Lately I was studying about new innovations in memory world such as ReRAM and Memristor. As DRAM (although it has become a commodity) has found its extensive use in mobile, PC, tablet and so on, that was an inclination too to know more about. While reviewing Cadence’s offering in memory subsystems, I came across this whitepaperwhich… Read More
Tag: dram
Qualcomm JEDEC Mobile Keynote: Memory Bandwidth and Thermal Limits
I went to some of the JEDEC mobile conference a couple of weeks ago. The opening keynote was by Richard Wietfeld of Qualcomm called The Need for Speed.
He emphasized that smartphones are really setting the pace these days in all things mobile and internet. Over 1/3 of access is on smartphones now. Over 4/5 of searches on smartphones… Read More
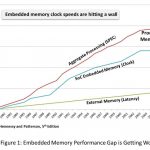
Current Embedded Memory Solutions Are Inadequate for 100G Ethernet
With an estimated 7 billion connected devices, the demand for rich content, including video, games, and mobile apps is skyrocketing. Service providers around the globe are scrambling to transform their networks to satisfy the overwhelming demand for content bandwidth. Over the next few years, they will be looking to network… Read More
The Business Case for Algorithmic Memories
Economic considerations are a primary driver in determining which technology solutions will be selected, and how they will be implemented in a company’s design environment. In the process of developing Memoir’s Algorithmic Memory technology and our Renaissance product line, we have held fast to two basic premises: Our technology… Read More
Mind the Gap — Overcoming the processor-memory performance gap to unlock SoC performance
Remember the processor-memory gap— a situation where the processor is forced to stall while waiting for a memory operation to complete? This was largely a result of the high latency required for off chip memory accesses. Haven’t we solved that problem now with SoCs? SoCs are typically architected with their processors … Read More
Keeping Moore’s Law Alive
At the GSA silicon summit yesterday the first keynote was by Subramanian Iyer of IBM on Keeping Moore’s Law Alive. He started off by asking the question “Is Moore’s Law in trouble?” and answered with an equivocal “maybe.”
Like some of the other speakers during the day, he pointed out that … Read More
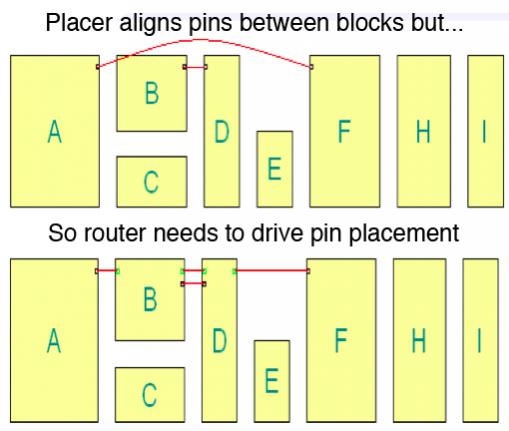
Channel Routing Memories
Back in the early days of ASIC when we had just two and then (wow!) three layers of metal, place and route was done by putting the standard cells in rows with gaps between them and then using a specialized router to do the interconnection. It would use one layer of metal horizontally and one vertically and avoid jogs. This was called a … Read More
Micron Races to Its Future
Perhaps no semiconductor company took it on the chin harder the last half of 2011 than Micron. And yet, perhaps no company was racing as hard as Micron to make a radical changeover. Micron is considered a bell weather on the overall health of the semiconductor industry given that DRAM, NAND and NOR Flash are used in some combination… Read More
Intel’s Back to the Future Buy of Micron
In an interview that Gordon Moore gave in early 2000, the former co-founder of Intel recounted how they abandoned the DRAM market in the early 1980s in order to exit the increasingly unprofitable business and focus on the promising, yet still young x86 processor market. Intel was also home to EEPROM and NOR Flash, two memory technologies… Read More
DRC+, DFM, CMP, Variablility
When I worked at Intel as a circuit design engineer I could talk directly with the technology development engineers to understand how to really push my DRAM designs and get the smallest possible memory cell layout that would still yield well, provide fast access time, and long refresh cycles.
(United States Patent 6661699. Inventor:… Read More