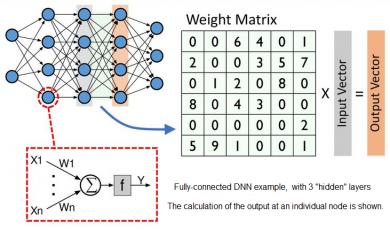
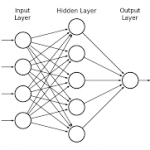
The basic principles used for neural networks have been understood for decades, what have changed to make them so successful in recent years are increased processing power, storage and training data. Layered on top of this is continued improvement in algorithms, often enabled by dramatic hardware performance improvements.… Read More
AI at the Edge
Frequent Semiwiki readers are well aware of the industry momentum behind machine learning applications. New opportunities are emerging at a rapid pace. High-level programming language semantics and compilers to capture and simulate neural network models have been developed to enhance developer productivity (link). Researchers… Read More
Architecture for Machine Learning Applications at the Edge
Machine learning applications in data centers (or “the cloud”) have pervasively changed our environment. Advances in speech recognition and natural language understanding have enabled personal assistants to augment our daily lifestyle. Image classification and object recognition techniques enrich our social media experience,… Read More
Avionics and Embedded FPGA IP
The design of electronic systems for aerospace applications shares many of the same constraints as apply to consumer products – e.g., cost (including NRE), power dissipation, size, time-to-market. Both market segments are driven to leverage the integration benefits of process scaling. … Read More
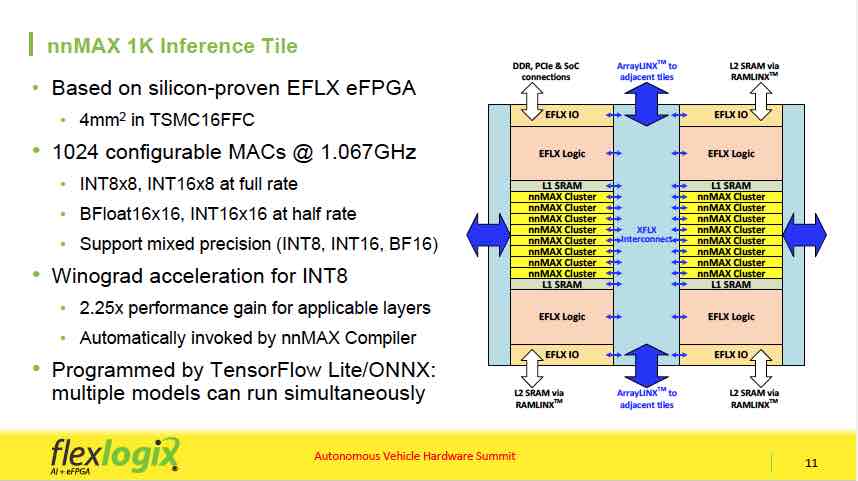
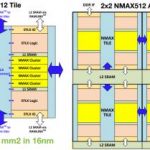
Neural Network Efficiency with Embedded FPGA’s
The traditional metrics for evaluating IP are performance, power, and area, commonly abbreviated as PPA. Viewed independently, PPA measures can be difficult to assess. As an example, design constraints that are purely based on performance, without concern for the associated power dissipation and circuit area, are increasingly… Read More
Machine Learning and Embedded FPGA IP
Machine learning-based applications have become prevalent across consumer, medical, and automotive markets. Still, the underlying architecture(s) and implementations are evolving rapidly, to best fit the throughput, latency, and power efficiency requirements of an ever increasing application space. Although ML is … Read More
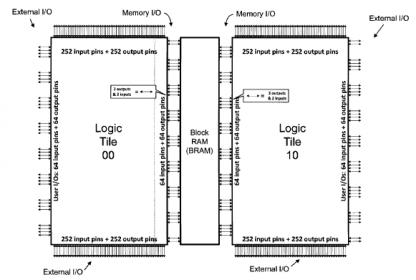
Block RAM integration for an Embedded FPGA
The upcoming Design Automation Conference in San Francisco includes a very interesting session –“Has the Time for Embedded FPGA Come at Last?” Periodically, I’ve been having coffee with the team at Flex Logix, to get their perspective on this very question – specifically, to learn about the key features that customers are seeking… Read More
Hard IP for an embedded FPGA
As Moore’s Law enables increased integration, the diversity of functionality in SoC designs has grown. Design teams are seeking to utilize outside technical expertise in key functional areas, and to accelerate their productivity by re-using existing designs that others have developed. The Intellectual Property (IP) industry… Read More
Configurability for Embedded FPGA Hard IP
IP providers need to evaluate several complex engineering problems when addressing customer requirements – perhaps the most intricate challenge is the degree of IP configurabilityavailable to satisfy unique customer applications. … Read More
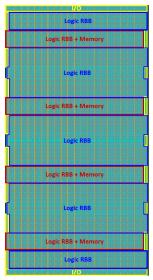
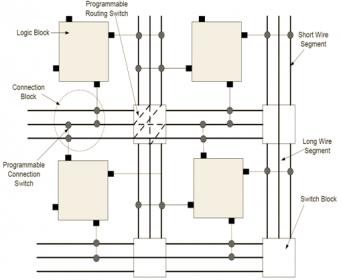
The hierarchical architecture of an embedded FPGA
The most powerful approach to managing the complexity of current SoC hardware is the identification of hierarchical instances with which to assemble the design. The development of the hierarchical design representation requires judicious assessment of the component definitions. The goals for clock distribution, power … Read More