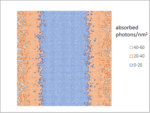
Whether EUV or DUV doesn’t matter at 20 nm pitch
The International Roadmap for Devices and Systems, 2022 Edition, indicates that the “2nm” node due in 2025 (this year) has a minimum (metal) half-pitch of 10 nm [1]. This is, in fact, less than the resolution of a current state-of-the-art EUV system, with a numerical aperture… Read More
Tag: sadp
Application-Specific Lithography: Patterning 5nm 5.5-Track Metal by DUV
At IEDM 2019, TSMC revealed two versions of 5nm standard cell layouts: a 5.5-track DUV-patterned version and a 6-track EUV-patterned version [1]. Although the metal pitches were not explicitly stated, later analyses of a 5nm product, namely, Apple’s A15 Bionic chip, revealed a cell height of 210 nm [2]. For the 6-track … Read More
BEOL Mask Reduction Using Spacer-Defined Vias and Cuts
In recent advanced nodes, via and cut patterning have constituted a larger and larger portion of the overall BEOL mask count. The advent of SALELE [1,2] caused mask count to increase for EUV as well, resulting in costs no longer being competitive with DUV down to 3nm [3]. Further development by TEL [4] has shown the possibility for… Read More
Extension of DUV Multipatterning Toward 3nm
China’s recent achievement of a 7nm-class foundry node using only DUV lithography [1] raises the question of how far DUV lithography can be extended by multipatterning. A recent publication at CSTIC 2023 indicates that Chinese groups are currently looking at extension of DUV-based multipatterning to 5nm, going so far… Read More
Etch Pitch Doubling Requirement for Cut-Friendly Track Metal Layouts: Escaping Lithography Wavelength Dependence
The 5nm foundry node saw the arrival of 6-track standard cells with four narrow routing tracks between wide power/ground rails (Figure 1a), with minimum pitches of around 30 nm [1]. The routing tracks require cuts [2] with widths comparable to the minimum half-pitch, to enable the via connections to the next metal layer with the… Read More
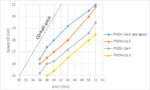
CD-Pitch Combinations Disfavored by EUV Stochastics
Ongoing investigations of EUV stochastics [1-3] have allowed us to map combinations of critical dimension (CD) and pitch which are expected to pose a severe risk of stochastic defects impacting the use of EUV lithography. Figure 1 shows a typical set of contours of fixed PNOK (i.e., the probability of a feature being Not OK due… Read More
Toshiba Cost Model for 3D NAND
Toshiba (now known as Kioxia) was the first company to propose a 3D stacked version of NAND Flash memory called BICS [1]. BICS (BIt Cost Scalable) Flash used explicit process cost reduction based on depositing and etching multiple layers at once, avoiding multiple lithography steps. This strategy replaced the usual approach… Read More
Application-Specific Lithography: 20nm Flash, 3D XPoint, 3D NAND Bit Lines
Nonvolatile memory capacity reached 64 Gb levels when NAND Flash half-pitch reached 20 nm [1]. Having reached 14 nm [2], NAND Flash half-pitch is no longer being reduced, now that it has entered the 3D era. However, recently, 3D XPoint has found applications within the Optane platform [3]. The lithography for patterning 20 nm half-pitch… Read More
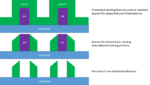
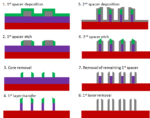
Feature-Selective Etching in SAQP for Sub-20 nm Patterning
Self-aligned quadruple patterning (SAQP) is the most widely available technology used for patterning feature pitches less than 38 nm, with a projected capability to reach 19 nm pitch. It is actually an integration of multiple process steps, already being used to pattern the fins of FinFETs [1] and 1X DRAM [2]. These steps, shown… Read More
Lithography Resolution Limits: Line End Gaps
In a previous article [1], the Rayleigh criterion was mentioned as the resolution limit for the distance between two features. On the other hand, in a following article [2], the minimum pitch was mentioned for the resolution limit for arrayed features. In this article, we reconcile the two by considering gaps between arrayed features,… Read More