SoC designers often have to make a, “red pill or blue pill,” decision when it comes to selecting process technology. Usually, a choice has to be made between performance, power and area, with one being prioritized at the expense of the others. However, as is pointed out in a recent paper by Mixel and NXP, designers can have the best of both worlds – the red pill and the blue pill – if they consider using a fully depleted silicon on insulator (FD-SOI) process. This is especially true because FD-SOI comes with an extensive ecosystem in the form of tool support and IP availability.
FD-SOI has been a niche technology compared to bulk CMOS, but with new demands from applications like IoT for low standby power and analog & digital performance, it may be ripe for a renaissance. In the paper titled “It’s Time to Look at FD-SOI (Again)” by Eric Hong, senior director of engineering at Mixel, and Nik Jedrzejewski, product line manager at NXP Semiconductors, they make the point that FD-SOI offers unique features that make it an excellent choice for IoT.
Mixel and NXP have worked together to provide designers a superior alternative to bulk CMOS processes. The paper highlights the NXP i.MX 7ULP platform for 28 FD-SOI which leveraged Mixel’s MIPI D-PHY IP.
Let’s look at what the authors have to say about the performance characteristics of FD-SOI devices. FD-SOI places an oxide insulation layer the under the entire transistor, which uses a thin channel with raised source and drain material. This construction provides for many interesting properties that can be exploited to improve chip design. This configuration reduces parasitics and short channel effects.
In bulk CMOS there is parasitic capacitance between the source, drain and the substrate. Also, in bulk CMOS two effects, gate-induced drain leakage (GIDL) and drain-induced barrier lowering (DIBL) play havoc with threshold voltage and high drain voltage turn-off, respectively. With FD-SOI, on the other hand, the buried oxide (BOX) layer shields the source & drain and allows for a thinner channel, improving the gate’s ability to turn off. The reduction of gate and parasitic capacitances mean that peak and dynamic power are reduced, and transconductance and ft are improved.
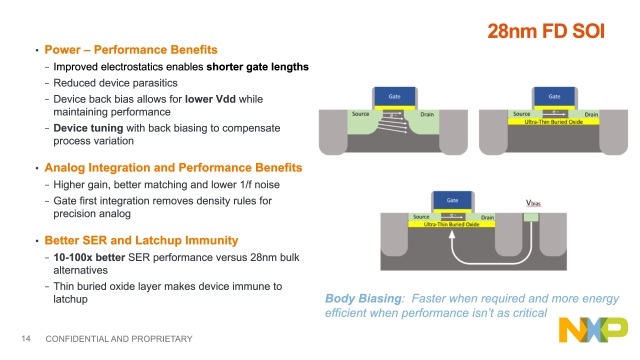
Perhaps the most interesting property of FD-SOI is that body-biasing of the substrate under the junction can easily be applied. This body biasing can even be modified dynamically depending on the operating characteristics needed at the time. To improve the already impressively low stand-by leakage, reverse body-biasing (RBB) can be applied. The authors report that leakage can be reduced by up to a factor of 50X with this technique.
By applying forward body-biasing (FBB), the threshold voltage can be lowered, allowing for improved performance and higher gate overdrive (Vdd-Vt). The authors mention cases where there has been more than a 60% performance improvement with a 1V supply. Mixel observed a power savings of 50% on a design at the fast corner (FF). The same design saw a 14% power reduction at the typical corner (TT). This was accomplished with a W/L reduction of 55% for the on-chip devices. Body biasing can also be used to compensate for die-to-die variations to improve yield.
The paper also includes details about how FD-SOI improves many of the performance characteristics of transistors when they are used in analog design. This alone makes reading the entire article worthwhile. FD-SOI offers not one, but many advantages for designs seeking to improve power, performance, area and yield.
NXP, working with Mixel, have assembled a very compelling platform for SOC design based on FD-SOI. The paper also includes a diagram showing the combined IP and blocks available for building application processors. There is a complete and well-established ecosystem ready to go for designers facing challenges with using bulk CMOS processes for their products. To get the full picture, read the paper here for more information.
Also Read:
New Processor Helps Move Inference to the Edge
Mixel Makes Major Move on MIPI D-PHY v2.5
MIPI gaining traction in vehicle ADAS and ADS
Share this post via:





Comments
One Reply to “FD-SOI Offers Refreshing Performance and Flexibility for Mobile Applications”
You must register or log in to view/post comments.