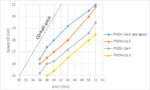
I recently posted an insightful article [1] published in 2013 on the cost of 3D NAND Flash by Dr. Andrew Walker, which has since received over 10,000 views on LinkedIn. The highlight was the plot of cost vs. the number of layers showing a minimum cost for some layer number, dependent on the etch sidewall angle. In this article, the same… Read More
Author: Fred Chen
Calculating the Maximum Density and Equivalent 2D Design Rule of 3D NAND Flash
The Complexities of the Resolution Limits of Advanced Lithography
For advanced lithography used to shrink semiconductor device features according to Moore’s Law, resolution limits are an obvious consideration. It is often perceived that the resolution limit is simply derived from a well-defined equation, but nothing can be further from the truth.
Optical Lithography: the fine print
… Read MoreHow Line Cuts Became Necessarily Separate Steps in Lithography
Pretty much all the semiconductor nodes in the last two decades have had at least one layer where the minimum pitch pushes the limitation of the state-of-the-art lithography tool, with a k1 factor < 0.5, i.e., the half-pitch is less than 0.5*wavelength/numerical aperture. A number of published reports [1-4] have touched upon… Read More
CD-Pitch Combinations Disfavored by EUV Stochastics
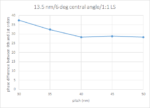
Ongoing investigations of EUV stochastics [1-3] have allowed us to map combinations of critical dimension (CD) and pitch which are expected to pose a severe risk of stochastic defects impacting the use of EUV lithography. Figure 1 shows a typical set of contours of fixed PNOK (i.e., the probability of a feature being Not OK due… Read More
Impact of Defocus and Illumination on Imaging of Pitch
In an earlier article [1], the resolution limit for the space between paired features was described by the Rayleigh criterion of ~0.6 wavelength/numerical aperture, where the numerical aperture (NA) represented the sine of the largest angle for a ray focused from the lens to a point. It is also given by the radius of the lens divided… Read More
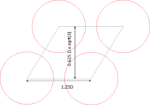
Toshiba Cost Model for 3D NAND
Toshiba (now known as Kioxia) was the first company to propose a 3D stacked version of NAND Flash memory called BICS [1]. BICS (BIt Cost Scalable) Flash used explicit process cost reduction based on depositing and etching multiple layers at once, avoiding multiple lithography steps. This strategy replaced the usual approach… Read More
Smartphone Processor Trends and Process Differences down through 7nm
This comparison of smartphone processors from different companies and fab processes was originally going to be a post, but with the growing information content, I had to put it into an article. Here, due to information availability, Apple, Huawei, and Samsung Exynos processors will get the most coverage, but a few Qualcomm Snapdragon
Fully Self-Aligned 6-Track and 7-Track Cell Process Integration
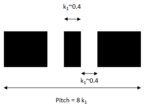
For the 10nm – 5nm nodes, the leading-edge foundries are designing cells which utilize 6 or 7 metal tracks, entailing a wide metal line for every 4 or 5 minimum width lines, respectively (Figure 1).
Figure 1. Left: a 7-track cell. Right: a 6-track cell.
This is a fundamental vulnerability for lithography, as defocus can change… Read More
Application-Specific Lithography: 20nm Flash, 3D XPoint, 3D NAND Bit Lines
Nonvolatile memory capacity reached 64 Gb levels when NAND Flash half-pitch reached 20 nm [1]. Having reached 14 nm [2], NAND Flash half-pitch is no longer being reduced, now that it has entered the 3D era. However, recently, 3D XPoint has found applications within the Optane platform [3]. The lithography for patterning 20 nm half-pitch… Read More
EUV faces Scylla and Charybdis
It is now time for the EUV community to realize they are caught between the proverbial Scylla and Charybdis. In Greek mythology, the two monsters terrorized ships that were unlucky enough to pass between them. By avoiding one, you approached the other.
S for Scylla, or Stochastics
Scylla was a former beautiful nymph turned into















The Foundry Model Is Morphing — Again