It’s a common electrical rule that when large amount of charge gets accumulated, it tries to break any of its surrounding isolation. Although it wouldn’t have been prominent in 1980s or 90s, protection for ICs from such damaging effects is a must, specifically in large mixed-signal designs of today, working at different voltages and at lower process nodes where gate oxide can become extremely thin and breakdown voltage can become very low.
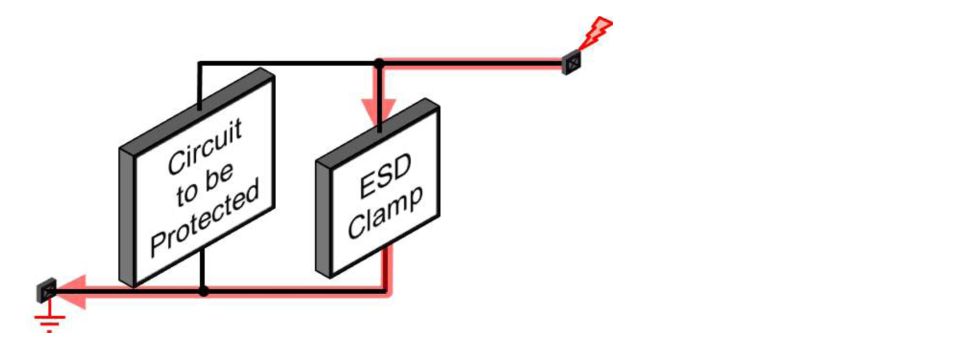
ESD(Electrostatic Discharge) failure in CMOS ICs can be caused due to thermal breakdown on high transient current or dielectric breakdown in gate oxide due to high voltage. If the IC does not fail immediately, it will gradually degrade in performance. In order to protect ICs from ESD, protection circuitry must be applied across IOs and power lines.
ESDA (ESD Association) puts the verification guidelines in three main steps- identifying the ESD vulnerable devices, verifying the implementation for ESD protection and checking completeness of each such device for its protection. SI2 also recommends a standard ESD protection design flow methodology at –
http://www.si2.org/openeda.si2.org/project/showfiles.php?group_id=82&release_id=558
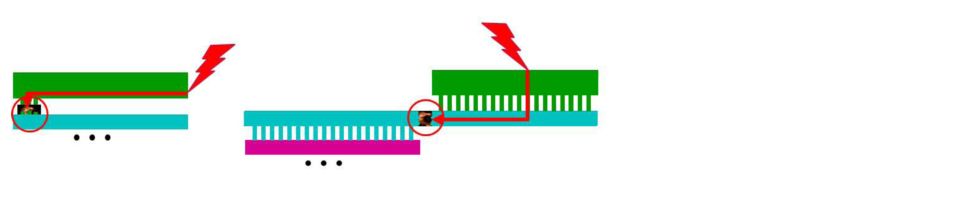
The burgeoning complexity and size of nanometer designs have made it utmost important that a full proof automated system must be implemented for checking ESD conditions being created during manufacturing and making sure that protection is built around IO pads such that any large voltage spikes are dissipated before they reach thin oxide devices and any internal circuitry of the IC. Mentor has developed a novel solution for this important problem. Its tool, Calibre PERC checks the topology of the design for appropriate implementation of ESD structures and their placement with respect to devices to be protected and the core of the IC. Calibre PERC implements all 39 ESD checks,recommended by ESDA, such as layout checks, netlist checks, current density checks etc. to name a few important ones. The current density check ensures interconnect robustness.
[ESD in metal interconnects]
The ESD verification is done at multiple levels from Cell to Package, intra-power and inter- power domains. Calibre PERC identifies external device configurations as ESD protection structures.
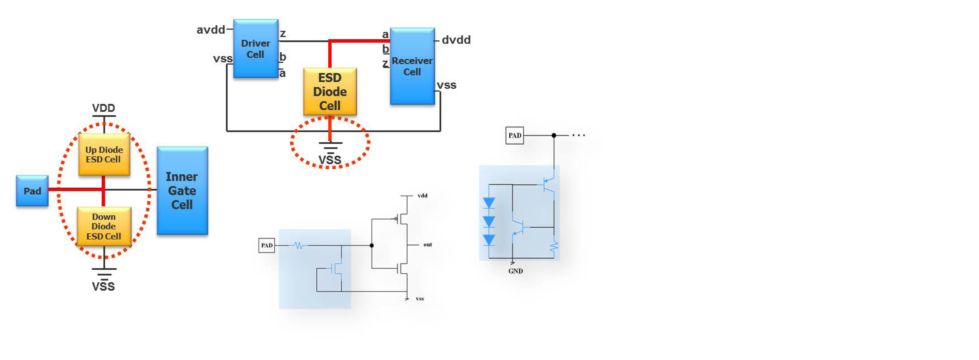
[Some commonly used ESD protection configurations]
Calibre PERC can be programmed to perform other tasks such as parasitic extraction of metal interconnects, design rule checks, current density calculation, electrical compliance etc. A very important aspect of Calibre PERC is that it performs AERC (Advanced Electrical Rule Checks) which can identify signal lines between power domains which work at different voltages in a mixed-signal design and ask for additional ERC configurations between these domains.
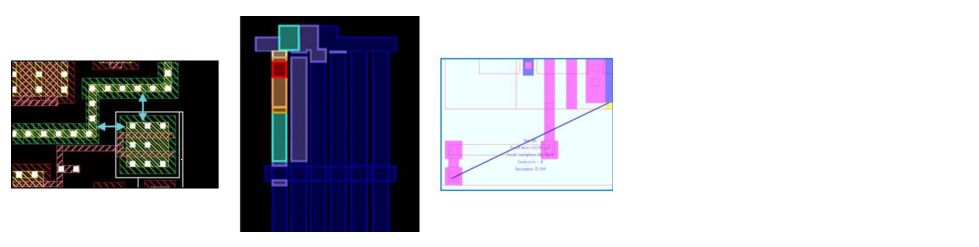
[P2P extraction, current density analysis and design rule checks on identified topologies]
A nice description of ESD and its protection application in Calibre PERC is given in Mentor’s whitepaper at –
Solving Electrostatic Discharge Design Issues with Calibre® PERC™
Calibre PERC provides a comprehensive, integral and complete, automated, error free solution for checking and correcting ESD conditions resulting into increased yield, performance and reliability of ICs.
Share this post via:







Comments
0 Replies to “ESD – Key issue for IC reliability, how to prevent?”
You must register or log in to view/post comments.