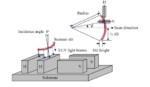
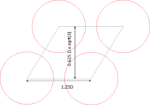
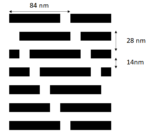
Stochastic defects continue to draw attention in the area of EUV lithography. It is now widely recognized that stochastic issues not only come from photon shot noise due to low (absorbed) EUV photon density, but also the resist material and process factors [1-4].
It stands to reason that resist absorption of EUV light, which is … Read More