Threads
XF\Mvc\Entity\ArrayCollection Object
(
[entities:protected] => Array
(
[23156] => ThemeHouse\XPress\XF\Entity\Thread Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 51
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\Thread
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[thread_id] => 23156
[node_id] => 2
[title] => IBM eyes deeper partnership with Rapidus for sub-1nm chip development
[reply_count] => 1
[view_count] => 74
[user_id] => 5
[username] => Daniel Nenni
[post_date] => 1752003852
[sticky] => 0
[discussion_state] => visible
[discussion_open] => 1
[discussion_type] => discussion
[first_post_id] => 88332
[first_post_reaction_score] => 0
[first_post_reactions] => []
[last_post_date] => 1752009795
[last_post_id] => 88334
[last_post_user_id] => 138292
[last_post_username] => MKWVentures
[prefix_id] => 0
[tags] => []
[custom_fields] => []
[vote_score] => 0
[vote_count] => 0
[type_data] => []
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
[User] => ThemeHouse\XLink\XF\Entity\User Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 48
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\User
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[user_id] => 5
[username] => Daniel Nenni
[username_date] => 0
[username_date_visible] => 0
[email] => dnenni@semiwiki.com
[custom_title] => Admin
[language_id] => 1
[style_id] => 0
[timezone] => America/Los_Angeles
[visible] => 1
[activity_visible] => 1
[user_group_id] => 3
[secondary_group_ids] => 4,5,132
[display_style_group_id] => 3
[permission_combination_id] => 88
[message_count] => 13876
[question_solution_count] => 0
[conversations_unread] => 0
[register_date] => 1280720820
[last_activity] => 1752012529
[last_summary_email_date] => 1605968657
[trophy_points] => 113
[alerts_unviewed] => 10
[alerts_unread] => 41
[avatar_date] => 1663211649
[avatar_width] => 110
[avatar_height] => 107
[avatar_highdpi] => 0
[gravatar] =>
[user_state] => valid
[security_lock] =>
[is_moderator] => 1
[is_admin] => 1
[is_banned] => 0
[reaction_score] => 6965
[warning_points] => 0
[is_staff] => 1
[secret_key] => 0HwyUVVHCwJotUUVEpvqAclfYJdGNPpw
[privacy_policy_accepted] => 0
[terms_accepted] => 0
[vote_score] => 0
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
[Forum] => XF\Entity\Forum Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 50
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\Forum
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[node_id] => 2
[discussion_count] => 7518
[message_count] => 52569
[last_post_id] => 88334
[last_post_date] => 1752009795
[last_post_user_id] => 138292
[last_post_username] => MKWVentures
[last_thread_id] => 23156
[last_thread_title] => IBM eyes deeper partnership with Rapidus for sub-1nm chip development
[last_thread_prefix_id] => 0
[moderate_threads] => 0
[moderate_replies] => 0
[allow_posting] => 1
[count_messages] => 1
[find_new] => 1
[allow_index] => allow
[index_criteria] =>
[field_cache] => []
[prefix_cache] => []
[prompt_cache] => []
[default_prefix_id] => 0
[default_sort_order] => last_post_date
[default_sort_direction] => desc
[list_date_limit_days] => 0
[require_prefix] => 0
[allowed_watch_notifications] => all
[min_tags] => 0
[forum_type_id] => discussion
[type_config] => {"allowed_thread_types":["poll"]}
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
[Node] => XF\Entity\Node Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 49
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\Node
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[node_id] => 2
[title] => SemiWiki Main Forum ( Ask the Experts! )
[description] => Post your questions to the experts here!
[node_name] =>
[node_type_id] => Forum
[parent_node_id] => 1
[display_order] => 1
[display_in_list] => 1
[lft] => 2
[rgt] => 3
[depth] => 1
[style_id] => 0
[effective_style_id] => 0
[breadcrumb_data] => {"1":{"node_id":1,"title":"Main Category","depth":0,"lft":1,"node_name":null,"node_type_id":"Category","display_in_list":true}}
[navigation_id] =>
[effective_navigation_id] =>
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
[23152] => ThemeHouse\XPress\XF\Entity\Thread Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 55
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\Thread
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[thread_id] => 23152
[node_id] => 2
[title] => One-third (32%) of projected US$1 trillion semiconductor supply could be at risk within a decade unless industry adapts to climate change
[reply_count] => 4
[view_count] => 189
[user_id] => 5
[username] => Daniel Nenni
[post_date] => 1751987456
[sticky] => 0
[discussion_state] => visible
[discussion_open] => 1
[discussion_type] => discussion
[first_post_id] => 88319
[first_post_reaction_score] => 0
[first_post_reactions] => []
[last_post_date] => 1752005872
[last_post_id] => 88333
[last_post_user_id] => 29779
[last_post_username] => tooLongInEDA
[prefix_id] => 0
[tags] => []
[custom_fields] => []
[vote_score] => 0
[vote_count] => 0
[type_data] => []
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
[User] => ThemeHouse\XLink\XF\Entity\User Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 48
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\User
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[user_id] => 5
[username] => Daniel Nenni
[username_date] => 0
[username_date_visible] => 0
[email] => dnenni@semiwiki.com
[custom_title] => Admin
[language_id] => 1
[style_id] => 0
[timezone] => America/Los_Angeles
[visible] => 1
[activity_visible] => 1
[user_group_id] => 3
[secondary_group_ids] => 4,5,132
[display_style_group_id] => 3
[permission_combination_id] => 88
[message_count] => 13876
[question_solution_count] => 0
[conversations_unread] => 0
[register_date] => 1280720820
[last_activity] => 1752012529
[last_summary_email_date] => 1605968657
[trophy_points] => 113
[alerts_unviewed] => 10
[alerts_unread] => 41
[avatar_date] => 1663211649
[avatar_width] => 110
[avatar_height] => 107
[avatar_highdpi] => 0
[gravatar] =>
[user_state] => valid
[security_lock] =>
[is_moderator] => 1
[is_admin] => 1
[is_banned] => 0
[reaction_score] => 6965
[warning_points] => 0
[is_staff] => 1
[secret_key] => 0HwyUVVHCwJotUUVEpvqAclfYJdGNPpw
[privacy_policy_accepted] => 0
[terms_accepted] => 0
[vote_score] => 0
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
[Forum] => XF\Entity\Forum Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 50
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\Forum
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[node_id] => 2
[discussion_count] => 7518
[message_count] => 52569
[last_post_id] => 88334
[last_post_date] => 1752009795
[last_post_user_id] => 138292
[last_post_username] => MKWVentures
[last_thread_id] => 23156
[last_thread_title] => IBM eyes deeper partnership with Rapidus for sub-1nm chip development
[last_thread_prefix_id] => 0
[moderate_threads] => 0
[moderate_replies] => 0
[allow_posting] => 1
[count_messages] => 1
[find_new] => 1
[allow_index] => allow
[index_criteria] =>
[field_cache] => []
[prefix_cache] => []
[prompt_cache] => []
[default_prefix_id] => 0
[default_sort_order] => last_post_date
[default_sort_direction] => desc
[list_date_limit_days] => 0
[require_prefix] => 0
[allowed_watch_notifications] => all
[min_tags] => 0
[forum_type_id] => discussion
[type_config] => {"allowed_thread_types":["poll"]}
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
[Node] => XF\Entity\Node Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 49
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\Node
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[node_id] => 2
[title] => SemiWiki Main Forum ( Ask the Experts! )
[description] => Post your questions to the experts here!
[node_name] =>
[node_type_id] => Forum
[parent_node_id] => 1
[display_order] => 1
[display_in_list] => 1
[lft] => 2
[rgt] => 3
[depth] => 1
[style_id] => 0
[effective_style_id] => 0
[breadcrumb_data] => {"1":{"node_id":1,"title":"Main Category","depth":0,"lft":1,"node_name":null,"node_type_id":"Category","display_in_list":true}}
[navigation_id] =>
[effective_navigation_id] =>
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
[23155] => ThemeHouse\XPress\XF\Entity\Thread Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 59
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\Thread
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[thread_id] => 23155
[node_id] => 2
[title] => IBM rolls out new chips and servers, aims for simplified AI
[reply_count] => 0
[view_count] => 95
[user_id] => 5
[username] => Daniel Nenni
[post_date] => 1752000406
[sticky] => 0
[discussion_state] => visible
[discussion_open] => 1
[discussion_type] => discussion
[first_post_id] => 88330
[first_post_reaction_score] => 0
[first_post_reactions] => []
[last_post_date] => 1752000406
[last_post_id] => 88330
[last_post_user_id] => 5
[last_post_username] => Daniel Nenni
[prefix_id] => 0
[tags] => []
[custom_fields] => []
[vote_score] => 0
[vote_count] => 0
[type_data] => []
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
[User] => ThemeHouse\XLink\XF\Entity\User Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 48
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\User
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[user_id] => 5
[username] => Daniel Nenni
[username_date] => 0
[username_date_visible] => 0
[email] => dnenni@semiwiki.com
[custom_title] => Admin
[language_id] => 1
[style_id] => 0
[timezone] => America/Los_Angeles
[visible] => 1
[activity_visible] => 1
[user_group_id] => 3
[secondary_group_ids] => 4,5,132
[display_style_group_id] => 3
[permission_combination_id] => 88
[message_count] => 13876
[question_solution_count] => 0
[conversations_unread] => 0
[register_date] => 1280720820
[last_activity] => 1752012529
[last_summary_email_date] => 1605968657
[trophy_points] => 113
[alerts_unviewed] => 10
[alerts_unread] => 41
[avatar_date] => 1663211649
[avatar_width] => 110
[avatar_height] => 107
[avatar_highdpi] => 0
[gravatar] =>
[user_state] => valid
[security_lock] =>
[is_moderator] => 1
[is_admin] => 1
[is_banned] => 0
[reaction_score] => 6965
[warning_points] => 0
[is_staff] => 1
[secret_key] => 0HwyUVVHCwJotUUVEpvqAclfYJdGNPpw
[privacy_policy_accepted] => 0
[terms_accepted] => 0
[vote_score] => 0
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
[Forum] => XF\Entity\Forum Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 50
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\Forum
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[node_id] => 2
[discussion_count] => 7518
[message_count] => 52569
[last_post_id] => 88334
[last_post_date] => 1752009795
[last_post_user_id] => 138292
[last_post_username] => MKWVentures
[last_thread_id] => 23156
[last_thread_title] => IBM eyes deeper partnership with Rapidus for sub-1nm chip development
[last_thread_prefix_id] => 0
[moderate_threads] => 0
[moderate_replies] => 0
[allow_posting] => 1
[count_messages] => 1
[find_new] => 1
[allow_index] => allow
[index_criteria] =>
[field_cache] => []
[prefix_cache] => []
[prompt_cache] => []
[default_prefix_id] => 0
[default_sort_order] => last_post_date
[default_sort_direction] => desc
[list_date_limit_days] => 0
[require_prefix] => 0
[allowed_watch_notifications] => all
[min_tags] => 0
[forum_type_id] => discussion
[type_config] => {"allowed_thread_types":["poll"]}
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
[Node] => XF\Entity\Node Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 49
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\Node
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[node_id] => 2
[title] => SemiWiki Main Forum ( Ask the Experts! )
[description] => Post your questions to the experts here!
[node_name] =>
[node_type_id] => Forum
[parent_node_id] => 1
[display_order] => 1
[display_in_list] => 1
[lft] => 2
[rgt] => 3
[depth] => 1
[style_id] => 0
[effective_style_id] => 0
[breadcrumb_data] => {"1":{"node_id":1,"title":"Main Category","depth":0,"lft":1,"node_name":null,"node_type_id":"Category","display_in_list":true}}
[navigation_id] =>
[effective_navigation_id] =>
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
[23154] => ThemeHouse\XPress\XF\Entity\Thread Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 63
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\Thread
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[thread_id] => 23154
[node_id] => 2
[title] => GlobalFoundries to Acquire MIPS to Accelerate AI and Compute Capabilities
[reply_count] => 4
[view_count] => 233
[user_id] => 5
[username] => Daniel Nenni
[post_date] => 1751991614
[sticky] => 0
[discussion_state] => visible
[discussion_open] => 1
[discussion_type] => discussion
[first_post_id] => 88321
[first_post_reaction_score] => 0
[first_post_reactions] => []
[last_post_date] => 1751997468
[last_post_id] => 88328
[last_post_user_id] => 12844
[last_post_username] => coldsolder215
[prefix_id] => 0
[tags] => []
[custom_fields] => []
[vote_score] => 0
[vote_count] => 0
[type_data] => []
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
[User] => ThemeHouse\XLink\XF\Entity\User Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 48
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\User
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[user_id] => 5
[username] => Daniel Nenni
[username_date] => 0
[username_date_visible] => 0
[email] => dnenni@semiwiki.com
[custom_title] => Admin
[language_id] => 1
[style_id] => 0
[timezone] => America/Los_Angeles
[visible] => 1
[activity_visible] => 1
[user_group_id] => 3
[secondary_group_ids] => 4,5,132
[display_style_group_id] => 3
[permission_combination_id] => 88
[message_count] => 13876
[question_solution_count] => 0
[conversations_unread] => 0
[register_date] => 1280720820
[last_activity] => 1752012529
[last_summary_email_date] => 1605968657
[trophy_points] => 113
[alerts_unviewed] => 10
[alerts_unread] => 41
[avatar_date] => 1663211649
[avatar_width] => 110
[avatar_height] => 107
[avatar_highdpi] => 0
[gravatar] =>
[user_state] => valid
[security_lock] =>
[is_moderator] => 1
[is_admin] => 1
[is_banned] => 0
[reaction_score] => 6965
[warning_points] => 0
[is_staff] => 1
[secret_key] => 0HwyUVVHCwJotUUVEpvqAclfYJdGNPpw
[privacy_policy_accepted] => 0
[terms_accepted] => 0
[vote_score] => 0
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
[Forum] => XF\Entity\Forum Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 50
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\Forum
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[node_id] => 2
[discussion_count] => 7518
[message_count] => 52569
[last_post_id] => 88334
[last_post_date] => 1752009795
[last_post_user_id] => 138292
[last_post_username] => MKWVentures
[last_thread_id] => 23156
[last_thread_title] => IBM eyes deeper partnership with Rapidus for sub-1nm chip development
[last_thread_prefix_id] => 0
[moderate_threads] => 0
[moderate_replies] => 0
[allow_posting] => 1
[count_messages] => 1
[find_new] => 1
[allow_index] => allow
[index_criteria] =>
[field_cache] => []
[prefix_cache] => []
[prompt_cache] => []
[default_prefix_id] => 0
[default_sort_order] => last_post_date
[default_sort_direction] => desc
[list_date_limit_days] => 0
[require_prefix] => 0
[allowed_watch_notifications] => all
[min_tags] => 0
[forum_type_id] => discussion
[type_config] => {"allowed_thread_types":["poll"]}
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
[Node] => XF\Entity\Node Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 49
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\Node
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[node_id] => 2
[title] => SemiWiki Main Forum ( Ask the Experts! )
[description] => Post your questions to the experts here!
[node_name] =>
[node_type_id] => Forum
[parent_node_id] => 1
[display_order] => 1
[display_in_list] => 1
[lft] => 2
[rgt] => 3
[depth] => 1
[style_id] => 0
[effective_style_id] => 0
[breadcrumb_data] => {"1":{"node_id":1,"title":"Main Category","depth":0,"lft":1,"node_name":null,"node_type_id":"Category","display_in_list":true}}
[navigation_id] =>
[effective_navigation_id] =>
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
[23153] => ThemeHouse\XPress\XF\Entity\Thread Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 67
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\Thread
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[thread_id] => 23153
[node_id] => 2
[title] => Global Semiconductor Sales Increase 19.8% Year-to-Year in May
[reply_count] => 0
[view_count] => 105
[user_id] => 5
[username] => Daniel Nenni
[post_date] => 1751989341
[sticky] => 0
[discussion_state] => visible
[discussion_open] => 1
[discussion_type] => discussion
[first_post_id] => 88320
[first_post_reaction_score] => 0
[first_post_reactions] => []
[last_post_date] => 1751989341
[last_post_id] => 88320
[last_post_user_id] => 5
[last_post_username] => Daniel Nenni
[prefix_id] => 0
[tags] => []
[custom_fields] => []
[vote_score] => 0
[vote_count] => 0
[type_data] => []
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
[User] => ThemeHouse\XLink\XF\Entity\User Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 48
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\User
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[user_id] => 5
[username] => Daniel Nenni
[username_date] => 0
[username_date_visible] => 0
[email] => dnenni@semiwiki.com
[custom_title] => Admin
[language_id] => 1
[style_id] => 0
[timezone] => America/Los_Angeles
[visible] => 1
[activity_visible] => 1
[user_group_id] => 3
[secondary_group_ids] => 4,5,132
[display_style_group_id] => 3
[permission_combination_id] => 88
[message_count] => 13876
[question_solution_count] => 0
[conversations_unread] => 0
[register_date] => 1280720820
[last_activity] => 1752012529
[last_summary_email_date] => 1605968657
[trophy_points] => 113
[alerts_unviewed] => 10
[alerts_unread] => 41
[avatar_date] => 1663211649
[avatar_width] => 110
[avatar_height] => 107
[avatar_highdpi] => 0
[gravatar] =>
[user_state] => valid
[security_lock] =>
[is_moderator] => 1
[is_admin] => 1
[is_banned] => 0
[reaction_score] => 6965
[warning_points] => 0
[is_staff] => 1
[secret_key] => 0HwyUVVHCwJotUUVEpvqAclfYJdGNPpw
[privacy_policy_accepted] => 0
[terms_accepted] => 0
[vote_score] => 0
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
[Forum] => XF\Entity\Forum Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 50
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\Forum
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[node_id] => 2
[discussion_count] => 7518
[message_count] => 52569
[last_post_id] => 88334
[last_post_date] => 1752009795
[last_post_user_id] => 138292
[last_post_username] => MKWVentures
[last_thread_id] => 23156
[last_thread_title] => IBM eyes deeper partnership with Rapidus for sub-1nm chip development
[last_thread_prefix_id] => 0
[moderate_threads] => 0
[moderate_replies] => 0
[allow_posting] => 1
[count_messages] => 1
[find_new] => 1
[allow_index] => allow
[index_criteria] =>
[field_cache] => []
[prefix_cache] => []
[prompt_cache] => []
[default_prefix_id] => 0
[default_sort_order] => last_post_date
[default_sort_direction] => desc
[list_date_limit_days] => 0
[require_prefix] => 0
[allowed_watch_notifications] => all
[min_tags] => 0
[forum_type_id] => discussion
[type_config] => {"allowed_thread_types":["poll"]}
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
[Node] => XF\Entity\Node Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 49
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\Node
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[node_id] => 2
[title] => SemiWiki Main Forum ( Ask the Experts! )
[description] => Post your questions to the experts here!
[node_name] =>
[node_type_id] => Forum
[parent_node_id] => 1
[display_order] => 1
[display_in_list] => 1
[lft] => 2
[rgt] => 3
[depth] => 1
[style_id] => 0
[effective_style_id] => 0
[breadcrumb_data] => {"1":{"node_id":1,"title":"Main Category","depth":0,"lft":1,"node_name":null,"node_type_id":"Category","display_in_list":true}}
[navigation_id] =>
[effective_navigation_id] =>
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
[23122] => ThemeHouse\XPress\XF\Entity\Thread Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 71
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\Thread
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[thread_id] => 23122
[node_id] => 2
[title] => Exclusive: Intel's new CEO explores big shift in chip manufacturing business
[reply_count] => 82
[view_count] => 11935
[user_id] => 332041
[username] => XYang2023
[post_date] => 1751421336
[sticky] => 0
[discussion_state] => visible
[discussion_open] => 1
[discussion_type] => discussion
[first_post_id] => 88142
[first_post_reaction_score] => 1
[first_post_reactions] => {"1":1}
[last_post_date] => 1751986317
[last_post_id] => 88318
[last_post_user_id] => 1305
[last_post_username] => KevinK
[prefix_id] => 0
[tags] => []
[custom_fields] => []
[vote_score] => 0
[vote_count] => 0
[type_data] => []
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
[User] => ThemeHouse\XLink\XF\Entity\User Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 68
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\User
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[user_id] => 332041
[username] => XYang2023
[username_date] => 0
[username_date_visible] => 0
[email] => xiao.yang17@gmail.com
[custom_title] =>
[language_id] => 1
[style_id] => 0
[timezone] => Australia/Sydney
[visible] => 1
[activity_visible] => 1
[user_group_id] => 2
[secondary_group_ids] =>
[display_style_group_id] => 2
[permission_combination_id] => 8
[message_count] => 1185
[question_solution_count] => 0
[conversations_unread] => 0
[register_date] => 1708819075
[last_activity] => 1751961761
[last_summary_email_date] => 1723213219
[trophy_points] => 113
[alerts_unviewed] => 4
[alerts_unread] => 7
[avatar_date] => 0
[avatar_width] => 0
[avatar_height] => 0
[avatar_highdpi] => 0
[gravatar] =>
[user_state] => valid
[security_lock] =>
[is_moderator] => 0
[is_admin] => 0
[is_banned] => 0
[reaction_score] => 716
[warning_points] => 0
[is_staff] => 0
[secret_key] => NBs1n4BMtljiqSmfC-EZI_MMUn9Rzevl
[privacy_policy_accepted] => 1708819075
[terms_accepted] => 1708819075
[vote_score] => 0
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
[Forum] => XF\Entity\Forum Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 50
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\Forum
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[node_id] => 2
[discussion_count] => 7518
[message_count] => 52569
[last_post_id] => 88334
[last_post_date] => 1752009795
[last_post_user_id] => 138292
[last_post_username] => MKWVentures
[last_thread_id] => 23156
[last_thread_title] => IBM eyes deeper partnership with Rapidus for sub-1nm chip development
[last_thread_prefix_id] => 0
[moderate_threads] => 0
[moderate_replies] => 0
[allow_posting] => 1
[count_messages] => 1
[find_new] => 1
[allow_index] => allow
[index_criteria] =>
[field_cache] => []
[prefix_cache] => []
[prompt_cache] => []
[default_prefix_id] => 0
[default_sort_order] => last_post_date
[default_sort_direction] => desc
[list_date_limit_days] => 0
[require_prefix] => 0
[allowed_watch_notifications] => all
[min_tags] => 0
[forum_type_id] => discussion
[type_config] => {"allowed_thread_types":["poll"]}
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
[Node] => XF\Entity\Node Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 49
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\Node
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[node_id] => 2
[title] => SemiWiki Main Forum ( Ask the Experts! )
[description] => Post your questions to the experts here!
[node_name] =>
[node_type_id] => Forum
[parent_node_id] => 1
[display_order] => 1
[display_in_list] => 1
[lft] => 2
[rgt] => 3
[depth] => 1
[style_id] => 0
[effective_style_id] => 0
[breadcrumb_data] => {"1":{"node_id":1,"title":"Main Category","depth":0,"lft":1,"node_name":null,"node_type_id":"Category","display_in_list":true}}
[navigation_id] =>
[effective_navigation_id] =>
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
[23135] => ThemeHouse\XPress\XF\Entity\Thread Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 75
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\Thread
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[thread_id] => 23135
[node_id] => 2
[title] => TSMC AZ President Rick Cassidy steps down; discrimination lawsuit revived
[reply_count] => 10
[view_count] => 975
[user_id] => 16950
[username] => benb
[post_date] => 1751887105
[sticky] => 0
[discussion_state] => visible
[discussion_open] => 1
[discussion_type] => discussion
[first_post_id] => 88275
[first_post_reaction_score] => 1
[first_post_reactions] => {"1":1,"4":1}
[last_post_date] => 1751985924
[last_post_id] => 88317
[last_post_user_id] => 5
[last_post_username] => Daniel Nenni
[prefix_id] => 0
[tags] => []
[custom_fields] => []
[vote_score] => 0
[vote_count] => 0
[type_data] => []
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
[User] => ThemeHouse\XLink\XF\Entity\User Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 72
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\User
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[user_id] => 16950
[username] => benb
[username_date] => 0
[username_date_visible] => 0
[email] => benjamin.bayer@gmail.com
[custom_title] =>
[language_id] => 1
[style_id] => 0
[timezone] => America/Denver
[visible] => 1
[activity_visible] => 1
[user_group_id] => 2
[secondary_group_ids] =>
[display_style_group_id] => 2
[permission_combination_id] => 8
[message_count] => 904
[question_solution_count] => 0
[conversations_unread] => 0
[register_date] => 1408581209
[last_activity] => 1751942701
[last_summary_email_date] => 1744640413
[trophy_points] => 93
[alerts_unviewed] => 25
[alerts_unread] => 25
[avatar_date] => 0
[avatar_width] => 0
[avatar_height] => 0
[avatar_highdpi] => 0
[gravatar] =>
[user_state] => valid
[security_lock] =>
[is_moderator] => 0
[is_admin] => 0
[is_banned] => 0
[reaction_score] => 518
[warning_points] => 0
[is_staff] => 0
[secret_key] => pcdvBC5BP5tkj0uVO3VFPzfjLoO6RVRR
[privacy_policy_accepted] => 0
[terms_accepted] => 0
[vote_score] => 0
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
[Forum] => XF\Entity\Forum Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 50
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\Forum
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[node_id] => 2
[discussion_count] => 7518
[message_count] => 52569
[last_post_id] => 88334
[last_post_date] => 1752009795
[last_post_user_id] => 138292
[last_post_username] => MKWVentures
[last_thread_id] => 23156
[last_thread_title] => IBM eyes deeper partnership with Rapidus for sub-1nm chip development
[last_thread_prefix_id] => 0
[moderate_threads] => 0
[moderate_replies] => 0
[allow_posting] => 1
[count_messages] => 1
[find_new] => 1
[allow_index] => allow
[index_criteria] =>
[field_cache] => []
[prefix_cache] => []
[prompt_cache] => []
[default_prefix_id] => 0
[default_sort_order] => last_post_date
[default_sort_direction] => desc
[list_date_limit_days] => 0
[require_prefix] => 0
[allowed_watch_notifications] => all
[min_tags] => 0
[forum_type_id] => discussion
[type_config] => {"allowed_thread_types":["poll"]}
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
[Node] => XF\Entity\Node Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 49
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\Node
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[node_id] => 2
[title] => SemiWiki Main Forum ( Ask the Experts! )
[description] => Post your questions to the experts here!
[node_name] =>
[node_type_id] => Forum
[parent_node_id] => 1
[display_order] => 1
[display_in_list] => 1
[lft] => 2
[rgt] => 3
[depth] => 1
[style_id] => 0
[effective_style_id] => 0
[breadcrumb_data] => {"1":{"node_id":1,"title":"Main Category","depth":0,"lft":1,"node_name":null,"node_type_id":"Category","display_in_list":true}}
[navigation_id] =>
[effective_navigation_id] =>
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
[23141] => ThemeHouse\XPress\XF\Entity\Thread Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 79
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\Thread
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[thread_id] => 23141
[node_id] => 2
[title] => New Intel Senior VP is from Cadence
[reply_count] => 3
[view_count] => 1058
[user_id] => 5
[username] => Daniel Nenni
[post_date] => 1751931496
[sticky] => 0
[discussion_state] => visible
[discussion_open] => 1
[discussion_type] => discussion
[first_post_id] => 88299
[first_post_reaction_score] => 1
[first_post_reactions] => {"1":1}
[last_post_date] => 1751976280
[last_post_id] => 88316
[last_post_user_id] => 90182
[last_post_username] => siliconbruh999
[prefix_id] => 0
[tags] => []
[custom_fields] => []
[vote_score] => 0
[vote_count] => 0
[type_data] => []
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
[User] => ThemeHouse\XLink\XF\Entity\User Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 48
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\User
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[user_id] => 5
[username] => Daniel Nenni
[username_date] => 0
[username_date_visible] => 0
[email] => dnenni@semiwiki.com
[custom_title] => Admin
[language_id] => 1
[style_id] => 0
[timezone] => America/Los_Angeles
[visible] => 1
[activity_visible] => 1
[user_group_id] => 3
[secondary_group_ids] => 4,5,132
[display_style_group_id] => 3
[permission_combination_id] => 88
[message_count] => 13876
[question_solution_count] => 0
[conversations_unread] => 0
[register_date] => 1280720820
[last_activity] => 1752012529
[last_summary_email_date] => 1605968657
[trophy_points] => 113
[alerts_unviewed] => 10
[alerts_unread] => 41
[avatar_date] => 1663211649
[avatar_width] => 110
[avatar_height] => 107
[avatar_highdpi] => 0
[gravatar] =>
[user_state] => valid
[security_lock] =>
[is_moderator] => 1
[is_admin] => 1
[is_banned] => 0
[reaction_score] => 6965
[warning_points] => 0
[is_staff] => 1
[secret_key] => 0HwyUVVHCwJotUUVEpvqAclfYJdGNPpw
[privacy_policy_accepted] => 0
[terms_accepted] => 0
[vote_score] => 0
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
[Forum] => XF\Entity\Forum Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 50
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\Forum
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[node_id] => 2
[discussion_count] => 7518
[message_count] => 52569
[last_post_id] => 88334
[last_post_date] => 1752009795
[last_post_user_id] => 138292
[last_post_username] => MKWVentures
[last_thread_id] => 23156
[last_thread_title] => IBM eyes deeper partnership with Rapidus for sub-1nm chip development
[last_thread_prefix_id] => 0
[moderate_threads] => 0
[moderate_replies] => 0
[allow_posting] => 1
[count_messages] => 1
[find_new] => 1
[allow_index] => allow
[index_criteria] =>
[field_cache] => []
[prefix_cache] => []
[prompt_cache] => []
[default_prefix_id] => 0
[default_sort_order] => last_post_date
[default_sort_direction] => desc
[list_date_limit_days] => 0
[require_prefix] => 0
[allowed_watch_notifications] => all
[min_tags] => 0
[forum_type_id] => discussion
[type_config] => {"allowed_thread_types":["poll"]}
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
[Node] => XF\Entity\Node Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 49
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\Node
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[node_id] => 2
[title] => SemiWiki Main Forum ( Ask the Experts! )
[description] => Post your questions to the experts here!
[node_name] =>
[node_type_id] => Forum
[parent_node_id] => 1
[display_order] => 1
[display_in_list] => 1
[lft] => 2
[rgt] => 3
[depth] => 1
[style_id] => 0
[effective_style_id] => 0
[breadcrumb_data] => {"1":{"node_id":1,"title":"Main Category","depth":0,"lft":1,"node_name":null,"node_type_id":"Category","display_in_list":true}}
[navigation_id] =>
[effective_navigation_id] =>
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
[23140] => ThemeHouse\XPress\XF\Entity\Thread Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 83
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\Thread
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[thread_id] => 23140
[node_id] => 2
[title] => Intel layoffs begin: Chipmaker is cutting many thousands of jobs
[reply_count] => 4
[view_count] => 728
[user_id] => 14042
[username] => hist78
[post_date] => 1751923769
[sticky] => 0
[discussion_state] => visible
[discussion_open] => 1
[discussion_type] => discussion
[first_post_id] => 88295
[first_post_reaction_score] => 1
[first_post_reactions] => {"1":1}
[last_post_date] => 1751961754
[last_post_id] => 88314
[last_post_user_id] => 332041
[last_post_username] => XYang2023
[prefix_id] => 0
[tags] => []
[custom_fields] => []
[vote_score] => 0
[vote_count] => 0
[type_data] => []
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
[User] => ThemeHouse\XLink\XF\Entity\User Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 80
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\User
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[user_id] => 14042
[username] => hist78
[username_date] => 0
[username_date_visible] => 0
[email] => ckckhcdc@gmail.com
[custom_title] =>
[language_id] => 1
[style_id] => 0
[timezone] => America/Los_Angeles
[visible] => 0
[activity_visible] => 0
[user_group_id] => 2
[secondary_group_ids] =>
[display_style_group_id] => 2
[permission_combination_id] => 8
[message_count] => 3593
[question_solution_count] => 0
[conversations_unread] => 0
[register_date] => 1389969050
[last_activity] => 1751998339
[last_summary_email_date] => 1605978520
[trophy_points] => 113
[alerts_unviewed] => 0
[alerts_unread] => 0
[avatar_date] => 1604959511
[avatar_width] => 807
[avatar_height] => 384
[avatar_highdpi] => 1
[gravatar] =>
[user_state] => valid
[security_lock] =>
[is_moderator] => 0
[is_admin] => 0
[is_banned] => 0
[reaction_score] => 3103
[warning_points] => 0
[is_staff] => 0
[secret_key] => 2YRSnPrl4fVQSdv3R6uqHxqi6BDQOXve
[privacy_policy_accepted] => 0
[terms_accepted] => 0
[vote_score] => 0
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
[Forum] => XF\Entity\Forum Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 50
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\Forum
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[node_id] => 2
[discussion_count] => 7518
[message_count] => 52569
[last_post_id] => 88334
[last_post_date] => 1752009795
[last_post_user_id] => 138292
[last_post_username] => MKWVentures
[last_thread_id] => 23156
[last_thread_title] => IBM eyes deeper partnership with Rapidus for sub-1nm chip development
[last_thread_prefix_id] => 0
[moderate_threads] => 0
[moderate_replies] => 0
[allow_posting] => 1
[count_messages] => 1
[find_new] => 1
[allow_index] => allow
[index_criteria] =>
[field_cache] => []
[prefix_cache] => []
[prompt_cache] => []
[default_prefix_id] => 0
[default_sort_order] => last_post_date
[default_sort_direction] => desc
[list_date_limit_days] => 0
[require_prefix] => 0
[allowed_watch_notifications] => all
[min_tags] => 0
[forum_type_id] => discussion
[type_config] => {"allowed_thread_types":["poll"]}
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
[Node] => XF\Entity\Node Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 49
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\Node
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[node_id] => 2
[title] => SemiWiki Main Forum ( Ask the Experts! )
[description] => Post your questions to the experts here!
[node_name] =>
[node_type_id] => Forum
[parent_node_id] => 1
[display_order] => 1
[display_in_list] => 1
[lft] => 2
[rgt] => 3
[depth] => 1
[style_id] => 0
[effective_style_id] => 0
[breadcrumb_data] => {"1":{"node_id":1,"title":"Main Category","depth":0,"lft":1,"node_name":null,"node_type_id":"Category","display_in_list":true}}
[navigation_id] =>
[effective_navigation_id] =>
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
[23139] => ThemeHouse\XPress\XF\Entity\Thread Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 87
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\Thread
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[thread_id] => 23139
[node_id] => 2
[title] => Esparanto ai Assets up for Sale
[reply_count] => 0
[view_count] => 203
[user_id] => 5
[username] => Daniel Nenni
[post_date] => 1751910959
[sticky] => 0
[discussion_state] => visible
[discussion_open] => 1
[discussion_type] => discussion
[first_post_id] => 88291
[first_post_reaction_score] => 0
[first_post_reactions] => []
[last_post_date] => 1751910959
[last_post_id] => 88291
[last_post_user_id] => 5
[last_post_username] => Daniel Nenni
[prefix_id] => 0
[tags] => []
[custom_fields] => []
[vote_score] => 0
[vote_count] => 0
[type_data] => []
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
[User] => ThemeHouse\XLink\XF\Entity\User Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 48
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\User
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[user_id] => 5
[username] => Daniel Nenni
[username_date] => 0
[username_date_visible] => 0
[email] => dnenni@semiwiki.com
[custom_title] => Admin
[language_id] => 1
[style_id] => 0
[timezone] => America/Los_Angeles
[visible] => 1
[activity_visible] => 1
[user_group_id] => 3
[secondary_group_ids] => 4,5,132
[display_style_group_id] => 3
[permission_combination_id] => 88
[message_count] => 13876
[question_solution_count] => 0
[conversations_unread] => 0
[register_date] => 1280720820
[last_activity] => 1752012529
[last_summary_email_date] => 1605968657
[trophy_points] => 113
[alerts_unviewed] => 10
[alerts_unread] => 41
[avatar_date] => 1663211649
[avatar_width] => 110
[avatar_height] => 107
[avatar_highdpi] => 0
[gravatar] =>
[user_state] => valid
[security_lock] =>
[is_moderator] => 1
[is_admin] => 1
[is_banned] => 0
[reaction_score] => 6965
[warning_points] => 0
[is_staff] => 1
[secret_key] => 0HwyUVVHCwJotUUVEpvqAclfYJdGNPpw
[privacy_policy_accepted] => 0
[terms_accepted] => 0
[vote_score] => 0
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
[Forum] => XF\Entity\Forum Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 50
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\Forum
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[node_id] => 2
[discussion_count] => 7518
[message_count] => 52569
[last_post_id] => 88334
[last_post_date] => 1752009795
[last_post_user_id] => 138292
[last_post_username] => MKWVentures
[last_thread_id] => 23156
[last_thread_title] => IBM eyes deeper partnership with Rapidus for sub-1nm chip development
[last_thread_prefix_id] => 0
[moderate_threads] => 0
[moderate_replies] => 0
[allow_posting] => 1
[count_messages] => 1
[find_new] => 1
[allow_index] => allow
[index_criteria] =>
[field_cache] => []
[prefix_cache] => []
[prompt_cache] => []
[default_prefix_id] => 0
[default_sort_order] => last_post_date
[default_sort_direction] => desc
[list_date_limit_days] => 0
[require_prefix] => 0
[allowed_watch_notifications] => all
[min_tags] => 0
[forum_type_id] => discussion
[type_config] => {"allowed_thread_types":["poll"]}
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
[Node] => XF\Entity\Node Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 49
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\Node
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[node_id] => 2
[title] => SemiWiki Main Forum ( Ask the Experts! )
[description] => Post your questions to the experts here!
[node_name] =>
[node_type_id] => Forum
[parent_node_id] => 1
[display_order] => 1
[display_in_list] => 1
[lft] => 2
[rgt] => 3
[depth] => 1
[style_id] => 0
[effective_style_id] => 0
[breadcrumb_data] => {"1":{"node_id":1,"title":"Main Category","depth":0,"lft":1,"node_name":null,"node_type_id":"Category","display_in_list":true}}
[navigation_id] =>
[effective_navigation_id] =>
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
[23137] => ThemeHouse\XPress\XF\Entity\Thread Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 91
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\Thread
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[thread_id] => 23137
[node_id] => 2
[title] => NVIDIA has Free AI Online Courses
[reply_count] => 0
[view_count] => 272
[user_id] => 5
[username] => Daniel Nenni
[post_date] => 1751906751
[sticky] => 0
[discussion_state] => visible
[discussion_open] => 1
[discussion_type] => discussion
[first_post_id] => 88288
[first_post_reaction_score] => 1
[first_post_reactions] => {"1":1}
[last_post_date] => 1751906751
[last_post_id] => 88288
[last_post_user_id] => 5
[last_post_username] => Daniel Nenni
[prefix_id] => 0
[tags] => []
[custom_fields] => []
[vote_score] => 0
[vote_count] => 0
[type_data] => []
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
[User] => ThemeHouse\XLink\XF\Entity\User Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 48
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\User
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[user_id] => 5
[username] => Daniel Nenni
[username_date] => 0
[username_date_visible] => 0
[email] => dnenni@semiwiki.com
[custom_title] => Admin
[language_id] => 1
[style_id] => 0
[timezone] => America/Los_Angeles
[visible] => 1
[activity_visible] => 1
[user_group_id] => 3
[secondary_group_ids] => 4,5,132
[display_style_group_id] => 3
[permission_combination_id] => 88
[message_count] => 13876
[question_solution_count] => 0
[conversations_unread] => 0
[register_date] => 1280720820
[last_activity] => 1752012529
[last_summary_email_date] => 1605968657
[trophy_points] => 113
[alerts_unviewed] => 10
[alerts_unread] => 41
[avatar_date] => 1663211649
[avatar_width] => 110
[avatar_height] => 107
[avatar_highdpi] => 0
[gravatar] =>
[user_state] => valid
[security_lock] =>
[is_moderator] => 1
[is_admin] => 1
[is_banned] => 0
[reaction_score] => 6965
[warning_points] => 0
[is_staff] => 1
[secret_key] => 0HwyUVVHCwJotUUVEpvqAclfYJdGNPpw
[privacy_policy_accepted] => 0
[terms_accepted] => 0
[vote_score] => 0
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
[Forum] => XF\Entity\Forum Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 50
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\Forum
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[node_id] => 2
[discussion_count] => 7518
[message_count] => 52569
[last_post_id] => 88334
[last_post_date] => 1752009795
[last_post_user_id] => 138292
[last_post_username] => MKWVentures
[last_thread_id] => 23156
[last_thread_title] => IBM eyes deeper partnership with Rapidus for sub-1nm chip development
[last_thread_prefix_id] => 0
[moderate_threads] => 0
[moderate_replies] => 0
[allow_posting] => 1
[count_messages] => 1
[find_new] => 1
[allow_index] => allow
[index_criteria] =>
[field_cache] => []
[prefix_cache] => []
[prompt_cache] => []
[default_prefix_id] => 0
[default_sort_order] => last_post_date
[default_sort_direction] => desc
[list_date_limit_days] => 0
[require_prefix] => 0
[allowed_watch_notifications] => all
[min_tags] => 0
[forum_type_id] => discussion
[type_config] => {"allowed_thread_types":["poll"]}
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
[Node] => XF\Entity\Node Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 49
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\Node
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[node_id] => 2
[title] => SemiWiki Main Forum ( Ask the Experts! )
[description] => Post your questions to the experts here!
[node_name] =>
[node_type_id] => Forum
[parent_node_id] => 1
[display_order] => 1
[display_in_list] => 1
[lft] => 2
[rgt] => 3
[depth] => 1
[style_id] => 0
[effective_style_id] => 0
[breadcrumb_data] => {"1":{"node_id":1,"title":"Main Category","depth":0,"lft":1,"node_name":null,"node_type_id":"Category","display_in_list":true}}
[navigation_id] =>
[effective_navigation_id] =>
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
[23136] => ThemeHouse\XPress\XF\Entity\Thread Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 95
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\Thread
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[thread_id] => 23136
[node_id] => 2
[title] => Samsung Electronics second-quarter profit likely to drop 39% on weak AI chip sales
[reply_count] => 1
[view_count] => 239
[user_id] => 5
[username] => Daniel Nenni
[post_date] => 1751903189
[sticky] => 0
[discussion_state] => visible
[discussion_open] => 1
[discussion_type] => discussion
[first_post_id] => 88284
[first_post_reaction_score] => 0
[first_post_reactions] => []
[last_post_date] => 1751903765
[last_post_id] => 88286
[last_post_user_id] => 138292
[last_post_username] => MKWVentures
[prefix_id] => 0
[tags] => []
[custom_fields] => []
[vote_score] => 0
[vote_count] => 0
[type_data] => []
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
[User] => ThemeHouse\XLink\XF\Entity\User Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 48
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\User
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[user_id] => 5
[username] => Daniel Nenni
[username_date] => 0
[username_date_visible] => 0
[email] => dnenni@semiwiki.com
[custom_title] => Admin
[language_id] => 1
[style_id] => 0
[timezone] => America/Los_Angeles
[visible] => 1
[activity_visible] => 1
[user_group_id] => 3
[secondary_group_ids] => 4,5,132
[display_style_group_id] => 3
[permission_combination_id] => 88
[message_count] => 13876
[question_solution_count] => 0
[conversations_unread] => 0
[register_date] => 1280720820
[last_activity] => 1752012529
[last_summary_email_date] => 1605968657
[trophy_points] => 113
[alerts_unviewed] => 10
[alerts_unread] => 41
[avatar_date] => 1663211649
[avatar_width] => 110
[avatar_height] => 107
[avatar_highdpi] => 0
[gravatar] =>
[user_state] => valid
[security_lock] =>
[is_moderator] => 1
[is_admin] => 1
[is_banned] => 0
[reaction_score] => 6965
[warning_points] => 0
[is_staff] => 1
[secret_key] => 0HwyUVVHCwJotUUVEpvqAclfYJdGNPpw
[privacy_policy_accepted] => 0
[terms_accepted] => 0
[vote_score] => 0
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
[Forum] => XF\Entity\Forum Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 50
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\Forum
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[node_id] => 2
[discussion_count] => 7518
[message_count] => 52569
[last_post_id] => 88334
[last_post_date] => 1752009795
[last_post_user_id] => 138292
[last_post_username] => MKWVentures
[last_thread_id] => 23156
[last_thread_title] => IBM eyes deeper partnership with Rapidus for sub-1nm chip development
[last_thread_prefix_id] => 0
[moderate_threads] => 0
[moderate_replies] => 0
[allow_posting] => 1
[count_messages] => 1
[find_new] => 1
[allow_index] => allow
[index_criteria] =>
[field_cache] => []
[prefix_cache] => []
[prompt_cache] => []
[default_prefix_id] => 0
[default_sort_order] => last_post_date
[default_sort_direction] => desc
[list_date_limit_days] => 0
[require_prefix] => 0
[allowed_watch_notifications] => all
[min_tags] => 0
[forum_type_id] => discussion
[type_config] => {"allowed_thread_types":["poll"]}
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
[Node] => XF\Entity\Node Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 49
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\Node
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[node_id] => 2
[title] => SemiWiki Main Forum ( Ask the Experts! )
[description] => Post your questions to the experts here!
[node_name] =>
[node_type_id] => Forum
[parent_node_id] => 1
[display_order] => 1
[display_in_list] => 1
[lft] => 2
[rgt] => 3
[depth] => 1
[style_id] => 0
[effective_style_id] => 0
[breadcrumb_data] => {"1":{"node_id":1,"title":"Main Category","depth":0,"lft":1,"node_name":null,"node_type_id":"Category","display_in_list":true}}
[navigation_id] =>
[effective_navigation_id] =>
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
[23131] => ThemeHouse\XPress\XF\Entity\Thread Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 99
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\Thread
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[thread_id] => 23131
[node_id] => 2
[title] => TSMC to Delay Japan Chip Plant and Prioritize U.S. to Avoid Trump Tariffs
[reply_count] => 6
[view_count] => 1292
[user_id] => 332041
[username] => XYang2023
[post_date] => 1751620259
[sticky] => 0
[discussion_state] => visible
[discussion_open] => 1
[discussion_type] => discussion
[first_post_id] => 88212
[first_post_reaction_score] => 1
[first_post_reactions] => {"4":1,"1":1}
[last_post_date] => 1751899393
[last_post_id] => 88282
[last_post_user_id] => 138292
[last_post_username] => MKWVentures
[prefix_id] => 0
[tags] => []
[custom_fields] => []
[vote_score] => 0
[vote_count] => 0
[type_data] => []
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
[User] => ThemeHouse\XLink\XF\Entity\User Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 68
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\User
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[user_id] => 332041
[username] => XYang2023
[username_date] => 0
[username_date_visible] => 0
[email] => xiao.yang17@gmail.com
[custom_title] =>
[language_id] => 1
[style_id] => 0
[timezone] => Australia/Sydney
[visible] => 1
[activity_visible] => 1
[user_group_id] => 2
[secondary_group_ids] =>
[display_style_group_id] => 2
[permission_combination_id] => 8
[message_count] => 1185
[question_solution_count] => 0
[conversations_unread] => 0
[register_date] => 1708819075
[last_activity] => 1751961761
[last_summary_email_date] => 1723213219
[trophy_points] => 113
[alerts_unviewed] => 4
[alerts_unread] => 7
[avatar_date] => 0
[avatar_width] => 0
[avatar_height] => 0
[avatar_highdpi] => 0
[gravatar] =>
[user_state] => valid
[security_lock] =>
[is_moderator] => 0
[is_admin] => 0
[is_banned] => 0
[reaction_score] => 716
[warning_points] => 0
[is_staff] => 0
[secret_key] => NBs1n4BMtljiqSmfC-EZI_MMUn9Rzevl
[privacy_policy_accepted] => 1708819075
[terms_accepted] => 1708819075
[vote_score] => 0
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
[Forum] => XF\Entity\Forum Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 50
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\Forum
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[node_id] => 2
[discussion_count] => 7518
[message_count] => 52569
[last_post_id] => 88334
[last_post_date] => 1752009795
[last_post_user_id] => 138292
[last_post_username] => MKWVentures
[last_thread_id] => 23156
[last_thread_title] => IBM eyes deeper partnership with Rapidus for sub-1nm chip development
[last_thread_prefix_id] => 0
[moderate_threads] => 0
[moderate_replies] => 0
[allow_posting] => 1
[count_messages] => 1
[find_new] => 1
[allow_index] => allow
[index_criteria] =>
[field_cache] => []
[prefix_cache] => []
[prompt_cache] => []
[default_prefix_id] => 0
[default_sort_order] => last_post_date
[default_sort_direction] => desc
[list_date_limit_days] => 0
[require_prefix] => 0
[allowed_watch_notifications] => all
[min_tags] => 0
[forum_type_id] => discussion
[type_config] => {"allowed_thread_types":["poll"]}
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
[Node] => XF\Entity\Node Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 49
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\Node
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[node_id] => 2
[title] => SemiWiki Main Forum ( Ask the Experts! )
[description] => Post your questions to the experts here!
[node_name] =>
[node_type_id] => Forum
[parent_node_id] => 1
[display_order] => 1
[display_in_list] => 1
[lft] => 2
[rgt] => 3
[depth] => 1
[style_id] => 0
[effective_style_id] => 0
[breadcrumb_data] => {"1":{"node_id":1,"title":"Main Category","depth":0,"lft":1,"node_name":null,"node_type_id":"Category","display_in_list":true}}
[navigation_id] =>
[effective_navigation_id] =>
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
[23133] => ThemeHouse\XPress\XF\Entity\Thread Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 103
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\Thread
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[thread_id] => 23133
[node_id] => 2
[title] => Samsung delaying completion of US chip plant due to lack of customers
[reply_count] => 5
[view_count] => 1906
[user_id] => 5
[username] => Daniel Nenni
[post_date] => 1751640597
[sticky] => 0
[discussion_state] => visible
[discussion_open] => 1
[discussion_type] => discussion
[first_post_id] => 88223
[first_post_reaction_score] => 3
[first_post_reactions] => {"1":3}
[last_post_date] => 1751898704
[last_post_id] => 88281
[last_post_user_id] => 138292
[last_post_username] => MKWVentures
[prefix_id] => 0
[tags] => []
[custom_fields] => []
[vote_score] => 0
[vote_count] => 0
[type_data] => []
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
[User] => ThemeHouse\XLink\XF\Entity\User Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 48
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\User
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[user_id] => 5
[username] => Daniel Nenni
[username_date] => 0
[username_date_visible] => 0
[email] => dnenni@semiwiki.com
[custom_title] => Admin
[language_id] => 1
[style_id] => 0
[timezone] => America/Los_Angeles
[visible] => 1
[activity_visible] => 1
[user_group_id] => 3
[secondary_group_ids] => 4,5,132
[display_style_group_id] => 3
[permission_combination_id] => 88
[message_count] => 13876
[question_solution_count] => 0
[conversations_unread] => 0
[register_date] => 1280720820
[last_activity] => 1752012529
[last_summary_email_date] => 1605968657
[trophy_points] => 113
[alerts_unviewed] => 10
[alerts_unread] => 41
[avatar_date] => 1663211649
[avatar_width] => 110
[avatar_height] => 107
[avatar_highdpi] => 0
[gravatar] =>
[user_state] => valid
[security_lock] =>
[is_moderator] => 1
[is_admin] => 1
[is_banned] => 0
[reaction_score] => 6965
[warning_points] => 0
[is_staff] => 1
[secret_key] => 0HwyUVVHCwJotUUVEpvqAclfYJdGNPpw
[privacy_policy_accepted] => 0
[terms_accepted] => 0
[vote_score] => 0
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
[Forum] => XF\Entity\Forum Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 50
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\Forum
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[node_id] => 2
[discussion_count] => 7518
[message_count] => 52569
[last_post_id] => 88334
[last_post_date] => 1752009795
[last_post_user_id] => 138292
[last_post_username] => MKWVentures
[last_thread_id] => 23156
[last_thread_title] => IBM eyes deeper partnership with Rapidus for sub-1nm chip development
[last_thread_prefix_id] => 0
[moderate_threads] => 0
[moderate_replies] => 0
[allow_posting] => 1
[count_messages] => 1
[find_new] => 1
[allow_index] => allow
[index_criteria] =>
[field_cache] => []
[prefix_cache] => []
[prompt_cache] => []
[default_prefix_id] => 0
[default_sort_order] => last_post_date
[default_sort_direction] => desc
[list_date_limit_days] => 0
[require_prefix] => 0
[allowed_watch_notifications] => all
[min_tags] => 0
[forum_type_id] => discussion
[type_config] => {"allowed_thread_types":["poll"]}
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
[Node] => XF\Entity\Node Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 49
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\Node
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[node_id] => 2
[title] => SemiWiki Main Forum ( Ask the Experts! )
[description] => Post your questions to the experts here!
[node_name] =>
[node_type_id] => Forum
[parent_node_id] => 1
[display_order] => 1
[display_in_list] => 1
[lft] => 2
[rgt] => 3
[depth] => 1
[style_id] => 0
[effective_style_id] => 0
[breadcrumb_data] => {"1":{"node_id":1,"title":"Main Category","depth":0,"lft":1,"node_name":null,"node_type_id":"Category","display_in_list":true}}
[navigation_id] =>
[effective_navigation_id] =>
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
[23123] => ThemeHouse\XPress\XF\Entity\Thread Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 107
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\Thread
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[thread_id] => 23123
[node_id] => 2
[title] => How far are perovskite solar cells?
[reply_count] => 10
[view_count] => 1382
[user_id] => 10499
[username] => Arthur Hanson
[post_date] => 1751456796
[sticky] => 0
[discussion_state] => visible
[discussion_open] => 1
[discussion_type] => discussion
[first_post_id] => 88156
[first_post_reaction_score] => 1
[first_post_reactions] => {"1":1}
[last_post_date] => 1751896575
[last_post_id] => 88280
[last_post_user_id] => 6522
[last_post_username] => IanD
[prefix_id] => 0
[tags] => []
[custom_fields] => []
[vote_score] => 0
[vote_count] => 0
[type_data] => []
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
[User] => ThemeHouse\XLink\XF\Entity\User Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 104
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\User
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[user_id] => 10499
[username] => Arthur Hanson
[username_date] => 0
[username_date_visible] => 0
[email] => a-j-hanson@att.net
[custom_title] =>
[language_id] => 1
[style_id] => 1
[timezone] => America/Los_Angeles
[visible] => 1
[activity_visible] => 1
[user_group_id] => 2
[secondary_group_ids] =>
[display_style_group_id] => 2
[permission_combination_id] => 8
[message_count] => 3256
[question_solution_count] => 0
[conversations_unread] => 0
[register_date] => 1366028460
[last_activity] => 1751760746
[last_summary_email_date] => 1606051785
[trophy_points] => 83
[alerts_unviewed] => 7
[alerts_unread] => 7
[avatar_date] => 0
[avatar_width] => 0
[avatar_height] => 0
[avatar_highdpi] => 0
[gravatar] =>
[user_state] => valid
[security_lock] =>
[is_moderator] => 0
[is_admin] => 0
[is_banned] => 0
[reaction_score] => 432
[warning_points] => 0
[is_staff] => 0
[secret_key] => ta_8_Pj20m6PDO6RnrGK-VnSP_vyhP_m
[privacy_policy_accepted] => 0
[terms_accepted] => 0
[vote_score] => 0
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
[Forum] => XF\Entity\Forum Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 50
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\Forum
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[node_id] => 2
[discussion_count] => 7518
[message_count] => 52569
[last_post_id] => 88334
[last_post_date] => 1752009795
[last_post_user_id] => 138292
[last_post_username] => MKWVentures
[last_thread_id] => 23156
[last_thread_title] => IBM eyes deeper partnership with Rapidus for sub-1nm chip development
[last_thread_prefix_id] => 0
[moderate_threads] => 0
[moderate_replies] => 0
[allow_posting] => 1
[count_messages] => 1
[find_new] => 1
[allow_index] => allow
[index_criteria] =>
[field_cache] => []
[prefix_cache] => []
[prompt_cache] => []
[default_prefix_id] => 0
[default_sort_order] => last_post_date
[default_sort_direction] => desc
[list_date_limit_days] => 0
[require_prefix] => 0
[allowed_watch_notifications] => all
[min_tags] => 0
[forum_type_id] => discussion
[type_config] => {"allowed_thread_types":["poll"]}
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
[Node] => XF\Entity\Node Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 49
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\Node
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[node_id] => 2
[title] => SemiWiki Main Forum ( Ask the Experts! )
[description] => Post your questions to the experts here!
[node_name] =>
[node_type_id] => Forum
[parent_node_id] => 1
[display_order] => 1
[display_in_list] => 1
[lft] => 2
[rgt] => 3
[depth] => 1
[style_id] => 0
[effective_style_id] => 0
[breadcrumb_data] => {"1":{"node_id":1,"title":"Main Category","depth":0,"lft":1,"node_name":null,"node_type_id":"Category","display_in_list":true}}
[navigation_id] =>
[effective_navigation_id] =>
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
[23134] => ThemeHouse\XPress\XF\Entity\Thread Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 111
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\Thread
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[thread_id] => 23134
[node_id] => 2
[title] => Is China Catching Up in Semiconductor Talent? Can Taiwan Still Nurture the Tech Talent It Needs?
[reply_count] => 0
[view_count] => 302
[user_id] => 398583
[username] => karin623
[post_date] => 1751802440
[sticky] => 0
[discussion_state] => visible
[discussion_open] => 1
[discussion_type] => discussion
[first_post_id] => 88256
[first_post_reaction_score] => 0
[first_post_reactions] => []
[last_post_date] => 1751802440
[last_post_id] => 88256
[last_post_user_id] => 398583
[last_post_username] => karin623
[prefix_id] => 0
[tags] => []
[custom_fields] => []
[vote_score] => 0
[vote_count] => 0
[type_data] => []
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
[User] => ThemeHouse\XLink\XF\Entity\User Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 108
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\User
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[user_id] => 398583
[username] => karin623
[username_date] => 0
[username_date_visible] => 0
[email] => karin623@gmail.com
[custom_title] =>
[language_id] => 1
[style_id] => 0
[timezone] => Asia/Hong_Kong
[visible] => 1
[activity_visible] => 1
[user_group_id] => 2
[secondary_group_ids] =>
[display_style_group_id] => 2
[permission_combination_id] => 8
[message_count] => 6
[question_solution_count] => 0
[conversations_unread] => 0
[register_date] => 1748753435
[last_activity] => 1751802441
[last_summary_email_date] => 1748753435
[trophy_points] => 3
[alerts_unviewed] => 1
[alerts_unread] => 1
[avatar_date] => 0
[avatar_width] => 0
[avatar_height] => 0
[avatar_highdpi] => 0
[gravatar] =>
[user_state] => valid
[security_lock] =>
[is_moderator] => 0
[is_admin] => 0
[is_banned] => 0
[reaction_score] => 6
[warning_points] => 0
[is_staff] => 0
[secret_key] => PBnrLVmUtkEL7YUKL8Ij_6L3tfKYRzDQ
[privacy_policy_accepted] => 1748753435
[terms_accepted] => 1748753435
[vote_score] => 0
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
[Forum] => XF\Entity\Forum Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 50
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\Forum
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[node_id] => 2
[discussion_count] => 7518
[message_count] => 52569
[last_post_id] => 88334
[last_post_date] => 1752009795
[last_post_user_id] => 138292
[last_post_username] => MKWVentures
[last_thread_id] => 23156
[last_thread_title] => IBM eyes deeper partnership with Rapidus for sub-1nm chip development
[last_thread_prefix_id] => 0
[moderate_threads] => 0
[moderate_replies] => 0
[allow_posting] => 1
[count_messages] => 1
[find_new] => 1
[allow_index] => allow
[index_criteria] =>
[field_cache] => []
[prefix_cache] => []
[prompt_cache] => []
[default_prefix_id] => 0
[default_sort_order] => last_post_date
[default_sort_direction] => desc
[list_date_limit_days] => 0
[require_prefix] => 0
[allowed_watch_notifications] => all
[min_tags] => 0
[forum_type_id] => discussion
[type_config] => {"allowed_thread_types":["poll"]}
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
[Node] => XF\Entity\Node Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 49
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\Node
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[node_id] => 2
[title] => SemiWiki Main Forum ( Ask the Experts! )
[description] => Post your questions to the experts here!
[node_name] =>
[node_type_id] => Forum
[parent_node_id] => 1
[display_order] => 1
[display_in_list] => 1
[lft] => 2
[rgt] => 3
[depth] => 1
[style_id] => 0
[effective_style_id] => 0
[breadcrumb_data] => {"1":{"node_id":1,"title":"Main Category","depth":0,"lft":1,"node_name":null,"node_type_id":"Category","display_in_list":true}}
[navigation_id] =>
[effective_navigation_id] =>
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
[23126] => ThemeHouse\XPress\XF\Entity\Thread Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 115
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\Thread
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[thread_id] => 23126
[node_id] => 2
[title] => NXP plans to close four 8-inch wafer fabs and expand production capacity to 12-inch wafers
[reply_count] => 4
[view_count] => 1617
[user_id] => 5
[username] => Daniel Nenni
[post_date] => 1751498383
[sticky] => 0
[discussion_state] => visible
[discussion_open] => 1
[discussion_type] => discussion
[first_post_id] => 88180
[first_post_reaction_score] => 1
[first_post_reactions] => {"1":1}
[last_post_date] => 1751788918
[last_post_id] => 88254
[last_post_user_id] => 19450
[last_post_username] => user nl
[prefix_id] => 0
[tags] => []
[custom_fields] => []
[vote_score] => 0
[vote_count] => 0
[type_data] => []
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
[User] => ThemeHouse\XLink\XF\Entity\User Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 48
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\User
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[user_id] => 5
[username] => Daniel Nenni
[username_date] => 0
[username_date_visible] => 0
[email] => dnenni@semiwiki.com
[custom_title] => Admin
[language_id] => 1
[style_id] => 0
[timezone] => America/Los_Angeles
[visible] => 1
[activity_visible] => 1
[user_group_id] => 3
[secondary_group_ids] => 4,5,132
[display_style_group_id] => 3
[permission_combination_id] => 88
[message_count] => 13876
[question_solution_count] => 0
[conversations_unread] => 0
[register_date] => 1280720820
[last_activity] => 1752012529
[last_summary_email_date] => 1605968657
[trophy_points] => 113
[alerts_unviewed] => 10
[alerts_unread] => 41
[avatar_date] => 1663211649
[avatar_width] => 110
[avatar_height] => 107
[avatar_highdpi] => 0
[gravatar] =>
[user_state] => valid
[security_lock] =>
[is_moderator] => 1
[is_admin] => 1
[is_banned] => 0
[reaction_score] => 6965
[warning_points] => 0
[is_staff] => 1
[secret_key] => 0HwyUVVHCwJotUUVEpvqAclfYJdGNPpw
[privacy_policy_accepted] => 0
[terms_accepted] => 0
[vote_score] => 0
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
[Forum] => XF\Entity\Forum Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 50
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\Forum
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[node_id] => 2
[discussion_count] => 7518
[message_count] => 52569
[last_post_id] => 88334
[last_post_date] => 1752009795
[last_post_user_id] => 138292
[last_post_username] => MKWVentures
[last_thread_id] => 23156
[last_thread_title] => IBM eyes deeper partnership with Rapidus for sub-1nm chip development
[last_thread_prefix_id] => 0
[moderate_threads] => 0
[moderate_replies] => 0
[allow_posting] => 1
[count_messages] => 1
[find_new] => 1
[allow_index] => allow
[index_criteria] =>
[field_cache] => []
[prefix_cache] => []
[prompt_cache] => []
[default_prefix_id] => 0
[default_sort_order] => last_post_date
[default_sort_direction] => desc
[list_date_limit_days] => 0
[require_prefix] => 0
[allowed_watch_notifications] => all
[min_tags] => 0
[forum_type_id] => discussion
[type_config] => {"allowed_thread_types":["poll"]}
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
[Node] => XF\Entity\Node Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 49
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\Node
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[node_id] => 2
[title] => SemiWiki Main Forum ( Ask the Experts! )
[description] => Post your questions to the experts here!
[node_name] =>
[node_type_id] => Forum
[parent_node_id] => 1
[display_order] => 1
[display_in_list] => 1
[lft] => 2
[rgt] => 3
[depth] => 1
[style_id] => 0
[effective_style_id] => 0
[breadcrumb_data] => {"1":{"node_id":1,"title":"Main Category","depth":0,"lft":1,"node_name":null,"node_type_id":"Category","display_in_list":true}}
[navigation_id] =>
[effective_navigation_id] =>
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
[23132] => ThemeHouse\XPress\XF\Entity\Thread Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 119
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\Thread
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[thread_id] => 23132
[node_id] => 2
[title] => UMC Reports Sales for June 2025
[reply_count] => 2
[view_count] => 759
[user_id] => 5
[username] => Daniel Nenni
[post_date] => 1751639772
[sticky] => 0
[discussion_state] => visible
[discussion_open] => 1
[discussion_type] => discussion
[first_post_id] => 88219
[first_post_reaction_score] => 1
[first_post_reactions] => {"1":1}
[last_post_date] => 1751640404
[last_post_id] => 88222
[last_post_user_id] => 5
[last_post_username] => Daniel Nenni
[prefix_id] => 0
[tags] => []
[custom_fields] => []
[vote_score] => 0
[vote_count] => 0
[type_data] => []
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
[User] => ThemeHouse\XLink\XF\Entity\User Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 48
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\User
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[user_id] => 5
[username] => Daniel Nenni
[username_date] => 0
[username_date_visible] => 0
[email] => dnenni@semiwiki.com
[custom_title] => Admin
[language_id] => 1
[style_id] => 0
[timezone] => America/Los_Angeles
[visible] => 1
[activity_visible] => 1
[user_group_id] => 3
[secondary_group_ids] => 4,5,132
[display_style_group_id] => 3
[permission_combination_id] => 88
[message_count] => 13876
[question_solution_count] => 0
[conversations_unread] => 0
[register_date] => 1280720820
[last_activity] => 1752012529
[last_summary_email_date] => 1605968657
[trophy_points] => 113
[alerts_unviewed] => 10
[alerts_unread] => 41
[avatar_date] => 1663211649
[avatar_width] => 110
[avatar_height] => 107
[avatar_highdpi] => 0
[gravatar] =>
[user_state] => valid
[security_lock] =>
[is_moderator] => 1
[is_admin] => 1
[is_banned] => 0
[reaction_score] => 6965
[warning_points] => 0
[is_staff] => 1
[secret_key] => 0HwyUVVHCwJotUUVEpvqAclfYJdGNPpw
[privacy_policy_accepted] => 0
[terms_accepted] => 0
[vote_score] => 0
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
[Forum] => XF\Entity\Forum Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 50
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\Forum
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[node_id] => 2
[discussion_count] => 7518
[message_count] => 52569
[last_post_id] => 88334
[last_post_date] => 1752009795
[last_post_user_id] => 138292
[last_post_username] => MKWVentures
[last_thread_id] => 23156
[last_thread_title] => IBM eyes deeper partnership with Rapidus for sub-1nm chip development
[last_thread_prefix_id] => 0
[moderate_threads] => 0
[moderate_replies] => 0
[allow_posting] => 1
[count_messages] => 1
[find_new] => 1
[allow_index] => allow
[index_criteria] =>
[field_cache] => []
[prefix_cache] => []
[prompt_cache] => []
[default_prefix_id] => 0
[default_sort_order] => last_post_date
[default_sort_direction] => desc
[list_date_limit_days] => 0
[require_prefix] => 0
[allowed_watch_notifications] => all
[min_tags] => 0
[forum_type_id] => discussion
[type_config] => {"allowed_thread_types":["poll"]}
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
[Node] => XF\Entity\Node Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 49
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\Node
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[node_id] => 2
[title] => SemiWiki Main Forum ( Ask the Experts! )
[description] => Post your questions to the experts here!
[node_name] =>
[node_type_id] => Forum
[parent_node_id] => 1
[display_order] => 1
[display_in_list] => 1
[lft] => 2
[rgt] => 3
[depth] => 1
[style_id] => 0
[effective_style_id] => 0
[breadcrumb_data] => {"1":{"node_id":1,"title":"Main Category","depth":0,"lft":1,"node_name":null,"node_type_id":"Category","display_in_list":true}}
[navigation_id] =>
[effective_navigation_id] =>
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
[23068] => ThemeHouse\XPress\XF\Entity\Thread Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 123
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\Thread
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[thread_id] => 23068
[node_id] => 2
[title] => SoftBank's Son pitches $1 trillion Arizona AI hub, Bloomberg News reports
[reply_count] => 8
[view_count] => 2329
[user_id] => 14042
[username] => hist78
[post_date] => 1750440912
[sticky] => 0
[discussion_state] => visible
[discussion_open] => 1
[discussion_type] => discussion
[first_post_id] => 87772
[first_post_reaction_score] => 0
[first_post_reactions] => {"4":1}
[last_post_date] => 1751632080
[last_post_id] => 88216
[last_post_user_id] => 20231
[last_post_username] => Barnsley
[prefix_id] => 0
[tags] => []
[custom_fields] => []
[vote_score] => 0
[vote_count] => 0
[type_data] => []
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
[User] => ThemeHouse\XLink\XF\Entity\User Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 80
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\User
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[user_id] => 14042
[username] => hist78
[username_date] => 0
[username_date_visible] => 0
[email] => ckckhcdc@gmail.com
[custom_title] =>
[language_id] => 1
[style_id] => 0
[timezone] => America/Los_Angeles
[visible] => 0
[activity_visible] => 0
[user_group_id] => 2
[secondary_group_ids] =>
[display_style_group_id] => 2
[permission_combination_id] => 8
[message_count] => 3593
[question_solution_count] => 0
[conversations_unread] => 0
[register_date] => 1389969050
[last_activity] => 1751998339
[last_summary_email_date] => 1605978520
[trophy_points] => 113
[alerts_unviewed] => 0
[alerts_unread] => 0
[avatar_date] => 1604959511
[avatar_width] => 807
[avatar_height] => 384
[avatar_highdpi] => 1
[gravatar] =>
[user_state] => valid
[security_lock] =>
[is_moderator] => 0
[is_admin] => 0
[is_banned] => 0
[reaction_score] => 3103
[warning_points] => 0
[is_staff] => 0
[secret_key] => 2YRSnPrl4fVQSdv3R6uqHxqi6BDQOXve
[privacy_policy_accepted] => 0
[terms_accepted] => 0
[vote_score] => 0
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
[Forum] => XF\Entity\Forum Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 50
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\Forum
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[node_id] => 2
[discussion_count] => 7518
[message_count] => 52569
[last_post_id] => 88334
[last_post_date] => 1752009795
[last_post_user_id] => 138292
[last_post_username] => MKWVentures
[last_thread_id] => 23156
[last_thread_title] => IBM eyes deeper partnership with Rapidus for sub-1nm chip development
[last_thread_prefix_id] => 0
[moderate_threads] => 0
[moderate_replies] => 0
[allow_posting] => 1
[count_messages] => 1
[find_new] => 1
[allow_index] => allow
[index_criteria] =>
[field_cache] => []
[prefix_cache] => []
[prompt_cache] => []
[default_prefix_id] => 0
[default_sort_order] => last_post_date
[default_sort_direction] => desc
[list_date_limit_days] => 0
[require_prefix] => 0
[allowed_watch_notifications] => all
[min_tags] => 0
[forum_type_id] => discussion
[type_config] => {"allowed_thread_types":["poll"]}
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
[Node] => XF\Entity\Node Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 49
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\Node
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[node_id] => 2
[title] => SemiWiki Main Forum ( Ask the Experts! )
[description] => Post your questions to the experts here!
[node_name] =>
[node_type_id] => Forum
[parent_node_id] => 1
[display_order] => 1
[display_in_list] => 1
[lft] => 2
[rgt] => 3
[depth] => 1
[style_id] => 0
[effective_style_id] => 0
[breadcrumb_data] => {"1":{"node_id":1,"title":"Main Category","depth":0,"lft":1,"node_name":null,"node_type_id":"Category","display_in_list":true}}
[navigation_id] =>
[effective_navigation_id] =>
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
[23085] => ThemeHouse\XPress\XF\Entity\Thread Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 127
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\Thread
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[thread_id] => 23085
[node_id] => 2
[title] => Taiwan has upped the ante in the cold war over chips
[reply_count] => 11
[view_count] => 2642
[user_id] => 14042
[username] => hist78
[post_date] => 1750904215
[sticky] => 0
[discussion_state] => visible
[discussion_open] => 1
[discussion_type] => discussion
[first_post_id] => 87928
[first_post_reaction_score] => 3
[first_post_reactions] => {"1":3}
[last_post_date] => 1751584986
[last_post_id] => 88205
[last_post_user_id] => 36448
[last_post_username] => Paul2
[prefix_id] => 0
[tags] => []
[custom_fields] => []
[vote_score] => 0
[vote_count] => 0
[type_data] => []
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
[User] => ThemeHouse\XLink\XF\Entity\User Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 80
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\User
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[user_id] => 14042
[username] => hist78
[username_date] => 0
[username_date_visible] => 0
[email] => ckckhcdc@gmail.com
[custom_title] =>
[language_id] => 1
[style_id] => 0
[timezone] => America/Los_Angeles
[visible] => 0
[activity_visible] => 0
[user_group_id] => 2
[secondary_group_ids] =>
[display_style_group_id] => 2
[permission_combination_id] => 8
[message_count] => 3593
[question_solution_count] => 0
[conversations_unread] => 0
[register_date] => 1389969050
[last_activity] => 1751998339
[last_summary_email_date] => 1605978520
[trophy_points] => 113
[alerts_unviewed] => 0
[alerts_unread] => 0
[avatar_date] => 1604959511
[avatar_width] => 807
[avatar_height] => 384
[avatar_highdpi] => 1
[gravatar] =>
[user_state] => valid
[security_lock] =>
[is_moderator] => 0
[is_admin] => 0
[is_banned] => 0
[reaction_score] => 3103
[warning_points] => 0
[is_staff] => 0
[secret_key] => 2YRSnPrl4fVQSdv3R6uqHxqi6BDQOXve
[privacy_policy_accepted] => 0
[terms_accepted] => 0
[vote_score] => 0
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
[Forum] => XF\Entity\Forum Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 50
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\Forum
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[node_id] => 2
[discussion_count] => 7518
[message_count] => 52569
[last_post_id] => 88334
[last_post_date] => 1752009795
[last_post_user_id] => 138292
[last_post_username] => MKWVentures
[last_thread_id] => 23156
[last_thread_title] => IBM eyes deeper partnership with Rapidus for sub-1nm chip development
[last_thread_prefix_id] => 0
[moderate_threads] => 0
[moderate_replies] => 0
[allow_posting] => 1
[count_messages] => 1
[find_new] => 1
[allow_index] => allow
[index_criteria] =>
[field_cache] => []
[prefix_cache] => []
[prompt_cache] => []
[default_prefix_id] => 0
[default_sort_order] => last_post_date
[default_sort_direction] => desc
[list_date_limit_days] => 0
[require_prefix] => 0
[allowed_watch_notifications] => all
[min_tags] => 0
[forum_type_id] => discussion
[type_config] => {"allowed_thread_types":["poll"]}
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
[Node] => XF\Entity\Node Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 49
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\Node
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[node_id] => 2
[title] => SemiWiki Main Forum ( Ask the Experts! )
[description] => Post your questions to the experts here!
[node_name] =>
[node_type_id] => Forum
[parent_node_id] => 1
[display_order] => 1
[display_in_list] => 1
[lft] => 2
[rgt] => 3
[depth] => 1
[style_id] => 0
[effective_style_id] => 0
[breadcrumb_data] => {"1":{"node_id":1,"title":"Main Category","depth":0,"lft":1,"node_name":null,"node_type_id":"Category","display_in_list":true}}
[navigation_id] =>
[effective_navigation_id] =>
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
)
[populated:protected] => 1
)
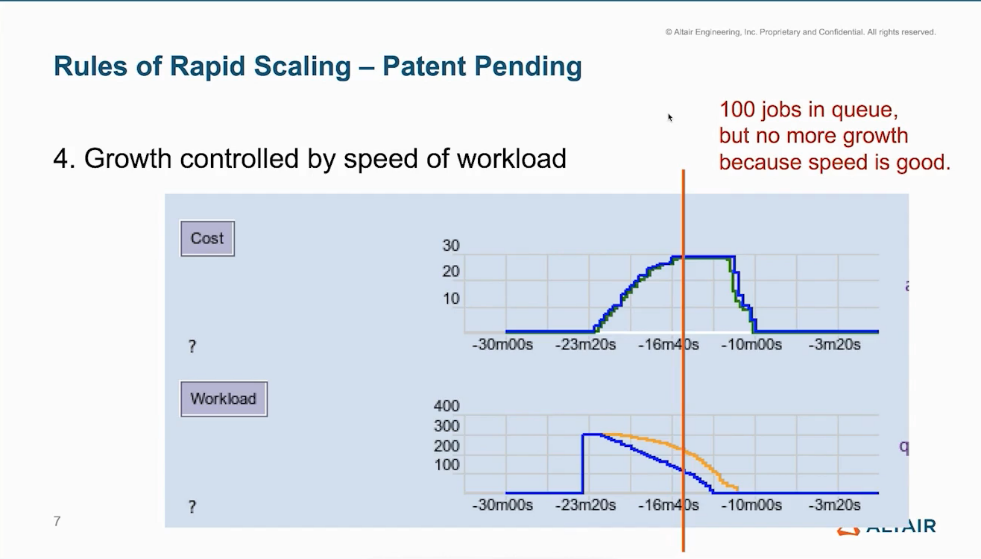
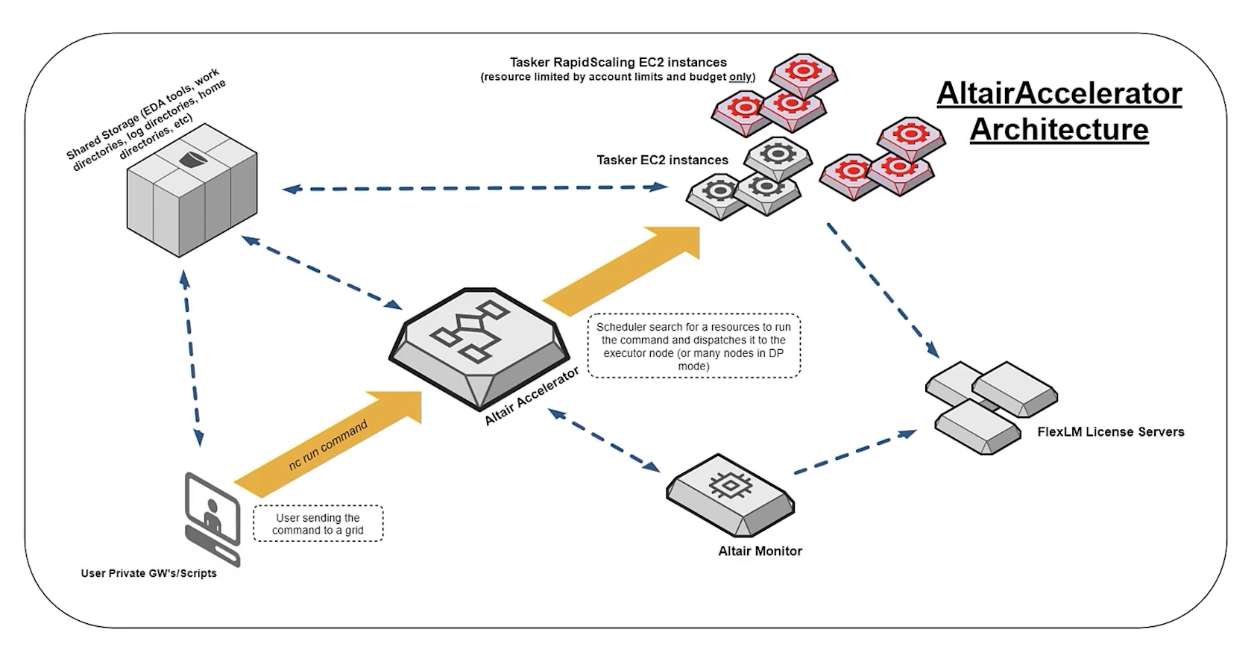
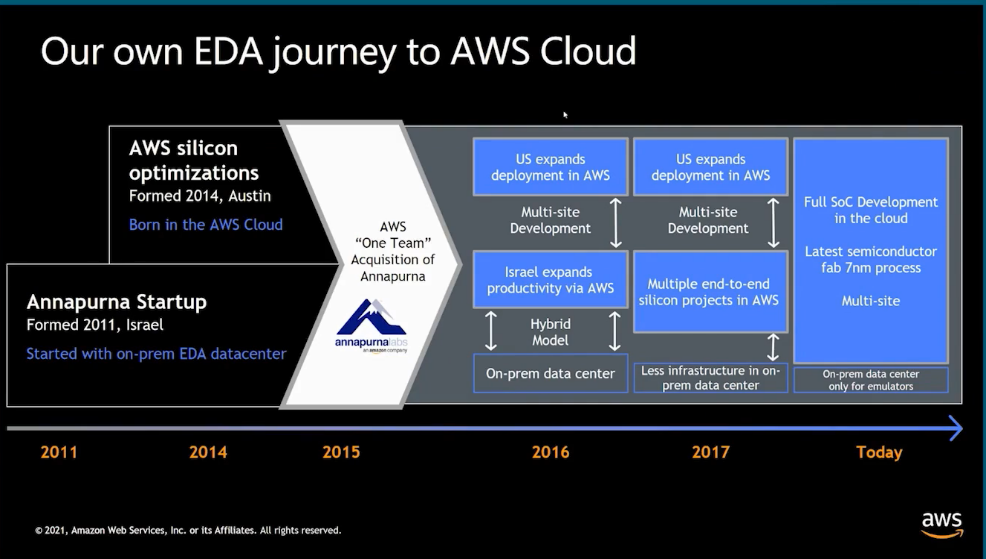





Comments
There are no comments yet.
You must register or log in to view/post comments.