Key Takeaways
- AI-powered innovation is reshaping data center infrastructure, leading to the concept of AI Factories.
- Designing and operating AI Factories requires multidisciplinary coordination and a new approach to infrastructure management.
- NVIDIA's AI Factory Digital Twin, powered by the Omniverse platform, integrates various data types for optimized design and operation.
- Cadence’s advanced simulation technology is a core enabler of NVIDIA’s digital twin strategy.
- The integration of simulation, open standards, and ecosystem collaboration is crucial for developing resilient and responsive next-generation data centers.
At NVIDIA’s recent GTC conference, a Cadence-NVIDIA joint session provided insights into how AI-powered innovation is reshaping the future of data center infrastructure. Led by Kourosh Nemati, Senior Data Center Cooling and Infrastructure Engineer from NVIDIA and Sherman Ikemoto, Sales Development Group Director from Cadence, the session dove into the critical challenges of building AI Factories, which are next-generation data centers optimized for accelerated computing. The talks showcased how digital twins and industrial simulation are transforming the design, deployment, and operation of these complex systems.
The Rise of the AI Factory
Kourosh opened the session by spotlighting how the data centers of the future aren’t just about racks and power but rather to be treated as AI Factories. These next-generation data centers are highly dynamic, compute-dense environments built to run massive AI workloads, support real-time inference, and train foundational models that power everything from drug discovery to autonomous systems. But with this transformation comes a new set of challenges. Designing, building, and operating an AI Factory requires multidisciplinary coordination between power, cooling, networking, and compute — with significantly tighter tolerances and higher performance demands than traditional data centers.
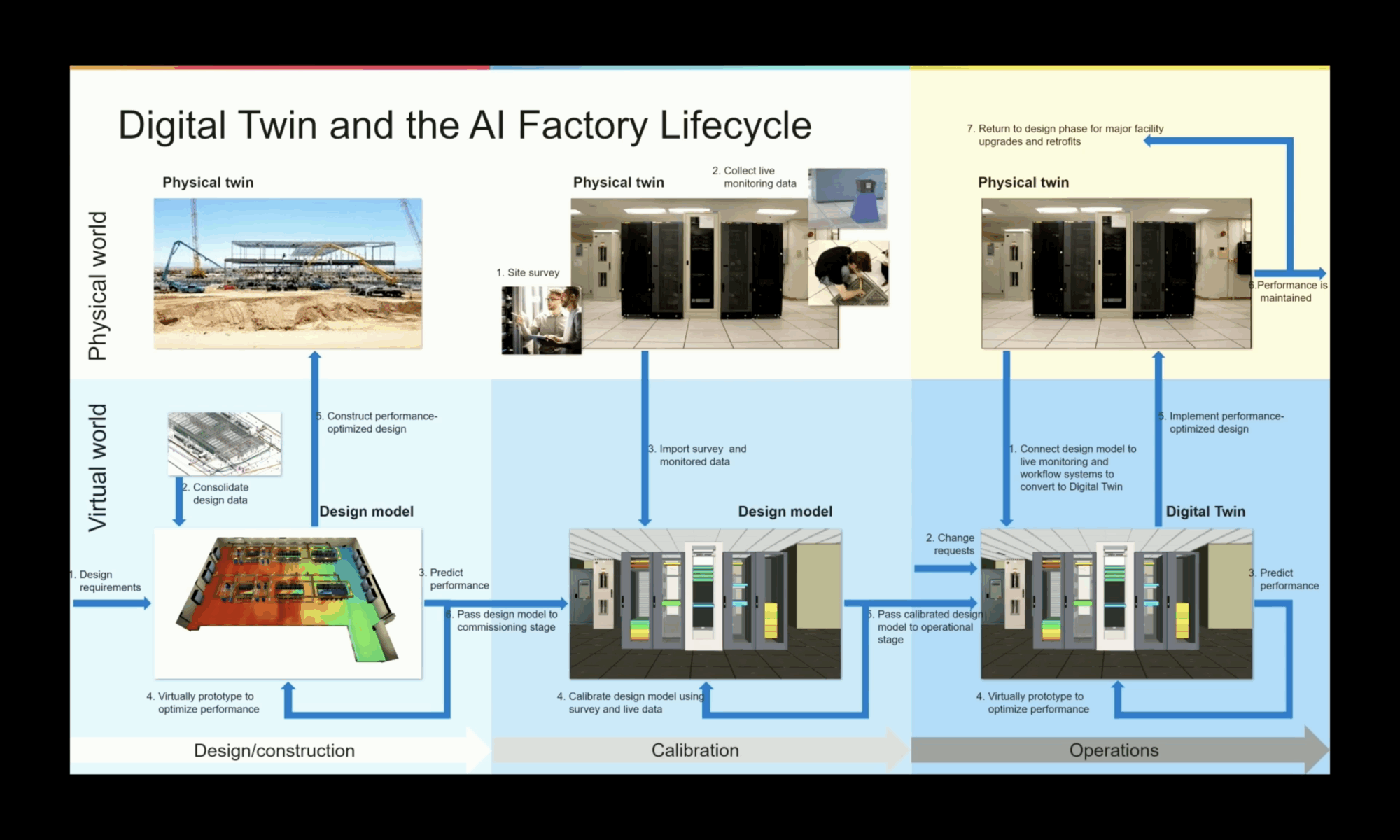
This level of complexity requires a new approach to designing, building and operating. An AI Factory Digital Twin is needed to simulate and manage everything from physical infrastructure to real-time operations.
Simulation: A New Era in Data Center Design
The centerpiece of this vision is NVIDIA’s AI Factory Digital Twin, built on the Omniverse platform and powered by the OpenUSD (Universal Scene Description) framework. It’s more than just a virtual replica, a continuously updating simulation engine that integrates mechanical, electrical, and thermal data into a single, unified environment. AI factories demand extreme levels of optimization to manage power density, thermal load, and operational efficiency. By using simulation in the design phase, engineers can evaluate “what-if” scenarios, test control logic, and spot failure points long before equipment is installed.
This approach helps accelerate deployment timelines and reduce operational risk.
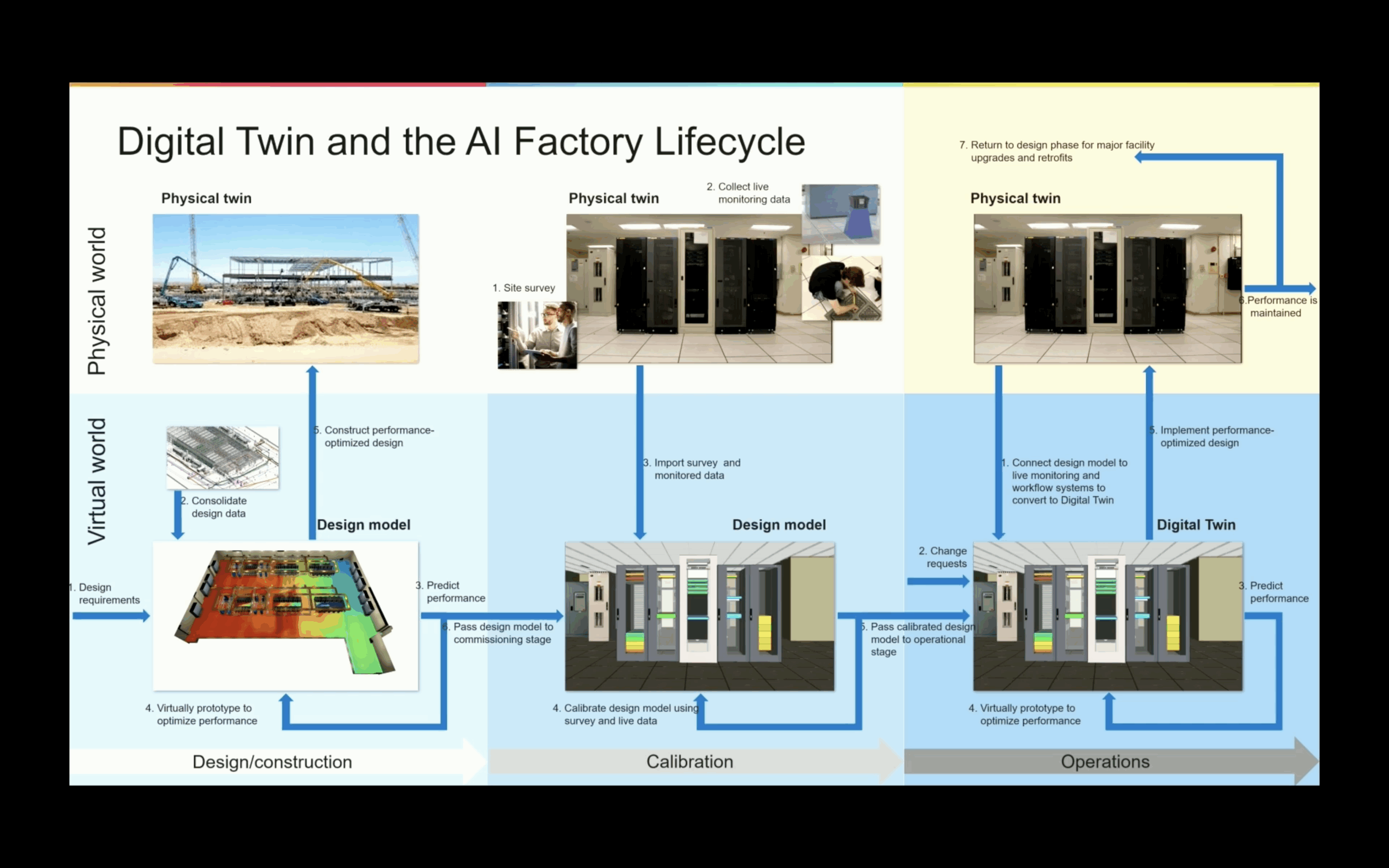
Cadence: Technology Behind the Digital Twin
Following Kourosh’s talk, Sherman detailed how multiphysics simulation powers the AI Factory Digital Twin. He described the need to move beyond siloed workflows and bring together disciplines such as electrical, thermal and structural, that often may have operated independently in the past, into a coordinated, data-driven design process. With traditional design tools, each team optimizes their own domain but when put together, they might not work efficiently as a system. This is why digital twins become mission critical.
Cadence’s advanced simulation technology is a core enabler of NVIDIA’s digital twin strategy. From detailed power integrity models to dynamic thermal simulations, these tools provide the physical accuracy needed to make decisions early, fast, and confidently.
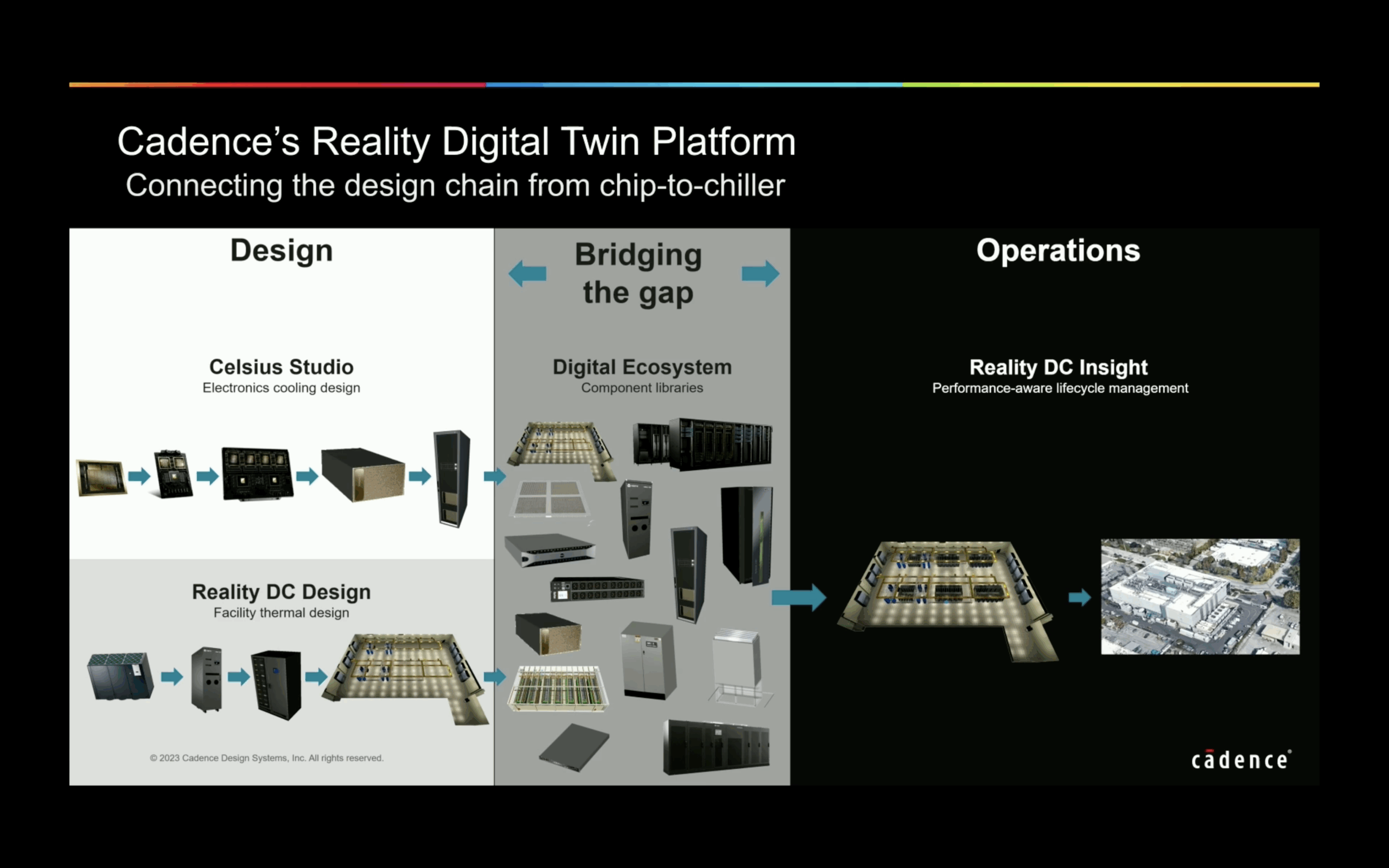
Sherman also emphasized Cadence’s commitment to interoperability. As a founding member of the OpenUSD-based digital twin standards group, Cadence is helping define how simulation data integrates with 3D models, real-time telemetry, and operational software.
Ecosystem Collaboration
Another major theme of the joint session was the importance of collaboration across the broader data center ecosystem. AI factories are not just a design challenge but a supply chain and operational challenge as well.
To this end, partners like Foxconn and Vertiv are playing a critical role. Foxconn, with its global manufacturing capabilities, is helping accelerate the production of modular AI factory components. Vertiv, a leader in power and cooling infrastructure, is working closely with NVIDIA and Cadence to simulate real-world behavior of critical equipment within the twin, ensuring that systems behave predictably under peak AI loads.

By simulating components like Coolant Distribution Units (CDUs), Power Distribution Units (PDUs), and Heating, Ventilation and Air Conditioning (HVAC) systems as part of the broader twin, these partners enable end-to-end validation of system behavior. This is a huge step forward in building next generation data centers that are both resilient and responsive to changing demands.
Summary
AI factories are complex, multidisciplinary systems that require new tools, new thinking, and deep collaboration. By integrating simulation, open standards, and a robust partner ecosystem, Cadence is collaborating with NVIDIA and the broader ecosystem to lay the foundation for a new era of AI infrastructure. Their tools not only reduce costs and risk, but also accelerate the delivery of AI-powered innovation across industries from healthcare and manufacturing to energy, finance, and scientific research.
Also Read:
How Cadence is Building the Physical Infrastructure of the AI Era
Big Picture PSS and Perspec Deployment
Metamorphic Test in AMS. Innovation in Verification
Share this post via:





Comments
There are no comments yet.
You must register or log in to view/post comments.