The topics of stochastics and blur in EUV lithography has been examined by myself for quite some time now [1,2], but I am happy to see that others are pursuing this direction seriously as well [3]. As advanced node half-pitch dimensions approach 10 nm and smaller, the size of molecules in the resist becomes impossible to ignore for… Read More
High-NA Hard Sell: EUV Multi-patterning Practices Revealed, Depth of Focus Not Mentioned
In High-NA EUV lithography systems, the numerical aperture (NA) is expanded from 0.33 to 0.55. This change has been marketed as allowing multi-patterning on the 0.33 NA EUV systems to be avoided. Only very recently have specific examples of this been provided [1]. In fact, it can be shown that double patterning has been implemented… Read More
Impact of Varying Electron Blur and Yield on Stochastic Fluctuations in EUV Resist
A comprehensive update to the EUV stochastic image model
In extreme ultraviolet (EUV) lithography, photoelectron/secondary electron blur and secondary electron yield are known to drive stochastic fluctuations in the resist [1-3], leading to the formation of random defects and the degradation of pattern fidelity at advanced
Stitched Multi-Patterning for Minimum Pitch Metal in DRAM Periphery
In a DRAM chip, the memory array contains features which are the most densely packed, but at least they are regularly arranged. Outside the array, the regularity is lost, but in the most difficult cases, the pitches can still be comparable with those within the array, though generally larger. Such features include the lowest metal… Read More
A Perfect Storm for EUV Lithography
Electron blur, stochastics, and now polarization, are all becoming stronger influences in EUV lithography as pitch continues to shrink
As EUV lithography continues to evolve, targeting smaller and smaller pitches, new physical limitations continue to emerge as formidable obstacles. While stochastic effects have long been… Read More
Variable Cell Height Track Pitch Scaling Beyond Lithography
Two approaches compared
With half-pitch approaching 10 nm, EUV patterning is heavily impacted by stochastic effects, which are aggravated from reduced image contrast from electron blur [1]. A two-mask (“LELE”: Litho-Etch-Litho-Etch) approach was proposed to pattern core features for self-aligned double patterning (SADP)… Read More
A Realistic Electron Blur Function Shape for EUV Resist Modeling
Peak probability at zero distance actually makes no sense
In lithography, it is often stated that the best resolution that can be achieved depends on wavelength and numerical aperture (NA), but this actually only applies to the so-called “aerial” image. When the image is actually formed in the resist layer, it also depends on an… Read More
Powering the Future: How Engineered Substrates and Material Innovation Drive the Semiconductor Revolution
Engineered substrate technology is driving an evolution within the semiconductor industry. As Moore’s Law reaches its limits, the focus is shifting from traditional planar wafer scaling to innovative material engineering and 3D integration. Companies like Soitec, Intel and Samsung are pioneering this transition, unlocking… Read More
Rethinking Multipatterning for 2nm Node
Whether EUV or DUV doesn’t matter at 20 nm pitch
The International Roadmap for Devices and Systems, 2022 Edition, indicates that the “2nm” node due in 2025 (this year) has a minimum (metal) half-pitch of 10 nm [1]. This is, in fact, less than the resolution of a current state-of-the-art EUV system, with a numerical aperture… Read More
Resist Loss Model for the EUV Stochastic Defectivity Cliffs
The occurrences of notorious stochastic defects in EUV lithography have resulted in CD or corresponding dose windows with the lower and higher bounds being characterized as “cliffs” [1-3], since the defect density increases exponentially when approaching these bounds. The defects at lower doses have been attributed to the… Read More


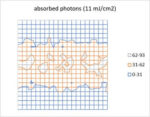
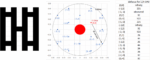



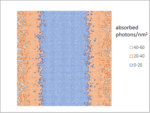
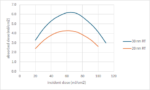
Facing the Quantum Nature of EUV Lithography