You are currently viewing SemiWiki as a guest which gives you limited access to the site. To view blog comments and experience other SemiWiki features you must be a registered member. Registration is fast, simple, and absolutely free so please,
join our community today!
WP_Term Object
(
[term_id] => 16126
[name] => Lithography
[slug] => lithography
[term_group] => 0
[term_taxonomy_id] => 16126
[taxonomy] => category
[description] =>
[parent] => 0
[count] => 184
[filter] => raw
[cat_ID] => 16126
[category_count] => 184
[category_description] =>
[cat_name] => Lithography
[category_nicename] => lithography
[category_parent] => 0
[is_post] =>
)
– KLA put up an excellent quarter and Guide
– Rising above the increasing tide of orders
– Confirms $75B capex in 2021 with upside
– Foundry & Logic continue to be the sweet spot for KLA
Business is very very good and getting better
-Revenues came in at $1.8B with EPS of $3.85, all above the range
-Guidance… Read More
In this article, we will explore the use of self-aligned litho-etch-litho-etch (SALELE) double patterning for BEOL metal layers in the 7nm node (40 nm minimum metal pitch [1]) with DUV, and 5nm node (28 nm minimum metal pitch [2]) with EUV. First, we mention the evidence that this technique is being used; Xilinx [3] disclosed the… Read More
At the SPIE Advanced Lithography Conference held in February, ASML presented the latest information on their Deep Ultraviolet (DUV) and Extreme Ultraviolet (EUV) exposure systems. I recently got to interview Mike Lercel of ASML to discuss the presentations.
DUV
Despite all the attention EUV is getting, most layers are still… Read More
I recently posted an insightful article [1] published in 2013 on the cost of 3D NAND Flash by Dr. Andrew Walker, which has since received over 10,000 views on LinkedIn. The highlight was the plot of cost vs. the number of layers showing a minimum cost for some layer number, dependent on the etch sidewall angle. In this article, the same… Read More
– ASML has good quarter driven by DUV & Logic (@72%)
– SMIC & other major customer slow EUV plans
– Logic (read that as TSMC) remains key demand led driver
– We are happy memory remains muted given cyclical potential
A very solid quarter with a continued road to growth
The quarter came in at Euro4,254B… Read More
For advanced lithography used to shrink semiconductor device features according to Moore’s Law, resolution limits are an obvious consideration. It is often perceived that the resolution limit is simply derived from a well-defined equation, but nothing can be further from the truth.
Optical Lithography: the fine print
…
Read More
The vast majority of the attention given to the introduction of each new advanced process node focuses on lithographic updates. The common metrics quoted are the transistors per mm**2 or the (high-density) SRAM bit cell area. Alternatively, detailed decomposition analysis may be applied using transmission electron microscopy… Read More
Pretty much all the semiconductor nodes in the last two decades have had at least one layer where the minimum pitch pushes the limitation of the state-of-the-art lithography tool, with a k1 factor < 0.5, i.e., the half-pitch is less than 0.5*wavelength/numerical aperture. A number of published reports [1-4] have touched upon… Read More
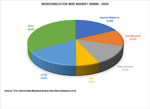
On December 2, 2019, I posted a SemiWiki article entitled “ASML Will Take Semiconductor Equipment Lead from Applied Materials in 2019.”Since losing its dominance for the first time since 1990 in 2019, Applied Materials is poised to lose its retake the 2020 lead in the semiconductor equipment market. ASML led the… Read More
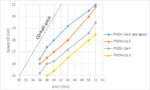
Ongoing investigations of EUV stochastics [1-3] have allowed us to map combinations of critical dimension (CD) and pitch which are expected to pose a severe risk of stochastic defects impacting the use of EUV lithography. Figure 1 shows a typical set of contours of fixed PNOK (i.e., the probability of a feature being Not OK due… Read More




The Name Changes but the Vision Remains the Same – ESD Alliance Through the Years