Threads
XF\Mvc\Entity\ArrayCollection Object
(
[entities:protected] => Array
(
[23174] => ThemeHouse\XPress\XF\Entity\Thread Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 51
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\Thread
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[thread_id] => 23174
[node_id] => 2
[title] => Semiconductor Fundamentals Are All Weak
[reply_count] => 2
[view_count] => 25
[user_id] => 5
[username] => Daniel Nenni
[post_date] => 1752456209
[sticky] => 0
[discussion_state] => visible
[discussion_open] => 1
[discussion_type] => discussion
[first_post_id] => 88492
[first_post_reaction_score] => 0
[first_post_reactions] => []
[last_post_date] => 1752456912
[last_post_id] => 88494
[last_post_user_id] => 5
[last_post_username] => Daniel Nenni
[prefix_id] => 0
[tags] => []
[custom_fields] => []
[vote_score] => 0
[vote_count] => 0
[type_data] => []
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
[User] => ThemeHouse\XLink\XF\Entity\User Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 48
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\User
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[user_id] => 5
[username] => Daniel Nenni
[username_date] => 0
[username_date_visible] => 0
[email] => dnenni@semiwiki.com
[custom_title] => Admin
[language_id] => 1
[style_id] => 0
[timezone] => America/Los_Angeles
[visible] => 1
[activity_visible] => 1
[user_group_id] => 3
[secondary_group_ids] => 4,5,132
[display_style_group_id] => 3
[permission_combination_id] => 88
[message_count] => 13911
[question_solution_count] => 0
[conversations_unread] => 0
[register_date] => 1280720820
[last_activity] => 1752455253
[last_summary_email_date] => 1605968657
[trophy_points] => 113
[alerts_unviewed] => 34
[alerts_unread] => 34
[avatar_date] => 1663211649
[avatar_width] => 110
[avatar_height] => 107
[avatar_highdpi] => 0
[gravatar] =>
[user_state] => valid
[security_lock] =>
[is_moderator] => 1
[is_admin] => 1
[is_banned] => 0
[reaction_score] => 7006
[warning_points] => 0
[is_staff] => 1
[secret_key] => 0HwyUVVHCwJotUUVEpvqAclfYJdGNPpw
[privacy_policy_accepted] => 0
[terms_accepted] => 0
[vote_score] => 0
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
[Forum] => XF\Entity\Forum Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 50
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\Forum
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[node_id] => 2
[discussion_count] => 7533
[message_count] => 52728
[last_post_id] => 88494
[last_post_date] => 1752456912
[last_post_user_id] => 5
[last_post_username] => Daniel Nenni
[last_thread_id] => 23174
[last_thread_title] => Semiconductor Fundamentals Are All Weak
[last_thread_prefix_id] => 0
[moderate_threads] => 0
[moderate_replies] => 0
[allow_posting] => 1
[count_messages] => 1
[find_new] => 1
[allow_index] => allow
[index_criteria] =>
[field_cache] => []
[prefix_cache] => []
[prompt_cache] => []
[default_prefix_id] => 0
[default_sort_order] => last_post_date
[default_sort_direction] => desc
[list_date_limit_days] => 0
[require_prefix] => 0
[allowed_watch_notifications] => all
[min_tags] => 0
[forum_type_id] => discussion
[type_config] => {"allowed_thread_types":["poll"]}
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
[Node] => XF\Entity\Node Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 49
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\Node
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[node_id] => 2
[title] => SemiWiki Main Forum ( Ask the Experts! )
[description] => Post your questions to the experts here!
[node_name] =>
[node_type_id] => Forum
[parent_node_id] => 1
[display_order] => 1
[display_in_list] => 1
[lft] => 2
[rgt] => 3
[depth] => 1
[style_id] => 0
[effective_style_id] => 0
[breadcrumb_data] => {"1":{"node_id":1,"title":"Main Category","depth":0,"lft":1,"node_name":null,"node_type_id":"Category","display_in_list":true}}
[navigation_id] =>
[effective_navigation_id] =>
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
[23172] => ThemeHouse\XPress\XF\Entity\Thread Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 55
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\Thread
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[thread_id] => 23172
[node_id] => 2
[title] => Intel Nova Lake-S uses TSMC N2 process Tape-Out
[reply_count] => 7
[view_count] => 317
[user_id] => 5
[username] => Daniel Nenni
[post_date] => 1752420774
[sticky] => 0
[discussion_state] => visible
[discussion_open] => 1
[discussion_type] => discussion
[first_post_id] => 88472
[first_post_reaction_score] => 1
[first_post_reactions] => {"1":1}
[last_post_date] => 1752455603
[last_post_id] => 88491
[last_post_user_id] => 5
[last_post_username] => Daniel Nenni
[prefix_id] => 0
[tags] => []
[custom_fields] => []
[vote_score] => 0
[vote_count] => 0
[type_data] => []
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
[User] => ThemeHouse\XLink\XF\Entity\User Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 48
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\User
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[user_id] => 5
[username] => Daniel Nenni
[username_date] => 0
[username_date_visible] => 0
[email] => dnenni@semiwiki.com
[custom_title] => Admin
[language_id] => 1
[style_id] => 0
[timezone] => America/Los_Angeles
[visible] => 1
[activity_visible] => 1
[user_group_id] => 3
[secondary_group_ids] => 4,5,132
[display_style_group_id] => 3
[permission_combination_id] => 88
[message_count] => 13911
[question_solution_count] => 0
[conversations_unread] => 0
[register_date] => 1280720820
[last_activity] => 1752455253
[last_summary_email_date] => 1605968657
[trophy_points] => 113
[alerts_unviewed] => 34
[alerts_unread] => 34
[avatar_date] => 1663211649
[avatar_width] => 110
[avatar_height] => 107
[avatar_highdpi] => 0
[gravatar] =>
[user_state] => valid
[security_lock] =>
[is_moderator] => 1
[is_admin] => 1
[is_banned] => 0
[reaction_score] => 7006
[warning_points] => 0
[is_staff] => 1
[secret_key] => 0HwyUVVHCwJotUUVEpvqAclfYJdGNPpw
[privacy_policy_accepted] => 0
[terms_accepted] => 0
[vote_score] => 0
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
[Forum] => XF\Entity\Forum Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 50
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\Forum
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[node_id] => 2
[discussion_count] => 7533
[message_count] => 52728
[last_post_id] => 88494
[last_post_date] => 1752456912
[last_post_user_id] => 5
[last_post_username] => Daniel Nenni
[last_thread_id] => 23174
[last_thread_title] => Semiconductor Fundamentals Are All Weak
[last_thread_prefix_id] => 0
[moderate_threads] => 0
[moderate_replies] => 0
[allow_posting] => 1
[count_messages] => 1
[find_new] => 1
[allow_index] => allow
[index_criteria] =>
[field_cache] => []
[prefix_cache] => []
[prompt_cache] => []
[default_prefix_id] => 0
[default_sort_order] => last_post_date
[default_sort_direction] => desc
[list_date_limit_days] => 0
[require_prefix] => 0
[allowed_watch_notifications] => all
[min_tags] => 0
[forum_type_id] => discussion
[type_config] => {"allowed_thread_types":["poll"]}
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
[Node] => XF\Entity\Node Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 49
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\Node
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[node_id] => 2
[title] => SemiWiki Main Forum ( Ask the Experts! )
[description] => Post your questions to the experts here!
[node_name] =>
[node_type_id] => Forum
[parent_node_id] => 1
[display_order] => 1
[display_in_list] => 1
[lft] => 2
[rgt] => 3
[depth] => 1
[style_id] => 0
[effective_style_id] => 0
[breadcrumb_data] => {"1":{"node_id":1,"title":"Main Category","depth":0,"lft":1,"node_name":null,"node_type_id":"Category","display_in_list":true}}
[navigation_id] =>
[effective_navigation_id] =>
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
[22690] => ThemeHouse\XPress\XF\Entity\Thread Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 59
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\Thread
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[thread_id] => 22690
[node_id] => 2
[title] => Huawei, the leader in Chinese semiconductor development… ‘Life or death’ for SMIC 5nm mass production next year
[reply_count] => 17
[view_count] => 8333
[user_id] => 5
[username] => Daniel Nenni
[post_date] => 1745605124
[sticky] => 0
[discussion_state] => visible
[discussion_open] => 1
[discussion_type] => discussion
[first_post_id] => 85511
[first_post_reaction_score] => 0
[first_post_reactions] => []
[last_post_date] => 1752448258
[last_post_id] => 88489
[last_post_user_id] => 5185
[last_post_username] => Fred Chen
[prefix_id] => 0
[tags] => []
[custom_fields] => []
[vote_score] => 0
[vote_count] => 0
[type_data] => []
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
[User] => ThemeHouse\XLink\XF\Entity\User Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 48
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\User
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[user_id] => 5
[username] => Daniel Nenni
[username_date] => 0
[username_date_visible] => 0
[email] => dnenni@semiwiki.com
[custom_title] => Admin
[language_id] => 1
[style_id] => 0
[timezone] => America/Los_Angeles
[visible] => 1
[activity_visible] => 1
[user_group_id] => 3
[secondary_group_ids] => 4,5,132
[display_style_group_id] => 3
[permission_combination_id] => 88
[message_count] => 13911
[question_solution_count] => 0
[conversations_unread] => 0
[register_date] => 1280720820
[last_activity] => 1752455253
[last_summary_email_date] => 1605968657
[trophy_points] => 113
[alerts_unviewed] => 34
[alerts_unread] => 34
[avatar_date] => 1663211649
[avatar_width] => 110
[avatar_height] => 107
[avatar_highdpi] => 0
[gravatar] =>
[user_state] => valid
[security_lock] =>
[is_moderator] => 1
[is_admin] => 1
[is_banned] => 0
[reaction_score] => 7006
[warning_points] => 0
[is_staff] => 1
[secret_key] => 0HwyUVVHCwJotUUVEpvqAclfYJdGNPpw
[privacy_policy_accepted] => 0
[terms_accepted] => 0
[vote_score] => 0
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
[Forum] => XF\Entity\Forum Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 50
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\Forum
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[node_id] => 2
[discussion_count] => 7533
[message_count] => 52728
[last_post_id] => 88494
[last_post_date] => 1752456912
[last_post_user_id] => 5
[last_post_username] => Daniel Nenni
[last_thread_id] => 23174
[last_thread_title] => Semiconductor Fundamentals Are All Weak
[last_thread_prefix_id] => 0
[moderate_threads] => 0
[moderate_replies] => 0
[allow_posting] => 1
[count_messages] => 1
[find_new] => 1
[allow_index] => allow
[index_criteria] =>
[field_cache] => []
[prefix_cache] => []
[prompt_cache] => []
[default_prefix_id] => 0
[default_sort_order] => last_post_date
[default_sort_direction] => desc
[list_date_limit_days] => 0
[require_prefix] => 0
[allowed_watch_notifications] => all
[min_tags] => 0
[forum_type_id] => discussion
[type_config] => {"allowed_thread_types":["poll"]}
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
[Node] => XF\Entity\Node Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 49
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\Node
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[node_id] => 2
[title] => SemiWiki Main Forum ( Ask the Experts! )
[description] => Post your questions to the experts here!
[node_name] =>
[node_type_id] => Forum
[parent_node_id] => 1
[display_order] => 1
[display_in_list] => 1
[lft] => 2
[rgt] => 3
[depth] => 1
[style_id] => 0
[effective_style_id] => 0
[breadcrumb_data] => {"1":{"node_id":1,"title":"Main Category","depth":0,"lft":1,"node_name":null,"node_type_id":"Category","display_in_list":true}}
[navigation_id] =>
[effective_navigation_id] =>
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
[23160] => ThemeHouse\XPress\XF\Entity\Thread Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 63
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\Thread
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[thread_id] => 23160
[node_id] => 2
[title] => Jeff Williams, Tim Cook's Tim Cook, stepping down from Apple
[reply_count] => 5
[view_count] => 1327
[user_id] => 14042
[username] => hist78
[post_date] => 1752095275
[sticky] => 0
[discussion_state] => visible
[discussion_open] => 1
[discussion_type] => discussion
[first_post_id] => 88371
[first_post_reaction_score] => 0
[first_post_reactions] => []
[last_post_date] => 1752444160
[last_post_id] => 88487
[last_post_user_id] => 35033
[last_post_username] => GYHTBT
[prefix_id] => 0
[tags] => []
[custom_fields] => []
[vote_score] => 0
[vote_count] => 0
[type_data] => []
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
[User] => ThemeHouse\XLink\XF\Entity\User Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 60
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\User
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[user_id] => 14042
[username] => hist78
[username_date] => 0
[username_date_visible] => 0
[email] => ckckhcdc@gmail.com
[custom_title] =>
[language_id] => 1
[style_id] => 0
[timezone] => America/Los_Angeles
[visible] => 0
[activity_visible] => 0
[user_group_id] => 2
[secondary_group_ids] =>
[display_style_group_id] => 2
[permission_combination_id] => 8
[message_count] => 3606
[question_solution_count] => 0
[conversations_unread] => 0
[register_date] => 1389969050
[last_activity] => 1752410271
[last_summary_email_date] => 1605978520
[trophy_points] => 113
[alerts_unviewed] => 2
[alerts_unread] => 5
[avatar_date] => 1604959511
[avatar_width] => 807
[avatar_height] => 384
[avatar_highdpi] => 1
[gravatar] =>
[user_state] => valid
[security_lock] =>
[is_moderator] => 0
[is_admin] => 0
[is_banned] => 0
[reaction_score] => 3128
[warning_points] => 0
[is_staff] => 0
[secret_key] => 2YRSnPrl4fVQSdv3R6uqHxqi6BDQOXve
[privacy_policy_accepted] => 0
[terms_accepted] => 0
[vote_score] => 0
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
[Forum] => XF\Entity\Forum Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 50
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\Forum
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[node_id] => 2
[discussion_count] => 7533
[message_count] => 52728
[last_post_id] => 88494
[last_post_date] => 1752456912
[last_post_user_id] => 5
[last_post_username] => Daniel Nenni
[last_thread_id] => 23174
[last_thread_title] => Semiconductor Fundamentals Are All Weak
[last_thread_prefix_id] => 0
[moderate_threads] => 0
[moderate_replies] => 0
[allow_posting] => 1
[count_messages] => 1
[find_new] => 1
[allow_index] => allow
[index_criteria] =>
[field_cache] => []
[prefix_cache] => []
[prompt_cache] => []
[default_prefix_id] => 0
[default_sort_order] => last_post_date
[default_sort_direction] => desc
[list_date_limit_days] => 0
[require_prefix] => 0
[allowed_watch_notifications] => all
[min_tags] => 0
[forum_type_id] => discussion
[type_config] => {"allowed_thread_types":["poll"]}
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
[Node] => XF\Entity\Node Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 49
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\Node
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[node_id] => 2
[title] => SemiWiki Main Forum ( Ask the Experts! )
[description] => Post your questions to the experts here!
[node_name] =>
[node_type_id] => Forum
[parent_node_id] => 1
[display_order] => 1
[display_in_list] => 1
[lft] => 2
[rgt] => 3
[depth] => 1
[style_id] => 0
[effective_style_id] => 0
[breadcrumb_data] => {"1":{"node_id":1,"title":"Main Category","depth":0,"lft":1,"node_name":null,"node_type_id":"Category","display_in_list":true}}
[navigation_id] =>
[effective_navigation_id] =>
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
[23173] => ThemeHouse\XPress\XF\Entity\Thread Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 67
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\Thread
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[thread_id] => 23173
[node_id] => 2
[title] => Three year prison sentence for man who shared ASML information with a person in Russia
[reply_count] => 0
[view_count] => 79
[user_id] => 5
[username] => Daniel Nenni
[post_date] => 1752441438
[sticky] => 0
[discussion_state] => visible
[discussion_open] => 1
[discussion_type] => discussion
[first_post_id] => 88486
[first_post_reaction_score] => 0
[first_post_reactions] => []
[last_post_date] => 1752441438
[last_post_id] => 88486
[last_post_user_id] => 5
[last_post_username] => Daniel Nenni
[prefix_id] => 0
[tags] => []
[custom_fields] => []
[vote_score] => 0
[vote_count] => 0
[type_data] => []
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
[User] => ThemeHouse\XLink\XF\Entity\User Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 48
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\User
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[user_id] => 5
[username] => Daniel Nenni
[username_date] => 0
[username_date_visible] => 0
[email] => dnenni@semiwiki.com
[custom_title] => Admin
[language_id] => 1
[style_id] => 0
[timezone] => America/Los_Angeles
[visible] => 1
[activity_visible] => 1
[user_group_id] => 3
[secondary_group_ids] => 4,5,132
[display_style_group_id] => 3
[permission_combination_id] => 88
[message_count] => 13911
[question_solution_count] => 0
[conversations_unread] => 0
[register_date] => 1280720820
[last_activity] => 1752455253
[last_summary_email_date] => 1605968657
[trophy_points] => 113
[alerts_unviewed] => 34
[alerts_unread] => 34
[avatar_date] => 1663211649
[avatar_width] => 110
[avatar_height] => 107
[avatar_highdpi] => 0
[gravatar] =>
[user_state] => valid
[security_lock] =>
[is_moderator] => 1
[is_admin] => 1
[is_banned] => 0
[reaction_score] => 7006
[warning_points] => 0
[is_staff] => 1
[secret_key] => 0HwyUVVHCwJotUUVEpvqAclfYJdGNPpw
[privacy_policy_accepted] => 0
[terms_accepted] => 0
[vote_score] => 0
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
[Forum] => XF\Entity\Forum Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 50
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\Forum
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[node_id] => 2
[discussion_count] => 7533
[message_count] => 52728
[last_post_id] => 88494
[last_post_date] => 1752456912
[last_post_user_id] => 5
[last_post_username] => Daniel Nenni
[last_thread_id] => 23174
[last_thread_title] => Semiconductor Fundamentals Are All Weak
[last_thread_prefix_id] => 0
[moderate_threads] => 0
[moderate_replies] => 0
[allow_posting] => 1
[count_messages] => 1
[find_new] => 1
[allow_index] => allow
[index_criteria] =>
[field_cache] => []
[prefix_cache] => []
[prompt_cache] => []
[default_prefix_id] => 0
[default_sort_order] => last_post_date
[default_sort_direction] => desc
[list_date_limit_days] => 0
[require_prefix] => 0
[allowed_watch_notifications] => all
[min_tags] => 0
[forum_type_id] => discussion
[type_config] => {"allowed_thread_types":["poll"]}
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
[Node] => XF\Entity\Node Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 49
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\Node
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[node_id] => 2
[title] => SemiWiki Main Forum ( Ask the Experts! )
[description] => Post your questions to the experts here!
[node_name] =>
[node_type_id] => Forum
[parent_node_id] => 1
[display_order] => 1
[display_in_list] => 1
[lft] => 2
[rgt] => 3
[depth] => 1
[style_id] => 0
[effective_style_id] => 0
[breadcrumb_data] => {"1":{"node_id":1,"title":"Main Category","depth":0,"lft":1,"node_name":null,"node_type_id":"Category","display_in_list":true}}
[navigation_id] =>
[effective_navigation_id] =>
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
[23162] => ThemeHouse\XPress\XF\Entity\Thread Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 71
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\Thread
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[thread_id] => 23162
[node_id] => 2
[title] => Intel’s CEO: ‘We are not in the top 10’ of leading chip companies
[reply_count] => 53
[view_count] => 5753
[user_id] => 332012
[username] => osnium
[post_date] => 1752113431
[sticky] => 0
[discussion_state] => visible
[discussion_open] => 1
[discussion_type] => discussion
[first_post_id] => 88377
[first_post_reaction_score] => 6
[first_post_reactions] => {"1":6}
[last_post_date] => 1752428037
[last_post_id] => 88484
[last_post_user_id] => 396
[last_post_username] => swka
[prefix_id] => 0
[tags] => []
[custom_fields] => []
[vote_score] => 0
[vote_count] => 0
[type_data] => []
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
[User] => ThemeHouse\XLink\XF\Entity\User Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 68
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\User
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[user_id] => 332012
[username] => osnium
[username_date] => 0
[username_date_visible] => 0
[email] => prelim_upturn_0p@icloud.com
[custom_title] =>
[language_id] => 1
[style_id] => 0
[timezone] => America/Los_Angeles
[visible] => 1
[activity_visible] => 1
[user_group_id] => 2
[secondary_group_ids] =>
[display_style_group_id] => 2
[permission_combination_id] => 8
[message_count] => 302
[question_solution_count] => 0
[conversations_unread] => 4
[register_date] => 1708476721
[last_activity] => 1752455379
[last_summary_email_date] => 1708476721
[trophy_points] => 43
[alerts_unviewed] => 9
[alerts_unread] => 9
[avatar_date] => 0
[avatar_width] => 0
[avatar_height] => 0
[avatar_highdpi] => 0
[gravatar] =>
[user_state] => valid
[security_lock] =>
[is_moderator] => 0
[is_admin] => 0
[is_banned] => 0
[reaction_score] => 237
[warning_points] => 0
[is_staff] => 0
[secret_key] => LslDOzdhXWoAXmgbm-AZIYJy2n9ao8Yy
[privacy_policy_accepted] => 1708476721
[terms_accepted] => 1708476721
[vote_score] => 0
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
[Forum] => XF\Entity\Forum Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 50
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\Forum
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[node_id] => 2
[discussion_count] => 7533
[message_count] => 52728
[last_post_id] => 88494
[last_post_date] => 1752456912
[last_post_user_id] => 5
[last_post_username] => Daniel Nenni
[last_thread_id] => 23174
[last_thread_title] => Semiconductor Fundamentals Are All Weak
[last_thread_prefix_id] => 0
[moderate_threads] => 0
[moderate_replies] => 0
[allow_posting] => 1
[count_messages] => 1
[find_new] => 1
[allow_index] => allow
[index_criteria] =>
[field_cache] => []
[prefix_cache] => []
[prompt_cache] => []
[default_prefix_id] => 0
[default_sort_order] => last_post_date
[default_sort_direction] => desc
[list_date_limit_days] => 0
[require_prefix] => 0
[allowed_watch_notifications] => all
[min_tags] => 0
[forum_type_id] => discussion
[type_config] => {"allowed_thread_types":["poll"]}
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
[Node] => XF\Entity\Node Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 49
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\Node
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[node_id] => 2
[title] => SemiWiki Main Forum ( Ask the Experts! )
[description] => Post your questions to the experts here!
[node_name] =>
[node_type_id] => Forum
[parent_node_id] => 1
[display_order] => 1
[display_in_list] => 1
[lft] => 2
[rgt] => 3
[depth] => 1
[style_id] => 0
[effective_style_id] => 0
[breadcrumb_data] => {"1":{"node_id":1,"title":"Main Category","depth":0,"lft":1,"node_name":null,"node_type_id":"Category","display_in_list":true}}
[navigation_id] =>
[effective_navigation_id] =>
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
[14021] => ThemeHouse\XPress\XF\Entity\Thread Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 75
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\Thread
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[thread_id] => 14021
[node_id] => 2
[title] => Radically Improved Battery, Uses Silicon instead of Graphite
[reply_count] => 20
[view_count] => 6614
[user_id] => 10499
[username] => Arthur Hanson
[post_date] => 1617796378
[sticky] => 0
[discussion_state] => visible
[discussion_open] => 1
[discussion_type] => discussion
[first_post_id] => 46387
[first_post_reaction_score] => 1
[first_post_reactions] => {"1":1}
[last_post_date] => 1752420778
[last_post_id] => 88473
[last_post_user_id] => 333239
[last_post_username] => Memphremagog
[prefix_id] => 0
[tags] => []
[custom_fields] => []
[vote_score] => 0
[vote_count] => 0
[type_data] => []
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
[User] => ThemeHouse\XLink\XF\Entity\User Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 72
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\User
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[user_id] => 10499
[username] => Arthur Hanson
[username_date] => 0
[username_date_visible] => 0
[email] => a-j-hanson@att.net
[custom_title] =>
[language_id] => 1
[style_id] => 1
[timezone] => America/Los_Angeles
[visible] => 1
[activity_visible] => 1
[user_group_id] => 2
[secondary_group_ids] =>
[display_style_group_id] => 2
[permission_combination_id] => 8
[message_count] => 3256
[question_solution_count] => 0
[conversations_unread] => 0
[register_date] => 1366028460
[last_activity] => 1751760746
[last_summary_email_date] => 1606051785
[trophy_points] => 83
[alerts_unviewed] => 9
[alerts_unread] => 9
[avatar_date] => 0
[avatar_width] => 0
[avatar_height] => 0
[avatar_highdpi] => 0
[gravatar] =>
[user_state] => valid
[security_lock] =>
[is_moderator] => 0
[is_admin] => 0
[is_banned] => 0
[reaction_score] => 432
[warning_points] => 0
[is_staff] => 0
[secret_key] => ta_8_Pj20m6PDO6RnrGK-VnSP_vyhP_m
[privacy_policy_accepted] => 0
[terms_accepted] => 0
[vote_score] => 0
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
[Forum] => XF\Entity\Forum Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 50
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\Forum
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[node_id] => 2
[discussion_count] => 7533
[message_count] => 52728
[last_post_id] => 88494
[last_post_date] => 1752456912
[last_post_user_id] => 5
[last_post_username] => Daniel Nenni
[last_thread_id] => 23174
[last_thread_title] => Semiconductor Fundamentals Are All Weak
[last_thread_prefix_id] => 0
[moderate_threads] => 0
[moderate_replies] => 0
[allow_posting] => 1
[count_messages] => 1
[find_new] => 1
[allow_index] => allow
[index_criteria] =>
[field_cache] => []
[prefix_cache] => []
[prompt_cache] => []
[default_prefix_id] => 0
[default_sort_order] => last_post_date
[default_sort_direction] => desc
[list_date_limit_days] => 0
[require_prefix] => 0
[allowed_watch_notifications] => all
[min_tags] => 0
[forum_type_id] => discussion
[type_config] => {"allowed_thread_types":["poll"]}
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
[Node] => XF\Entity\Node Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 49
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\Node
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[node_id] => 2
[title] => SemiWiki Main Forum ( Ask the Experts! )
[description] => Post your questions to the experts here!
[node_name] =>
[node_type_id] => Forum
[parent_node_id] => 1
[display_order] => 1
[display_in_list] => 1
[lft] => 2
[rgt] => 3
[depth] => 1
[style_id] => 0
[effective_style_id] => 0
[breadcrumb_data] => {"1":{"node_id":1,"title":"Main Category","depth":0,"lft":1,"node_name":null,"node_type_id":"Category","display_in_list":true}}
[navigation_id] =>
[effective_navigation_id] =>
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
[23165] => ThemeHouse\XPress\XF\Entity\Thread Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 79
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\Thread
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[thread_id] => 23165
[node_id] => 2
[title] => Nvidia CEO Huang to meet Trump before China trip, source says
[reply_count] => 7
[view_count] => 1123
[user_id] => 5
[username] => Daniel Nenni
[post_date] => 1752183333
[sticky] => 0
[discussion_state] => visible
[discussion_open] => 1
[discussion_type] => discussion
[first_post_id] => 88405
[first_post_reaction_score] => 1
[first_post_reactions] => {"3":1}
[last_post_date] => 1752419200
[last_post_id] => 88471
[last_post_user_id] => 5
[last_post_username] => Daniel Nenni
[prefix_id] => 0
[tags] => []
[custom_fields] => []
[vote_score] => 0
[vote_count] => 0
[type_data] => []
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
[User] => ThemeHouse\XLink\XF\Entity\User Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 48
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\User
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[user_id] => 5
[username] => Daniel Nenni
[username_date] => 0
[username_date_visible] => 0
[email] => dnenni@semiwiki.com
[custom_title] => Admin
[language_id] => 1
[style_id] => 0
[timezone] => America/Los_Angeles
[visible] => 1
[activity_visible] => 1
[user_group_id] => 3
[secondary_group_ids] => 4,5,132
[display_style_group_id] => 3
[permission_combination_id] => 88
[message_count] => 13911
[question_solution_count] => 0
[conversations_unread] => 0
[register_date] => 1280720820
[last_activity] => 1752455253
[last_summary_email_date] => 1605968657
[trophy_points] => 113
[alerts_unviewed] => 34
[alerts_unread] => 34
[avatar_date] => 1663211649
[avatar_width] => 110
[avatar_height] => 107
[avatar_highdpi] => 0
[gravatar] =>
[user_state] => valid
[security_lock] =>
[is_moderator] => 1
[is_admin] => 1
[is_banned] => 0
[reaction_score] => 7006
[warning_points] => 0
[is_staff] => 1
[secret_key] => 0HwyUVVHCwJotUUVEpvqAclfYJdGNPpw
[privacy_policy_accepted] => 0
[terms_accepted] => 0
[vote_score] => 0
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
[Forum] => XF\Entity\Forum Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 50
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\Forum
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[node_id] => 2
[discussion_count] => 7533
[message_count] => 52728
[last_post_id] => 88494
[last_post_date] => 1752456912
[last_post_user_id] => 5
[last_post_username] => Daniel Nenni
[last_thread_id] => 23174
[last_thread_title] => Semiconductor Fundamentals Are All Weak
[last_thread_prefix_id] => 0
[moderate_threads] => 0
[moderate_replies] => 0
[allow_posting] => 1
[count_messages] => 1
[find_new] => 1
[allow_index] => allow
[index_criteria] =>
[field_cache] => []
[prefix_cache] => []
[prompt_cache] => []
[default_prefix_id] => 0
[default_sort_order] => last_post_date
[default_sort_direction] => desc
[list_date_limit_days] => 0
[require_prefix] => 0
[allowed_watch_notifications] => all
[min_tags] => 0
[forum_type_id] => discussion
[type_config] => {"allowed_thread_types":["poll"]}
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
[Node] => XF\Entity\Node Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 49
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\Node
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[node_id] => 2
[title] => SemiWiki Main Forum ( Ask the Experts! )
[description] => Post your questions to the experts here!
[node_name] =>
[node_type_id] => Forum
[parent_node_id] => 1
[display_order] => 1
[display_in_list] => 1
[lft] => 2
[rgt] => 3
[depth] => 1
[style_id] => 0
[effective_style_id] => 0
[breadcrumb_data] => {"1":{"node_id":1,"title":"Main Category","depth":0,"lft":1,"node_name":null,"node_type_id":"Category","display_in_list":true}}
[navigation_id] =>
[effective_navigation_id] =>
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
[22788] => ThemeHouse\XPress\XF\Entity\Thread Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 83
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\Thread
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[thread_id] => 22788
[node_id] => 2
[title] => GlobalWafers to open U.S.' first 12-inch silicon wafer fab soon
[reply_count] => 3
[view_count] => 2705
[user_id] => 5
[username] => Daniel Nenni
[post_date] => 1747070249
[sticky] => 0
[discussion_state] => visible
[discussion_open] => 1
[discussion_type] => discussion
[first_post_id] => 86148
[first_post_reaction_score] => 4
[first_post_reactions] => {"1":4}
[last_post_date] => 1752389073
[last_post_id] => 88460
[last_post_user_id] => 398779
[last_post_username] => xu fei
[prefix_id] => 0
[tags] => []
[custom_fields] => []
[vote_score] => 0
[vote_count] => 0
[type_data] => []
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
[User] => ThemeHouse\XLink\XF\Entity\User Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 48
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\User
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[user_id] => 5
[username] => Daniel Nenni
[username_date] => 0
[username_date_visible] => 0
[email] => dnenni@semiwiki.com
[custom_title] => Admin
[language_id] => 1
[style_id] => 0
[timezone] => America/Los_Angeles
[visible] => 1
[activity_visible] => 1
[user_group_id] => 3
[secondary_group_ids] => 4,5,132
[display_style_group_id] => 3
[permission_combination_id] => 88
[message_count] => 13911
[question_solution_count] => 0
[conversations_unread] => 0
[register_date] => 1280720820
[last_activity] => 1752455253
[last_summary_email_date] => 1605968657
[trophy_points] => 113
[alerts_unviewed] => 34
[alerts_unread] => 34
[avatar_date] => 1663211649
[avatar_width] => 110
[avatar_height] => 107
[avatar_highdpi] => 0
[gravatar] =>
[user_state] => valid
[security_lock] =>
[is_moderator] => 1
[is_admin] => 1
[is_banned] => 0
[reaction_score] => 7006
[warning_points] => 0
[is_staff] => 1
[secret_key] => 0HwyUVVHCwJotUUVEpvqAclfYJdGNPpw
[privacy_policy_accepted] => 0
[terms_accepted] => 0
[vote_score] => 0
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
[Forum] => XF\Entity\Forum Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 50
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\Forum
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[node_id] => 2
[discussion_count] => 7533
[message_count] => 52728
[last_post_id] => 88494
[last_post_date] => 1752456912
[last_post_user_id] => 5
[last_post_username] => Daniel Nenni
[last_thread_id] => 23174
[last_thread_title] => Semiconductor Fundamentals Are All Weak
[last_thread_prefix_id] => 0
[moderate_threads] => 0
[moderate_replies] => 0
[allow_posting] => 1
[count_messages] => 1
[find_new] => 1
[allow_index] => allow
[index_criteria] =>
[field_cache] => []
[prefix_cache] => []
[prompt_cache] => []
[default_prefix_id] => 0
[default_sort_order] => last_post_date
[default_sort_direction] => desc
[list_date_limit_days] => 0
[require_prefix] => 0
[allowed_watch_notifications] => all
[min_tags] => 0
[forum_type_id] => discussion
[type_config] => {"allowed_thread_types":["poll"]}
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
[Node] => XF\Entity\Node Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 49
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\Node
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[node_id] => 2
[title] => SemiWiki Main Forum ( Ask the Experts! )
[description] => Post your questions to the experts here!
[node_name] =>
[node_type_id] => Forum
[parent_node_id] => 1
[display_order] => 1
[display_in_list] => 1
[lft] => 2
[rgt] => 3
[depth] => 1
[style_id] => 0
[effective_style_id] => 0
[breadcrumb_data] => {"1":{"node_id":1,"title":"Main Category","depth":0,"lft":1,"node_name":null,"node_type_id":"Category","display_in_list":true}}
[navigation_id] =>
[effective_navigation_id] =>
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
[23074] => ThemeHouse\XPress\XF\Entity\Thread Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 87
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\Thread
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[thread_id] => 23074
[node_id] => 2
[title] => Is Silicon Carbide the future of Semiconductors?
[reply_count] => 9
[view_count] => 1358
[user_id] => 10499
[username] => Arthur Hanson
[post_date] => 1750693545
[sticky] => 0
[discussion_state] => visible
[discussion_open] => 1
[discussion_type] => discussion
[first_post_id] => 87856
[first_post_reaction_score] => 0
[first_post_reactions] => []
[last_post_date] => 1752388205
[last_post_id] => 88458
[last_post_user_id] => 398779
[last_post_username] => xu fei
[prefix_id] => 0
[tags] => []
[custom_fields] => []
[vote_score] => 0
[vote_count] => 0
[type_data] => []
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
[User] => ThemeHouse\XLink\XF\Entity\User Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 72
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\User
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[user_id] => 10499
[username] => Arthur Hanson
[username_date] => 0
[username_date_visible] => 0
[email] => a-j-hanson@att.net
[custom_title] =>
[language_id] => 1
[style_id] => 1
[timezone] => America/Los_Angeles
[visible] => 1
[activity_visible] => 1
[user_group_id] => 2
[secondary_group_ids] =>
[display_style_group_id] => 2
[permission_combination_id] => 8
[message_count] => 3256
[question_solution_count] => 0
[conversations_unread] => 0
[register_date] => 1366028460
[last_activity] => 1751760746
[last_summary_email_date] => 1606051785
[trophy_points] => 83
[alerts_unviewed] => 9
[alerts_unread] => 9
[avatar_date] => 0
[avatar_width] => 0
[avatar_height] => 0
[avatar_highdpi] => 0
[gravatar] =>
[user_state] => valid
[security_lock] =>
[is_moderator] => 0
[is_admin] => 0
[is_banned] => 0
[reaction_score] => 432
[warning_points] => 0
[is_staff] => 0
[secret_key] => ta_8_Pj20m6PDO6RnrGK-VnSP_vyhP_m
[privacy_policy_accepted] => 0
[terms_accepted] => 0
[vote_score] => 0
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
[Forum] => XF\Entity\Forum Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 50
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\Forum
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[node_id] => 2
[discussion_count] => 7533
[message_count] => 52728
[last_post_id] => 88494
[last_post_date] => 1752456912
[last_post_user_id] => 5
[last_post_username] => Daniel Nenni
[last_thread_id] => 23174
[last_thread_title] => Semiconductor Fundamentals Are All Weak
[last_thread_prefix_id] => 0
[moderate_threads] => 0
[moderate_replies] => 0
[allow_posting] => 1
[count_messages] => 1
[find_new] => 1
[allow_index] => allow
[index_criteria] =>
[field_cache] => []
[prefix_cache] => []
[prompt_cache] => []
[default_prefix_id] => 0
[default_sort_order] => last_post_date
[default_sort_direction] => desc
[list_date_limit_days] => 0
[require_prefix] => 0
[allowed_watch_notifications] => all
[min_tags] => 0
[forum_type_id] => discussion
[type_config] => {"allowed_thread_types":["poll"]}
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
[Node] => XF\Entity\Node Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 49
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\Node
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[node_id] => 2
[title] => SemiWiki Main Forum ( Ask the Experts! )
[description] => Post your questions to the experts here!
[node_name] =>
[node_type_id] => Forum
[parent_node_id] => 1
[display_order] => 1
[display_in_list] => 1
[lft] => 2
[rgt] => 3
[depth] => 1
[style_id] => 0
[effective_style_id] => 0
[breadcrumb_data] => {"1":{"node_id":1,"title":"Main Category","depth":0,"lft":1,"node_name":null,"node_type_id":"Category","display_in_list":true}}
[navigation_id] =>
[effective_navigation_id] =>
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
[23108] => ThemeHouse\XPress\XF\Entity\Thread Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 91
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\Thread
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[thread_id] => 23108
[node_id] => 2
[title] => Better Battery Technologies to Change the Entire Electric Ecosystem
[reply_count] => 1
[view_count] => 400
[user_id] => 10499
[username] => Arthur Hanson
[post_date] => 1751284865
[sticky] => 0
[discussion_state] => visible
[discussion_open] => 1
[discussion_type] => discussion
[first_post_id] => 88066
[first_post_reaction_score] => 0
[first_post_reactions] => []
[last_post_date] => 1752387997
[last_post_id] => 88457
[last_post_user_id] => 398779
[last_post_username] => xu fei
[prefix_id] => 0
[tags] => []
[custom_fields] => []
[vote_score] => 0
[vote_count] => 0
[type_data] => []
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
[User] => ThemeHouse\XLink\XF\Entity\User Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 72
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\User
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[user_id] => 10499
[username] => Arthur Hanson
[username_date] => 0
[username_date_visible] => 0
[email] => a-j-hanson@att.net
[custom_title] =>
[language_id] => 1
[style_id] => 1
[timezone] => America/Los_Angeles
[visible] => 1
[activity_visible] => 1
[user_group_id] => 2
[secondary_group_ids] =>
[display_style_group_id] => 2
[permission_combination_id] => 8
[message_count] => 3256
[question_solution_count] => 0
[conversations_unread] => 0
[register_date] => 1366028460
[last_activity] => 1751760746
[last_summary_email_date] => 1606051785
[trophy_points] => 83
[alerts_unviewed] => 9
[alerts_unread] => 9
[avatar_date] => 0
[avatar_width] => 0
[avatar_height] => 0
[avatar_highdpi] => 0
[gravatar] =>
[user_state] => valid
[security_lock] =>
[is_moderator] => 0
[is_admin] => 0
[is_banned] => 0
[reaction_score] => 432
[warning_points] => 0
[is_staff] => 0
[secret_key] => ta_8_Pj20m6PDO6RnrGK-VnSP_vyhP_m
[privacy_policy_accepted] => 0
[terms_accepted] => 0
[vote_score] => 0
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
[Forum] => XF\Entity\Forum Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 50
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\Forum
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[node_id] => 2
[discussion_count] => 7533
[message_count] => 52728
[last_post_id] => 88494
[last_post_date] => 1752456912
[last_post_user_id] => 5
[last_post_username] => Daniel Nenni
[last_thread_id] => 23174
[last_thread_title] => Semiconductor Fundamentals Are All Weak
[last_thread_prefix_id] => 0
[moderate_threads] => 0
[moderate_replies] => 0
[allow_posting] => 1
[count_messages] => 1
[find_new] => 1
[allow_index] => allow
[index_criteria] =>
[field_cache] => []
[prefix_cache] => []
[prompt_cache] => []
[default_prefix_id] => 0
[default_sort_order] => last_post_date
[default_sort_direction] => desc
[list_date_limit_days] => 0
[require_prefix] => 0
[allowed_watch_notifications] => all
[min_tags] => 0
[forum_type_id] => discussion
[type_config] => {"allowed_thread_types":["poll"]}
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
[Node] => XF\Entity\Node Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 49
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\Node
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[node_id] => 2
[title] => SemiWiki Main Forum ( Ask the Experts! )
[description] => Post your questions to the experts here!
[node_name] =>
[node_type_id] => Forum
[parent_node_id] => 1
[display_order] => 1
[display_in_list] => 1
[lft] => 2
[rgt] => 3
[depth] => 1
[style_id] => 0
[effective_style_id] => 0
[breadcrumb_data] => {"1":{"node_id":1,"title":"Main Category","depth":0,"lft":1,"node_name":null,"node_type_id":"Category","display_in_list":true}}
[navigation_id] =>
[effective_navigation_id] =>
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
[23088] => ThemeHouse\XPress\XF\Entity\Thread Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 95
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\Thread
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[thread_id] => 23088
[node_id] => 2
[title] => Semiconductor foundry landscape to transform by 2030
[reply_count] => 6
[view_count] => 7861
[user_id] => 5
[username] => Daniel Nenni
[post_date] => 1750976263
[sticky] => 0
[discussion_state] => visible
[discussion_open] => 1
[discussion_type] => discussion
[first_post_id] => 87943
[first_post_reaction_score] => 3
[first_post_reactions] => {"1":3}
[last_post_date] => 1752387896
[last_post_id] => 88456
[last_post_user_id] => 398779
[last_post_username] => xu fei
[prefix_id] => 0
[tags] => []
[custom_fields] => []
[vote_score] => 0
[vote_count] => 0
[type_data] => []
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
[User] => ThemeHouse\XLink\XF\Entity\User Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 48
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\User
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[user_id] => 5
[username] => Daniel Nenni
[username_date] => 0
[username_date_visible] => 0
[email] => dnenni@semiwiki.com
[custom_title] => Admin
[language_id] => 1
[style_id] => 0
[timezone] => America/Los_Angeles
[visible] => 1
[activity_visible] => 1
[user_group_id] => 3
[secondary_group_ids] => 4,5,132
[display_style_group_id] => 3
[permission_combination_id] => 88
[message_count] => 13911
[question_solution_count] => 0
[conversations_unread] => 0
[register_date] => 1280720820
[last_activity] => 1752455253
[last_summary_email_date] => 1605968657
[trophy_points] => 113
[alerts_unviewed] => 34
[alerts_unread] => 34
[avatar_date] => 1663211649
[avatar_width] => 110
[avatar_height] => 107
[avatar_highdpi] => 0
[gravatar] =>
[user_state] => valid
[security_lock] =>
[is_moderator] => 1
[is_admin] => 1
[is_banned] => 0
[reaction_score] => 7006
[warning_points] => 0
[is_staff] => 1
[secret_key] => 0HwyUVVHCwJotUUVEpvqAclfYJdGNPpw
[privacy_policy_accepted] => 0
[terms_accepted] => 0
[vote_score] => 0
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
[Forum] => XF\Entity\Forum Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 50
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\Forum
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[node_id] => 2
[discussion_count] => 7533
[message_count] => 52728
[last_post_id] => 88494
[last_post_date] => 1752456912
[last_post_user_id] => 5
[last_post_username] => Daniel Nenni
[last_thread_id] => 23174
[last_thread_title] => Semiconductor Fundamentals Are All Weak
[last_thread_prefix_id] => 0
[moderate_threads] => 0
[moderate_replies] => 0
[allow_posting] => 1
[count_messages] => 1
[find_new] => 1
[allow_index] => allow
[index_criteria] =>
[field_cache] => []
[prefix_cache] => []
[prompt_cache] => []
[default_prefix_id] => 0
[default_sort_order] => last_post_date
[default_sort_direction] => desc
[list_date_limit_days] => 0
[require_prefix] => 0
[allowed_watch_notifications] => all
[min_tags] => 0
[forum_type_id] => discussion
[type_config] => {"allowed_thread_types":["poll"]}
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
[Node] => XF\Entity\Node Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 49
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\Node
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[node_id] => 2
[title] => SemiWiki Main Forum ( Ask the Experts! )
[description] => Post your questions to the experts here!
[node_name] =>
[node_type_id] => Forum
[parent_node_id] => 1
[display_order] => 1
[display_in_list] => 1
[lft] => 2
[rgt] => 3
[depth] => 1
[style_id] => 0
[effective_style_id] => 0
[breadcrumb_data] => {"1":{"node_id":1,"title":"Main Category","depth":0,"lft":1,"node_name":null,"node_type_id":"Category","display_in_list":true}}
[navigation_id] =>
[effective_navigation_id] =>
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
[23140] => ThemeHouse\XPress\XF\Entity\Thread Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 99
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\Thread
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[thread_id] => 23140
[node_id] => 2
[title] => Intel layoffs begin: Chipmaker is cutting many thousands of jobs
[reply_count] => 9
[view_count] => 2173
[user_id] => 14042
[username] => hist78
[post_date] => 1751923769
[sticky] => 0
[discussion_state] => visible
[discussion_open] => 1
[discussion_type] => discussion
[first_post_id] => 88295
[first_post_reaction_score] => 2
[first_post_reactions] => {"1":2}
[last_post_date] => 1752387280
[last_post_id] => 88453
[last_post_user_id] => 398779
[last_post_username] => xu fei
[prefix_id] => 0
[tags] => []
[custom_fields] => []
[vote_score] => 0
[vote_count] => 0
[type_data] => []
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
[User] => ThemeHouse\XLink\XF\Entity\User Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 60
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\User
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[user_id] => 14042
[username] => hist78
[username_date] => 0
[username_date_visible] => 0
[email] => ckckhcdc@gmail.com
[custom_title] =>
[language_id] => 1
[style_id] => 0
[timezone] => America/Los_Angeles
[visible] => 0
[activity_visible] => 0
[user_group_id] => 2
[secondary_group_ids] =>
[display_style_group_id] => 2
[permission_combination_id] => 8
[message_count] => 3606
[question_solution_count] => 0
[conversations_unread] => 0
[register_date] => 1389969050
[last_activity] => 1752410271
[last_summary_email_date] => 1605978520
[trophy_points] => 113
[alerts_unviewed] => 2
[alerts_unread] => 5
[avatar_date] => 1604959511
[avatar_width] => 807
[avatar_height] => 384
[avatar_highdpi] => 1
[gravatar] =>
[user_state] => valid
[security_lock] =>
[is_moderator] => 0
[is_admin] => 0
[is_banned] => 0
[reaction_score] => 3128
[warning_points] => 0
[is_staff] => 0
[secret_key] => 2YRSnPrl4fVQSdv3R6uqHxqi6BDQOXve
[privacy_policy_accepted] => 0
[terms_accepted] => 0
[vote_score] => 0
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
[Forum] => XF\Entity\Forum Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 50
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\Forum
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[node_id] => 2
[discussion_count] => 7533
[message_count] => 52728
[last_post_id] => 88494
[last_post_date] => 1752456912
[last_post_user_id] => 5
[last_post_username] => Daniel Nenni
[last_thread_id] => 23174
[last_thread_title] => Semiconductor Fundamentals Are All Weak
[last_thread_prefix_id] => 0
[moderate_threads] => 0
[moderate_replies] => 0
[allow_posting] => 1
[count_messages] => 1
[find_new] => 1
[allow_index] => allow
[index_criteria] =>
[field_cache] => []
[prefix_cache] => []
[prompt_cache] => []
[default_prefix_id] => 0
[default_sort_order] => last_post_date
[default_sort_direction] => desc
[list_date_limit_days] => 0
[require_prefix] => 0
[allowed_watch_notifications] => all
[min_tags] => 0
[forum_type_id] => discussion
[type_config] => {"allowed_thread_types":["poll"]}
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
[Node] => XF\Entity\Node Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 49
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\Node
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[node_id] => 2
[title] => SemiWiki Main Forum ( Ask the Experts! )
[description] => Post your questions to the experts here!
[node_name] =>
[node_type_id] => Forum
[parent_node_id] => 1
[display_order] => 1
[display_in_list] => 1
[lft] => 2
[rgt] => 3
[depth] => 1
[style_id] => 0
[effective_style_id] => 0
[breadcrumb_data] => {"1":{"node_id":1,"title":"Main Category","depth":0,"lft":1,"node_name":null,"node_type_id":"Category","display_in_list":true}}
[navigation_id] =>
[effective_navigation_id] =>
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
[23171] => ThemeHouse\XPress\XF\Entity\Thread Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 103
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\Thread
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[thread_id] => 23171
[node_id] => 2
[title] => Intel’s Gamble: Bringing in UMC to Tap into Taiwan’s Secret Sauce
[reply_count] => 1
[view_count] => 191
[user_id] => 398583
[username] => karin623
[post_date] => 1752382853
[sticky] => 0
[discussion_state] => visible
[discussion_open] => 1
[discussion_type] => discussion
[first_post_id] => 88449
[first_post_reaction_score] => 0
[first_post_reactions] => []
[last_post_date] => 1752385101
[last_post_id] => 88450
[last_post_user_id] => 331287
[last_post_username] => psantodomingo
[prefix_id] => 0
[tags] => []
[custom_fields] => []
[vote_score] => 0
[vote_count] => 0
[type_data] => []
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
[User] => ThemeHouse\XLink\XF\Entity\User Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 100
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\User
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[user_id] => 398583
[username] => karin623
[username_date] => 0
[username_date_visible] => 0
[email] => karin623@gmail.com
[custom_title] =>
[language_id] => 1
[style_id] => 0
[timezone] => Asia/Hong_Kong
[visible] => 1
[activity_visible] => 1
[user_group_id] => 2
[secondary_group_ids] =>
[display_style_group_id] => 2
[permission_combination_id] => 8
[message_count] => 7
[question_solution_count] => 0
[conversations_unread] => 0
[register_date] => 1748753435
[last_activity] => 1752382931
[last_summary_email_date] => 1748753435
[trophy_points] => 3
[alerts_unviewed] => 1
[alerts_unread] => 2
[avatar_date] => 0
[avatar_width] => 0
[avatar_height] => 0
[avatar_highdpi] => 0
[gravatar] =>
[user_state] => valid
[security_lock] =>
[is_moderator] => 0
[is_admin] => 0
[is_banned] => 0
[reaction_score] => 6
[warning_points] => 0
[is_staff] => 0
[secret_key] => PBnrLVmUtkEL7YUKL8Ij_6L3tfKYRzDQ
[privacy_policy_accepted] => 1748753435
[terms_accepted] => 1748753435
[vote_score] => 0
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
[Forum] => XF\Entity\Forum Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 50
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\Forum
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[node_id] => 2
[discussion_count] => 7533
[message_count] => 52728
[last_post_id] => 88494
[last_post_date] => 1752456912
[last_post_user_id] => 5
[last_post_username] => Daniel Nenni
[last_thread_id] => 23174
[last_thread_title] => Semiconductor Fundamentals Are All Weak
[last_thread_prefix_id] => 0
[moderate_threads] => 0
[moderate_replies] => 0
[allow_posting] => 1
[count_messages] => 1
[find_new] => 1
[allow_index] => allow
[index_criteria] =>
[field_cache] => []
[prefix_cache] => []
[prompt_cache] => []
[default_prefix_id] => 0
[default_sort_order] => last_post_date
[default_sort_direction] => desc
[list_date_limit_days] => 0
[require_prefix] => 0
[allowed_watch_notifications] => all
[min_tags] => 0
[forum_type_id] => discussion
[type_config] => {"allowed_thread_types":["poll"]}
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
[Node] => XF\Entity\Node Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 49
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\Node
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[node_id] => 2
[title] => SemiWiki Main Forum ( Ask the Experts! )
[description] => Post your questions to the experts here!
[node_name] =>
[node_type_id] => Forum
[parent_node_id] => 1
[display_order] => 1
[display_in_list] => 1
[lft] => 2
[rgt] => 3
[depth] => 1
[style_id] => 0
[effective_style_id] => 0
[breadcrumb_data] => {"1":{"node_id":1,"title":"Main Category","depth":0,"lft":1,"node_name":null,"node_type_id":"Category","display_in_list":true}}
[navigation_id] =>
[effective_navigation_id] =>
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
[23168] => ThemeHouse\XPress\XF\Entity\Thread Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 107
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\Thread
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[thread_id] => 23168
[node_id] => 2
[title] => TSMC Exits GaN Foundry Business — Is IDM the Winning Formula for Gallium Nitride?
[reply_count] => 5
[view_count] => 1310
[user_id] => 5
[username] => Daniel Nenni
[post_date] => 1752251830
[sticky] => 0
[discussion_state] => visible
[discussion_open] => 1
[discussion_type] => discussion
[first_post_id] => 88420
[first_post_reaction_score] => 2
[first_post_reactions] => {"1":2}
[last_post_date] => 1752371755
[last_post_id] => 88444
[last_post_user_id] => 36448
[last_post_username] => Paul2
[prefix_id] => 0
[tags] => []
[custom_fields] => []
[vote_score] => 0
[vote_count] => 0
[type_data] => []
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
[User] => ThemeHouse\XLink\XF\Entity\User Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 48
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\User
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[user_id] => 5
[username] => Daniel Nenni
[username_date] => 0
[username_date_visible] => 0
[email] => dnenni@semiwiki.com
[custom_title] => Admin
[language_id] => 1
[style_id] => 0
[timezone] => America/Los_Angeles
[visible] => 1
[activity_visible] => 1
[user_group_id] => 3
[secondary_group_ids] => 4,5,132
[display_style_group_id] => 3
[permission_combination_id] => 88
[message_count] => 13911
[question_solution_count] => 0
[conversations_unread] => 0
[register_date] => 1280720820
[last_activity] => 1752455253
[last_summary_email_date] => 1605968657
[trophy_points] => 113
[alerts_unviewed] => 34
[alerts_unread] => 34
[avatar_date] => 1663211649
[avatar_width] => 110
[avatar_height] => 107
[avatar_highdpi] => 0
[gravatar] =>
[user_state] => valid
[security_lock] =>
[is_moderator] => 1
[is_admin] => 1
[is_banned] => 0
[reaction_score] => 7006
[warning_points] => 0
[is_staff] => 1
[secret_key] => 0HwyUVVHCwJotUUVEpvqAclfYJdGNPpw
[privacy_policy_accepted] => 0
[terms_accepted] => 0
[vote_score] => 0
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
[Forum] => XF\Entity\Forum Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 50
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\Forum
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[node_id] => 2
[discussion_count] => 7533
[message_count] => 52728
[last_post_id] => 88494
[last_post_date] => 1752456912
[last_post_user_id] => 5
[last_post_username] => Daniel Nenni
[last_thread_id] => 23174
[last_thread_title] => Semiconductor Fundamentals Are All Weak
[last_thread_prefix_id] => 0
[moderate_threads] => 0
[moderate_replies] => 0
[allow_posting] => 1
[count_messages] => 1
[find_new] => 1
[allow_index] => allow
[index_criteria] =>
[field_cache] => []
[prefix_cache] => []
[prompt_cache] => []
[default_prefix_id] => 0
[default_sort_order] => last_post_date
[default_sort_direction] => desc
[list_date_limit_days] => 0
[require_prefix] => 0
[allowed_watch_notifications] => all
[min_tags] => 0
[forum_type_id] => discussion
[type_config] => {"allowed_thread_types":["poll"]}
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
[Node] => XF\Entity\Node Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 49
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\Node
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[node_id] => 2
[title] => SemiWiki Main Forum ( Ask the Experts! )
[description] => Post your questions to the experts here!
[node_name] =>
[node_type_id] => Forum
[parent_node_id] => 1
[display_order] => 1
[display_in_list] => 1
[lft] => 2
[rgt] => 3
[depth] => 1
[style_id] => 0
[effective_style_id] => 0
[breadcrumb_data] => {"1":{"node_id":1,"title":"Main Category","depth":0,"lft":1,"node_name":null,"node_type_id":"Category","display_in_list":true}}
[navigation_id] =>
[effective_navigation_id] =>
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
[23167] => ThemeHouse\XPress\XF\Entity\Thread Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 111
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\Thread
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[thread_id] => 23167
[node_id] => 2
[title] => RealSense spins out from Intel, secures $50 million to drive AI vision in robotics
[reply_count] => 0
[view_count] => 572
[user_id] => 5
[username] => Daniel Nenni
[post_date] => 1752246754
[sticky] => 0
[discussion_state] => visible
[discussion_open] => 1
[discussion_type] => discussion
[first_post_id] => 88419
[first_post_reaction_score] => 1
[first_post_reactions] => {"1":1}
[last_post_date] => 1752246754
[last_post_id] => 88419
[last_post_user_id] => 5
[last_post_username] => Daniel Nenni
[prefix_id] => 0
[tags] => []
[custom_fields] => []
[vote_score] => 0
[vote_count] => 0
[type_data] => []
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
[User] => ThemeHouse\XLink\XF\Entity\User Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 48
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\User
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[user_id] => 5
[username] => Daniel Nenni
[username_date] => 0
[username_date_visible] => 0
[email] => dnenni@semiwiki.com
[custom_title] => Admin
[language_id] => 1
[style_id] => 0
[timezone] => America/Los_Angeles
[visible] => 1
[activity_visible] => 1
[user_group_id] => 3
[secondary_group_ids] => 4,5,132
[display_style_group_id] => 3
[permission_combination_id] => 88
[message_count] => 13911
[question_solution_count] => 0
[conversations_unread] => 0
[register_date] => 1280720820
[last_activity] => 1752455253
[last_summary_email_date] => 1605968657
[trophy_points] => 113
[alerts_unviewed] => 34
[alerts_unread] => 34
[avatar_date] => 1663211649
[avatar_width] => 110
[avatar_height] => 107
[avatar_highdpi] => 0
[gravatar] =>
[user_state] => valid
[security_lock] =>
[is_moderator] => 1
[is_admin] => 1
[is_banned] => 0
[reaction_score] => 7006
[warning_points] => 0
[is_staff] => 1
[secret_key] => 0HwyUVVHCwJotUUVEpvqAclfYJdGNPpw
[privacy_policy_accepted] => 0
[terms_accepted] => 0
[vote_score] => 0
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
[Forum] => XF\Entity\Forum Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 50
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\Forum
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[node_id] => 2
[discussion_count] => 7533
[message_count] => 52728
[last_post_id] => 88494
[last_post_date] => 1752456912
[last_post_user_id] => 5
[last_post_username] => Daniel Nenni
[last_thread_id] => 23174
[last_thread_title] => Semiconductor Fundamentals Are All Weak
[last_thread_prefix_id] => 0
[moderate_threads] => 0
[moderate_replies] => 0
[allow_posting] => 1
[count_messages] => 1
[find_new] => 1
[allow_index] => allow
[index_criteria] =>
[field_cache] => []
[prefix_cache] => []
[prompt_cache] => []
[default_prefix_id] => 0
[default_sort_order] => last_post_date
[default_sort_direction] => desc
[list_date_limit_days] => 0
[require_prefix] => 0
[allowed_watch_notifications] => all
[min_tags] => 0
[forum_type_id] => discussion
[type_config] => {"allowed_thread_types":["poll"]}
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
[Node] => XF\Entity\Node Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 49
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\Node
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[node_id] => 2
[title] => SemiWiki Main Forum ( Ask the Experts! )
[description] => Post your questions to the experts here!
[node_name] =>
[node_type_id] => Forum
[parent_node_id] => 1
[display_order] => 1
[display_in_list] => 1
[lft] => 2
[rgt] => 3
[depth] => 1
[style_id] => 0
[effective_style_id] => 0
[breadcrumb_data] => {"1":{"node_id":1,"title":"Main Category","depth":0,"lft":1,"node_name":null,"node_type_id":"Category","display_in_list":true}}
[navigation_id] =>
[effective_navigation_id] =>
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
[23161] => ThemeHouse\XPress\XF\Entity\Thread Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 115
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\Thread
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[thread_id] => 23161
[node_id] => 2
[title] => IBM Power11 appears 50% denser on the same Samsung 7nm process?
[reply_count] => 8
[view_count] => 1301
[user_id] => 35301
[username] => Xebec
[post_date] => 1752098963
[sticky] => 0
[discussion_state] => visible
[discussion_open] => 1
[discussion_type] => discussion
[first_post_id] => 88373
[first_post_reaction_score] => 0
[first_post_reactions] => []
[last_post_date] => 1752216236
[last_post_id] => 88417
[last_post_user_id] => 323155
[last_post_username] => Maximus
[prefix_id] => 0
[tags] => []
[custom_fields] => []
[vote_score] => 0
[vote_count] => 0
[type_data] => []
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
[User] => ThemeHouse\XLink\XF\Entity\User Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 112
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\User
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[user_id] => 35301
[username] => Xebec
[username_date] => 0
[username_date_visible] => 0
[email] => john.heritage@gmail.com
[custom_title] =>
[language_id] => 1
[style_id] => 0
[timezone] => America/New_York
[visible] => 1
[activity_visible] => 1
[user_group_id] => 2
[secondary_group_ids] =>
[display_style_group_id] => 2
[permission_combination_id] => 8
[message_count] => 1077
[question_solution_count] => 0
[conversations_unread] => 0
[register_date] => 1598710106
[last_activity] => 1752423208
[last_summary_email_date] => 1631629203
[trophy_points] => 113
[alerts_unviewed] => 0
[alerts_unread] => 3
[avatar_date] => 0
[avatar_width] => 0
[avatar_height] => 0
[avatar_highdpi] => 0
[gravatar] =>
[user_state] => valid
[security_lock] =>
[is_moderator] => 0
[is_admin] => 0
[is_banned] => 0
[reaction_score] => 1159
[warning_points] => 0
[is_staff] => 0
[secret_key] => Y7XyJgQMBi7ZiDtuAyqNGDrBQQsi8JB4
[privacy_policy_accepted] => 1598710106
[terms_accepted] => 1598710106
[vote_score] => 0
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
[Forum] => XF\Entity\Forum Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 50
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\Forum
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[node_id] => 2
[discussion_count] => 7533
[message_count] => 52728
[last_post_id] => 88494
[last_post_date] => 1752456912
[last_post_user_id] => 5
[last_post_username] => Daniel Nenni
[last_thread_id] => 23174
[last_thread_title] => Semiconductor Fundamentals Are All Weak
[last_thread_prefix_id] => 0
[moderate_threads] => 0
[moderate_replies] => 0
[allow_posting] => 1
[count_messages] => 1
[find_new] => 1
[allow_index] => allow
[index_criteria] =>
[field_cache] => []
[prefix_cache] => []
[prompt_cache] => []
[default_prefix_id] => 0
[default_sort_order] => last_post_date
[default_sort_direction] => desc
[list_date_limit_days] => 0
[require_prefix] => 0
[allowed_watch_notifications] => all
[min_tags] => 0
[forum_type_id] => discussion
[type_config] => {"allowed_thread_types":["poll"]}
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
[Node] => XF\Entity\Node Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 49
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\Node
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[node_id] => 2
[title] => SemiWiki Main Forum ( Ask the Experts! )
[description] => Post your questions to the experts here!
[node_name] =>
[node_type_id] => Forum
[parent_node_id] => 1
[display_order] => 1
[display_in_list] => 1
[lft] => 2
[rgt] => 3
[depth] => 1
[style_id] => 0
[effective_style_id] => 0
[breadcrumb_data] => {"1":{"node_id":1,"title":"Main Category","depth":0,"lft":1,"node_name":null,"node_type_id":"Category","display_in_list":true}}
[navigation_id] =>
[effective_navigation_id] =>
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
[23164] => ThemeHouse\XPress\XF\Entity\Thread Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 119
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\Thread
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[thread_id] => 23164
[node_id] => 2
[title] => Humanoid robot startup Diligent taps Cruise executives as it looks beyond healthcare
[reply_count] => 0
[view_count] => 373
[user_id] => 5
[username] => Daniel Nenni
[post_date] => 1752160056
[sticky] => 0
[discussion_state] => visible
[discussion_open] => 1
[discussion_type] => discussion
[first_post_id] => 88390
[first_post_reaction_score] => 1
[first_post_reactions] => {"1":1}
[last_post_date] => 1752160056
[last_post_id] => 88390
[last_post_user_id] => 5
[last_post_username] => Daniel Nenni
[prefix_id] => 0
[tags] => []
[custom_fields] => []
[vote_score] => 0
[vote_count] => 0
[type_data] => []
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
[User] => ThemeHouse\XLink\XF\Entity\User Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 48
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\User
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[user_id] => 5
[username] => Daniel Nenni
[username_date] => 0
[username_date_visible] => 0
[email] => dnenni@semiwiki.com
[custom_title] => Admin
[language_id] => 1
[style_id] => 0
[timezone] => America/Los_Angeles
[visible] => 1
[activity_visible] => 1
[user_group_id] => 3
[secondary_group_ids] => 4,5,132
[display_style_group_id] => 3
[permission_combination_id] => 88
[message_count] => 13911
[question_solution_count] => 0
[conversations_unread] => 0
[register_date] => 1280720820
[last_activity] => 1752455253
[last_summary_email_date] => 1605968657
[trophy_points] => 113
[alerts_unviewed] => 34
[alerts_unread] => 34
[avatar_date] => 1663211649
[avatar_width] => 110
[avatar_height] => 107
[avatar_highdpi] => 0
[gravatar] =>
[user_state] => valid
[security_lock] =>
[is_moderator] => 1
[is_admin] => 1
[is_banned] => 0
[reaction_score] => 7006
[warning_points] => 0
[is_staff] => 1
[secret_key] => 0HwyUVVHCwJotUUVEpvqAclfYJdGNPpw
[privacy_policy_accepted] => 0
[terms_accepted] => 0
[vote_score] => 0
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
[Forum] => XF\Entity\Forum Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 50
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\Forum
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[node_id] => 2
[discussion_count] => 7533
[message_count] => 52728
[last_post_id] => 88494
[last_post_date] => 1752456912
[last_post_user_id] => 5
[last_post_username] => Daniel Nenni
[last_thread_id] => 23174
[last_thread_title] => Semiconductor Fundamentals Are All Weak
[last_thread_prefix_id] => 0
[moderate_threads] => 0
[moderate_replies] => 0
[allow_posting] => 1
[count_messages] => 1
[find_new] => 1
[allow_index] => allow
[index_criteria] =>
[field_cache] => []
[prefix_cache] => []
[prompt_cache] => []
[default_prefix_id] => 0
[default_sort_order] => last_post_date
[default_sort_direction] => desc
[list_date_limit_days] => 0
[require_prefix] => 0
[allowed_watch_notifications] => all
[min_tags] => 0
[forum_type_id] => discussion
[type_config] => {"allowed_thread_types":["poll"]}
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
[Node] => XF\Entity\Node Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 49
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\Node
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[node_id] => 2
[title] => SemiWiki Main Forum ( Ask the Experts! )
[description] => Post your questions to the experts here!
[node_name] =>
[node_type_id] => Forum
[parent_node_id] => 1
[display_order] => 1
[display_in_list] => 1
[lft] => 2
[rgt] => 3
[depth] => 1
[style_id] => 0
[effective_style_id] => 0
[breadcrumb_data] => {"1":{"node_id":1,"title":"Main Category","depth":0,"lft":1,"node_name":null,"node_type_id":"Category","display_in_list":true}}
[navigation_id] =>
[effective_navigation_id] =>
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
[23069] => ThemeHouse\XPress\XF\Entity\Thread Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 123
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\Thread
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[thread_id] => 23069
[node_id] => 2
[title] => Intel will outsource marketing to Accenture and AI, laying off many of its own workers
[reply_count] => 63
[view_count] => 9934
[user_id] => 332041
[username] => XYang2023
[post_date] => 1750456841
[sticky] => 0
[discussion_state] => visible
[discussion_open] => 1
[discussion_type] => discussion
[first_post_id] => 87785
[first_post_reaction_score] => 0
[first_post_reactions] => []
[last_post_date] => 1752155985
[last_post_id] => 88387
[last_post_user_id] => 90182
[last_post_username] => siliconbruh999
[prefix_id] => 0
[tags] => []
[custom_fields] => []
[vote_score] => 0
[vote_count] => 0
[type_data] => []
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
[User] => ThemeHouse\XLink\XF\Entity\User Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 120
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\User
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[user_id] => 332041
[username] => XYang2023
[username_date] => 0
[username_date_visible] => 0
[email] => xiao.yang17@gmail.com
[custom_title] =>
[language_id] => 1
[style_id] => 0
[timezone] => Australia/Sydney
[visible] => 1
[activity_visible] => 1
[user_group_id] => 2
[secondary_group_ids] =>
[display_style_group_id] => 2
[permission_combination_id] => 8
[message_count] => 1196
[question_solution_count] => 0
[conversations_unread] => 0
[register_date] => 1708819075
[last_activity] => 1752411100
[last_summary_email_date] => 1723213219
[trophy_points] => 113
[alerts_unviewed] => 4
[alerts_unread] => 5
[avatar_date] => 0
[avatar_width] => 0
[avatar_height] => 0
[avatar_highdpi] => 0
[gravatar] =>
[user_state] => valid
[security_lock] =>
[is_moderator] => 0
[is_admin] => 0
[is_banned] => 0
[reaction_score] => 722
[warning_points] => 0
[is_staff] => 0
[secret_key] => NBs1n4BMtljiqSmfC-EZI_MMUn9Rzevl
[privacy_policy_accepted] => 1708819075
[terms_accepted] => 1708819075
[vote_score] => 0
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
[Forum] => XF\Entity\Forum Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 50
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\Forum
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[node_id] => 2
[discussion_count] => 7533
[message_count] => 52728
[last_post_id] => 88494
[last_post_date] => 1752456912
[last_post_user_id] => 5
[last_post_username] => Daniel Nenni
[last_thread_id] => 23174
[last_thread_title] => Semiconductor Fundamentals Are All Weak
[last_thread_prefix_id] => 0
[moderate_threads] => 0
[moderate_replies] => 0
[allow_posting] => 1
[count_messages] => 1
[find_new] => 1
[allow_index] => allow
[index_criteria] =>
[field_cache] => []
[prefix_cache] => []
[prompt_cache] => []
[default_prefix_id] => 0
[default_sort_order] => last_post_date
[default_sort_direction] => desc
[list_date_limit_days] => 0
[require_prefix] => 0
[allowed_watch_notifications] => all
[min_tags] => 0
[forum_type_id] => discussion
[type_config] => {"allowed_thread_types":["poll"]}
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
[Node] => XF\Entity\Node Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 49
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\Node
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[node_id] => 2
[title] => SemiWiki Main Forum ( Ask the Experts! )
[description] => Post your questions to the experts here!
[node_name] =>
[node_type_id] => Forum
[parent_node_id] => 1
[display_order] => 1
[display_in_list] => 1
[lft] => 2
[rgt] => 3
[depth] => 1
[style_id] => 0
[effective_style_id] => 0
[breadcrumb_data] => {"1":{"node_id":1,"title":"Main Category","depth":0,"lft":1,"node_name":null,"node_type_id":"Category","display_in_list":true}}
[navigation_id] =>
[effective_navigation_id] =>
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
[23163] => ThemeHouse\XPress\XF\Entity\Thread Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 127
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\Thread
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[thread_id] => 23163
[node_id] => 2
[title] => TSMC June 2025 Revenue Report @ 40%
[reply_count] => 0
[view_count] => 725
[user_id] => 5
[username] => Daniel Nenni
[post_date] => 1752126889
[sticky] => 0
[discussion_state] => visible
[discussion_open] => 1
[discussion_type] => discussion
[first_post_id] => 88381
[first_post_reaction_score] => 2
[first_post_reactions] => {"1":2}
[last_post_date] => 1752126889
[last_post_id] => 88381
[last_post_user_id] => 5
[last_post_username] => Daniel Nenni
[prefix_id] => 0
[tags] => []
[custom_fields] => []
[vote_score] => 0
[vote_count] => 0
[type_data] => []
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
[User] => ThemeHouse\XLink\XF\Entity\User Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 48
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\User
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[user_id] => 5
[username] => Daniel Nenni
[username_date] => 0
[username_date_visible] => 0
[email] => dnenni@semiwiki.com
[custom_title] => Admin
[language_id] => 1
[style_id] => 0
[timezone] => America/Los_Angeles
[visible] => 1
[activity_visible] => 1
[user_group_id] => 3
[secondary_group_ids] => 4,5,132
[display_style_group_id] => 3
[permission_combination_id] => 88
[message_count] => 13911
[question_solution_count] => 0
[conversations_unread] => 0
[register_date] => 1280720820
[last_activity] => 1752455253
[last_summary_email_date] => 1605968657
[trophy_points] => 113
[alerts_unviewed] => 34
[alerts_unread] => 34
[avatar_date] => 1663211649
[avatar_width] => 110
[avatar_height] => 107
[avatar_highdpi] => 0
[gravatar] =>
[user_state] => valid
[security_lock] =>
[is_moderator] => 1
[is_admin] => 1
[is_banned] => 0
[reaction_score] => 7006
[warning_points] => 0
[is_staff] => 1
[secret_key] => 0HwyUVVHCwJotUUVEpvqAclfYJdGNPpw
[privacy_policy_accepted] => 0
[terms_accepted] => 0
[vote_score] => 0
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
[Forum] => XF\Entity\Forum Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 50
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\Forum
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[node_id] => 2
[discussion_count] => 7533
[message_count] => 52728
[last_post_id] => 88494
[last_post_date] => 1752456912
[last_post_user_id] => 5
[last_post_username] => Daniel Nenni
[last_thread_id] => 23174
[last_thread_title] => Semiconductor Fundamentals Are All Weak
[last_thread_prefix_id] => 0
[moderate_threads] => 0
[moderate_replies] => 0
[allow_posting] => 1
[count_messages] => 1
[find_new] => 1
[allow_index] => allow
[index_criteria] =>
[field_cache] => []
[prefix_cache] => []
[prompt_cache] => []
[default_prefix_id] => 0
[default_sort_order] => last_post_date
[default_sort_direction] => desc
[list_date_limit_days] => 0
[require_prefix] => 0
[allowed_watch_notifications] => all
[min_tags] => 0
[forum_type_id] => discussion
[type_config] => {"allowed_thread_types":["poll"]}
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
[Node] => XF\Entity\Node Object
(
[_uniqueEntityId:XF\Mvc\Entity\Entity:private] => 49
[rootClass:protected] => XF\Entity\Node
[_useReplaceInto:protected] =>
[_newValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_values:protected] => Array
(
[node_id] => 2
[title] => SemiWiki Main Forum ( Ask the Experts! )
[description] => Post your questions to the experts here!
[node_name] =>
[node_type_id] => Forum
[parent_node_id] => 1
[display_order] => 1
[display_in_list] => 1
[lft] => 2
[rgt] => 3
[depth] => 1
[style_id] => 0
[effective_style_id] => 0
[breadcrumb_data] => {"1":{"node_id":1,"title":"Main Category","depth":0,"lft":1,"node_name":null,"node_type_id":"Category","display_in_list":true}}
[navigation_id] =>
[effective_navigation_id] =>
)
[_relations:protected] => Array
(
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
)
[_previousValues:protected] => Array
(
)
[_options:protected] => Array
(
)
[_deleted:protected] =>
[_readOnly:protected] =>
[_writePending:protected] =>
[_writeRunning:protected] =>
[_errors:protected] => Array
(
)
[_whenSaveable:protected] => Array
(
)
[_cascadeSave:protected] => Array
(
)
[_behaviors:protected] =>
)
)
[populated:protected] => 1
)
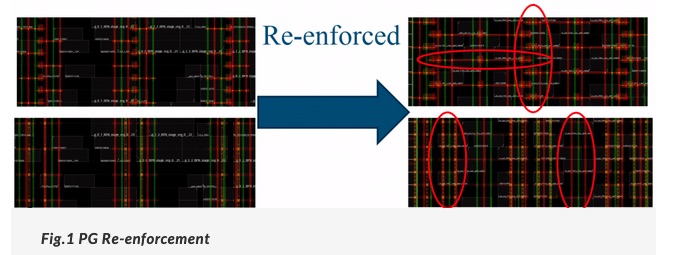






Comments
There are no comments yet.
You must register or log in to view/post comments.