In the recent DRAM jargon, “1X”, “1Y”, “1Z”, etc. have been used to express all the sub-20 nm process generations. It is almost possible now to match them to real numbers which are roughly the half-pitch of the DRAM active area, such as 1X=18, 1Y ~ 17, etc. At this rate, 14 nm is somewhere around
ASML More Covid Concerns and Impact
- Covid related Revenue Rec causes rev/EPS miss
- Sharp order drop reflects H2 industry uncertainty
- EUV remains solid- Memory/Logic mix is better
Results were in line after correcting Covid Caused Revenue Rec issue-
ASML reported revenues of Euro3.3B and EPS of Euro1.79 as revenues from two EUV systems was not recognized, due to … Read More
Application-Specific Lithography: The 5nm 6-Track Cell
An update is now available here: Application-Specific Lithography: Patterning 5nm 5.5-Track Metal by DUV
The 5nm foundry (e.g., TSMC) node may see the introduction of 6-track cells (two double-width rails plus four minimum-width dense lines) with a minimum metal pitch in the neighborhood of 30 nm. IMEC had studied a representative… Read More
The Stochastic Impact of Defocus in EUV Lithography
The stochastic nature of imaging has received a great deal of attention in the area of EUV lithography. The density of EUV photons reaching the wafer is low enough [1] that the natural variation in the number of photons arriving at a given location can give rise to a relatively large standard deviation.
In recent studies [2,3], it … Read More
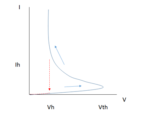
Can Threshold Switches Replace Transistors in the Memory Cell?
The overwhelming majority of transistors produced in the world are used in memory cells, either as the memory itself (Flash, SRAM), or as the access device (DRAM). Yet, it is not necessary to have a transistor in every memory cell. In 2015, 3D XPoint, the first major product based on transistor-less memory cells, was announced [1].
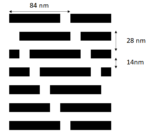
Feature-Selective Etching in SAQP for Sub-20 nm Patterning
Self-aligned quadruple patterning (SAQP) is the most widely available technology used for patterning feature pitches less than 38 nm, with a projected capability to reach 19 nm pitch. It is actually an integration of multiple process steps, already being used to pattern the fins of FinFETs [1] and 1X DRAM [2]. These steps, shown… Read More
Contact Resistance: The Silent Device Scaling Barrier
Moore’s Law has been about device density, specifically transistor density, increasing every certain number of years. Although cost is the most easily grasped advantage, there are two other benefits: higher performance (speed) and reduced power. When these benefits are compromised, they can also pose a scaling limitation.
The Uncertain Phase Shifts of EUV Masks
EUV (Extreme UltraViolet) lithography has received attention within the semiconductor industry since its development inception in 1997 with the formation of the EUV LLC [1], and more recently, since the 7nm node began, with limited use by Samsung and TSMC being touted as key advantages [2, 3]. As with any key critical technology,
MOSFET Gate Length Scaling Limit at Reduced Threshold Voltages
As transistor dimensions shrink to follow Moore’s Law, the functionality of the gate used to switch on or off the current is actually being degraded by the short channel effect (SCE) [1-5]. Moreover, the simultaneous reduction of voltage aggravates the degradation, as will be discussed below.
A Practical Lower Limit of… Read More
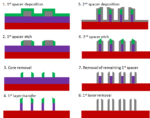
Reliable Line Cutting for Spacer-based Patterning
Spacer-defined patterning is an expected requirement for advanced semiconductor patterning nodes with feature sizes of 25 nm or less. As the required gaps between features go well below the lithography tool’s resolution limit, the use of cut exposures to separate features is used more often, especially in chips produced… Read More





CEO Interview with Aftkhar Aslam of yieldWerx