2000 with AMD's Athlon — AMD hit marketing gold with its 1 GHz Athlon, beat Intel by a nose
[reply_count] => 2
[view_count] => 420
[user_id] => 36640
[username] => soAsian
[post_date] => 1772998302
[sticky] => 0
[discussion_state] => visible
[discussion_open] => 1
[discussion_type] => discussion
[first_post_id] => 98182
[first_post_reaction_score] => 1
[first_post_reactions] => {"1":1}
[last_post_date] => 1773066206
[last_post_id] => 98194
[last_post_user_id] => 35301
[last_post_username] => Xebec
[prefix_id] => 0
[tags] => []
[custom_fields] => []
[vote_score] => 0
[vote_count] => 0
[featured] => 0
[type_data] => []
[index_state] => default
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
[User] => ThemeHouse\XLink\XF\Entity\User Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 98
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\User
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[user_id] => 36640
[username] => soAsian
[username_date] => 0
[username_date_visible] => 0
[email] => jackmtsai@gmail.com
[custom_title] =>
[language_id] => 1
[style_id] => 0
[style_variation] =>
[timezone] => America/Chicago
[visible] => 1
[activity_visible] => 1
[user_group_id] => 2
[secondary_group_ids] =>
[display_style_group_id] => 2
[permission_combination_id] => 8
[message_count] => 404
[question_solution_count] => 0
[conversations_unread] => 0
[register_date] => 1608139716
[last_activity] => 1773354169
[last_summary_email_date] => 1719670845
[trophy_points] => 63
[alerts_unviewed] => 1
[alerts_unread] => 1
[avatar_date] => 0
[avatar_width] => 0
[avatar_height] => 0
[avatar_highdpi] => 0
[avatar_optimized] => 0
[gravatar] =>
[user_state] => valid
[security_lock] =>
[is_moderator] => 0
[is_admin] => 0
[is_banned] => 0
[reaction_score] => 366
[warning_points] => 0
[is_staff] => 0
[secret_key] => 2oKeCTFkGUpMro5tcmj7WaY9HksB13Kw
[privacy_policy_accepted] => 1608139716
[terms_accepted] => 1608139716
[vote_score] => 0
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
[Forum] => XF\Entity\Forum Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 56
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\Forum
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[node_id] => 2
[discussion_count] => 8402
[message_count] => 61611
[last_post_id] => 98305
[last_post_date] => 1773398181
[last_post_user_id] => 19450
[last_post_username] => user nl
[last_thread_id] => 24737
[last_thread_title] => The Great AI Silicon Shortage
[last_thread_prefix_id] => 0
[moderate_threads] => 0
[moderate_replies] => 0
[allow_posting] => 1
[count_messages] => 1
[auto_feature] => 0
[find_new] => 1
[allow_index] => allow
[index_criteria] =>
[field_cache] => []
[prefix_cache] => []
[prompt_cache] => []
[default_prefix_id] => 0
[default_sort_order] => last_post_date
[default_sort_direction] => desc
[list_date_limit_days] => 0
[require_prefix] => 0
[allowed_watch_notifications] => all
[min_tags] => 0
[forum_type_id] => discussion
[type_config] => {"allowed_thread_types":["poll"]}
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
[Node] => XF\Entity\Node Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 55
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\Node
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[node_id] => 2
[title] => SemiWiki Main Forum ( Ask the Experts! )
[description] => Post your questions to the experts here!
[node_name] =>
[node_type_id] => Forum
[parent_node_id] => 1
[display_order] => 1
[display_in_list] => 1
[lft] => 2
[rgt] => 3
[depth] => 1
[style_id] => 0
[effective_style_id] => 0
[breadcrumb_data] => {"1":{"node_id":1,"title":"Main Category","depth":0,"lft":1,"node_name":null,"node_type_id":"Category","display_in_list":true}}
[navigation_id] =>
[effective_navigation_id] =>
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
[24694] => ThemeHouse\XPress\XF\Entity\Thread Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 125
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\Thread
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[thread_id] => 24694
[node_id] => 2
[title] => Global Semiconductor Projects February 2026
[reply_count] => 0
[view_count] => 788
[user_id] => 5
[username] => Daniel Nenni
[post_date] => 1773052741
[sticky] => 0
[discussion_state] => visible
[discussion_open] => 1
[discussion_type] => discussion
[first_post_id] => 98193
[first_post_reaction_score] => 0
[first_post_reactions] => []
[last_post_date] => 1773052741
[last_post_id] => 98193
[last_post_user_id] => 5
[last_post_username] => Daniel Nenni
[prefix_id] => 0
[tags] => []
[custom_fields] => []
[vote_score] => 0
[vote_count] => 0
[featured] => 0
[type_data] => []
[index_state] => default
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
[User] => ThemeHouse\XLink\XF\Entity\User Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 58
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\User
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[user_id] => 5
[username] => Daniel Nenni
[username_date] => 0
[username_date_visible] => 0
[email] => dnenni@semiwiki.com
[custom_title] => Admin
[language_id] => 1
[style_id] => 0
[style_variation] =>
[timezone] => America/Los_Angeles
[visible] => 1
[activity_visible] => 1
[user_group_id] => 3
[secondary_group_ids] => 4,5,132
[display_style_group_id] => 3
[permission_combination_id] => 88
[message_count] => 15351
[question_solution_count] => 0
[conversations_unread] => 0
[register_date] => 1280720820
[last_activity] => 1773398127
[last_summary_email_date] => 1605968657
[trophy_points] => 113
[alerts_unviewed] => 47
[alerts_unread] => 47
[avatar_date] => 1663211649
[avatar_width] => 110
[avatar_height] => 107
[avatar_highdpi] => 0
[avatar_optimized] => 0
[gravatar] =>
[user_state] => valid
[security_lock] =>
[is_moderator] => 1
[is_admin] => 1
[is_banned] => 0
[reaction_score] => 9203
[warning_points] => 0
[is_staff] => 1
[secret_key] => 0HwyUVVHCwJotUUVEpvqAclfYJdGNPpw
[privacy_policy_accepted] => 0
[terms_accepted] => 0
[vote_score] => 0
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
[Forum] => XF\Entity\Forum Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 56
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\Forum
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[node_id] => 2
[discussion_count] => 8402
[message_count] => 61611
[last_post_id] => 98305
[last_post_date] => 1773398181
[last_post_user_id] => 19450
[last_post_username] => user nl
[last_thread_id] => 24737
[last_thread_title] => The Great AI Silicon Shortage
[last_thread_prefix_id] => 0
[moderate_threads] => 0
[moderate_replies] => 0
[allow_posting] => 1
[count_messages] => 1
[auto_feature] => 0
[find_new] => 1
[allow_index] => allow
[index_criteria] =>
[field_cache] => []
[prefix_cache] => []
[prompt_cache] => []
[default_prefix_id] => 0
[default_sort_order] => last_post_date
[default_sort_direction] => desc
[list_date_limit_days] => 0
[require_prefix] => 0
[allowed_watch_notifications] => all
[min_tags] => 0
[forum_type_id] => discussion
[type_config] => {"allowed_thread_types":["poll"]}
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
[Node] => XF\Entity\Node Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 55
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\Node
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[node_id] => 2
[title] => SemiWiki Main Forum ( Ask the Experts! )
[description] => Post your questions to the experts here!
[node_name] =>
[node_type_id] => Forum
[parent_node_id] => 1
[display_order] => 1
[display_in_list] => 1
[lft] => 2
[rgt] => 3
[depth] => 1
[style_id] => 0
[effective_style_id] => 0
[breadcrumb_data] => {"1":{"node_id":1,"title":"Main Category","depth":0,"lft":1,"node_name":null,"node_type_id":"Category","display_in_list":true}}
[navigation_id] =>
[effective_navigation_id] =>
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
[24684] => ThemeHouse\XPress\XF\Entity\Thread Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 129
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\Thread
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[thread_id] => 24684
[node_id] => 2
[title] => Build China’s ASML
[reply_count] => 19
[view_count] => 2180
[user_id] => 19450
[username] => user nl
[post_date] => 1772785293
[sticky] => 0
[discussion_state] => visible
[discussion_open] => 1
[discussion_type] => discussion
[first_post_id] => 98120
[first_post_reaction_score] => 0
[first_post_reactions] => []
[last_post_date] => 1773037576
[last_post_id] => 98192
[last_post_user_id] => 5185
[last_post_username] => Fred Chen
[prefix_id] => 0
[tags] => []
[custom_fields] => []
[vote_score] => 0
[vote_count] => 0
[featured] => 0
[type_data] => []
[index_state] => default
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
[User] => ThemeHouse\XLink\XF\Entity\User Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 54
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\User
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[user_id] => 19450
[username] => user nl
[username_date] => 0
[username_date_visible] => 0
[email] => mauricehmjanssen@gmail.com
[custom_title] =>
[language_id] => 1
[style_id] => 0
[style_variation] =>
[timezone] => Europe/Amsterdam
[visible] => 1
[activity_visible] => 1
[user_group_id] => 2
[secondary_group_ids] =>
[display_style_group_id] => 2
[permission_combination_id] => 8
[message_count] => 462
[question_solution_count] => 0
[conversations_unread] => 0
[register_date] => 1424291496
[last_activity] => 1773399233
[last_summary_email_date] =>
[trophy_points] => 63
[alerts_unviewed] => 0
[alerts_unread] => 0
[avatar_date] => 1726169369
[avatar_width] => 384
[avatar_height] => 384
[avatar_highdpi] => 1
[avatar_optimized] => 0
[gravatar] =>
[user_state] => valid
[security_lock] =>
[is_moderator] => 0
[is_admin] => 0
[is_banned] => 0
[reaction_score] => 345
[warning_points] => 0
[is_staff] => 0
[secret_key] => V-1lb5_AW69yhzqA5ok9b64U0fMjJiqf
[privacy_policy_accepted] => 0
[terms_accepted] => 0
[vote_score] => 0
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
[Forum] => XF\Entity\Forum Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 56
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\Forum
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[node_id] => 2
[discussion_count] => 8402
[message_count] => 61611
[last_post_id] => 98305
[last_post_date] => 1773398181
[last_post_user_id] => 19450
[last_post_username] => user nl
[last_thread_id] => 24737
[last_thread_title] => The Great AI Silicon Shortage
[last_thread_prefix_id] => 0
[moderate_threads] => 0
[moderate_replies] => 0
[allow_posting] => 1
[count_messages] => 1
[auto_feature] => 0
[find_new] => 1
[allow_index] => allow
[index_criteria] =>
[field_cache] => []
[prefix_cache] => []
[prompt_cache] => []
[default_prefix_id] => 0
[default_sort_order] => last_post_date
[default_sort_direction] => desc
[list_date_limit_days] => 0
[require_prefix] => 0
[allowed_watch_notifications] => all
[min_tags] => 0
[forum_type_id] => discussion
[type_config] => {"allowed_thread_types":["poll"]}
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
[Node] => XF\Entity\Node Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 55
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\Node
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[node_id] => 2
[title] => SemiWiki Main Forum ( Ask the Experts! )
[description] => Post your questions to the experts here!
[node_name] =>
[node_type_id] => Forum
[parent_node_id] => 1
[display_order] => 1
[display_in_list] => 1
[lft] => 2
[rgt] => 3
[depth] => 1
[style_id] => 0
[effective_style_id] => 0
[breadcrumb_data] => {"1":{"node_id":1,"title":"Main Category","depth":0,"lft":1,"node_name":null,"node_type_id":"Category","display_in_list":true}}
[navigation_id] =>
[effective_navigation_id] =>
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
[24691] => ThemeHouse\XPress\XF\Entity\Thread Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 133
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\Thread
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[thread_id] => 24691
[node_id] => 2
[title] => Elon Musk kills résumés for chip hires and wants these 3 bullet points
[reply_count] => 8
[view_count] => 1577
[user_id] => 5
[username] => Daniel Nenni
[post_date] => 1772969672
[sticky] => 0
[discussion_state] => visible
[discussion_open] => 1
[discussion_type] => discussion
[first_post_id] => 98176
[first_post_reaction_score] => 4
[first_post_reactions] => {"1":4}
[last_post_date] => 1773035448
[last_post_id] => 98189
[last_post_user_id] => 396
[last_post_username] => swka
[prefix_id] => 0
[tags] => []
[custom_fields] => []
[vote_score] => 0
[vote_count] => 0
[featured] => 0
[type_data] => []
[index_state] => default
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
[User] => ThemeHouse\XLink\XF\Entity\User Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 58
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\User
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[user_id] => 5
[username] => Daniel Nenni
[username_date] => 0
[username_date_visible] => 0
[email] => dnenni@semiwiki.com
[custom_title] => Admin
[language_id] => 1
[style_id] => 0
[style_variation] =>
[timezone] => America/Los_Angeles
[visible] => 1
[activity_visible] => 1
[user_group_id] => 3
[secondary_group_ids] => 4,5,132
[display_style_group_id] => 3
[permission_combination_id] => 88
[message_count] => 15351
[question_solution_count] => 0
[conversations_unread] => 0
[register_date] => 1280720820
[last_activity] => 1773398127
[last_summary_email_date] => 1605968657
[trophy_points] => 113
[alerts_unviewed] => 47
[alerts_unread] => 47
[avatar_date] => 1663211649
[avatar_width] => 110
[avatar_height] => 107
[avatar_highdpi] => 0
[avatar_optimized] => 0
[gravatar] =>
[user_state] => valid
[security_lock] =>
[is_moderator] => 1
[is_admin] => 1
[is_banned] => 0
[reaction_score] => 9203
[warning_points] => 0
[is_staff] => 1
[secret_key] => 0HwyUVVHCwJotUUVEpvqAclfYJdGNPpw
[privacy_policy_accepted] => 0
[terms_accepted] => 0
[vote_score] => 0
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
[Forum] => XF\Entity\Forum Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 56
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\Forum
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[node_id] => 2
[discussion_count] => 8402
[message_count] => 61611
[last_post_id] => 98305
[last_post_date] => 1773398181
[last_post_user_id] => 19450
[last_post_username] => user nl
[last_thread_id] => 24737
[last_thread_title] => The Great AI Silicon Shortage
[last_thread_prefix_id] => 0
[moderate_threads] => 0
[moderate_replies] => 0
[allow_posting] => 1
[count_messages] => 1
[auto_feature] => 0
[find_new] => 1
[allow_index] => allow
[index_criteria] =>
[field_cache] => []
[prefix_cache] => []
[prompt_cache] => []
[default_prefix_id] => 0
[default_sort_order] => last_post_date
[default_sort_direction] => desc
[list_date_limit_days] => 0
[require_prefix] => 0
[allowed_watch_notifications] => all
[min_tags] => 0
[forum_type_id] => discussion
[type_config] => {"allowed_thread_types":["poll"]}
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
[Node] => XF\Entity\Node Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 55
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\Node
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[node_id] => 2
[title] => SemiWiki Main Forum ( Ask the Experts! )
[description] => Post your questions to the experts here!
[node_name] =>
[node_type_id] => Forum
[parent_node_id] => 1
[display_order] => 1
[display_in_list] => 1
[lft] => 2
[rgt] => 3
[depth] => 1
[style_id] => 0
[effective_style_id] => 0
[breadcrumb_data] => {"1":{"node_id":1,"title":"Main Category","depth":0,"lft":1,"node_name":null,"node_type_id":"Category","display_in_list":true}}
[navigation_id] =>
[effective_navigation_id] =>
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
)
[populated:protected] => 1
)

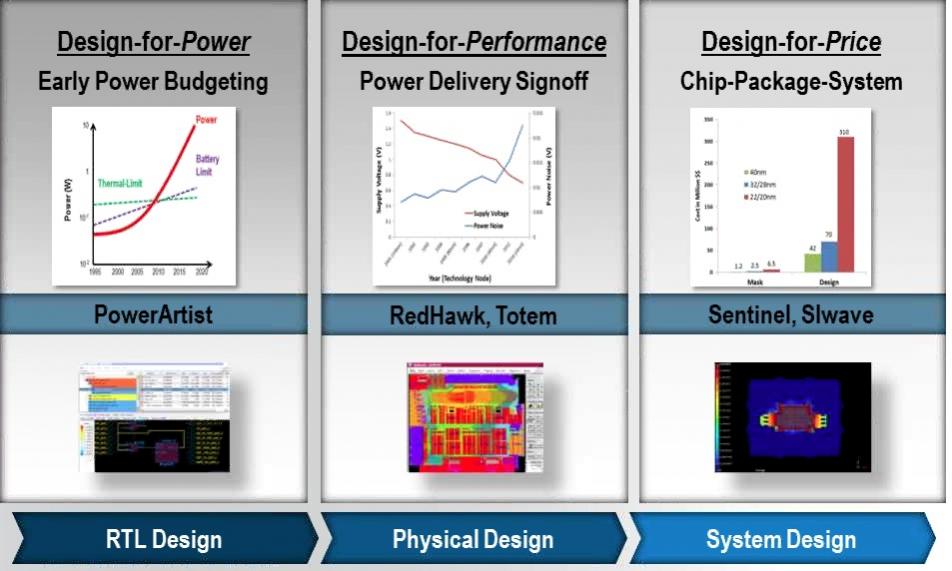
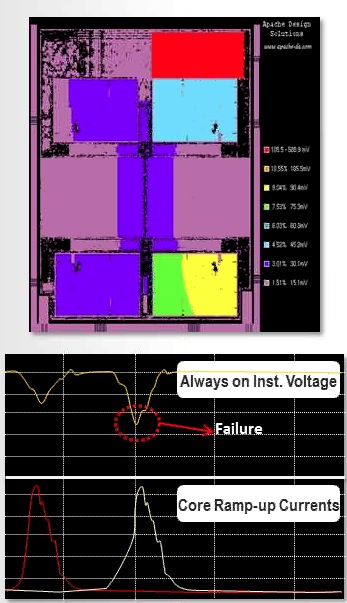
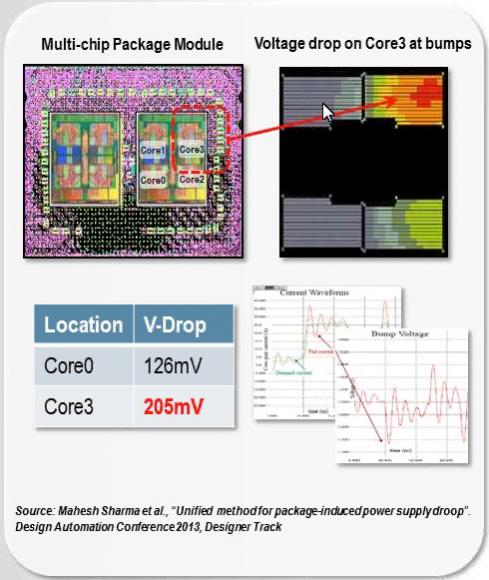
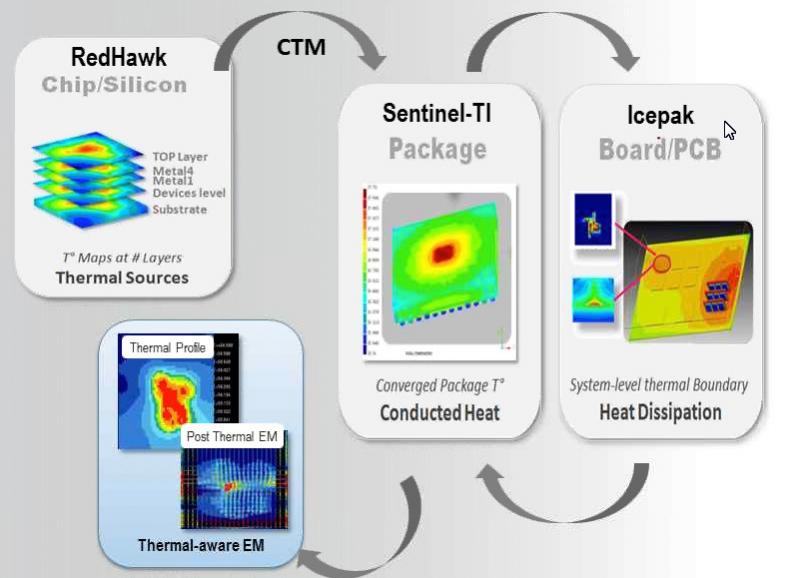








Comments
There are no comments yet.
You must register or log in to view/post comments.