
High-speed communication is a critical component for many applications, most notably in the data center. The serializer/deserializer physical interface, or SerDes PHY is the backbone of many different forms of high-speed communication for this application. Use cases include on chip, between chips, between boards and racks and across and between data centers. The requirements run from long reach to ultra-short reach. Satisfying all these requirements demands outstanding engineering and attention to detail.
I was able to preview a webinar from Synopsys recently that does a great job taking the viewer on a tour of all these applications. The webinar is presented by Manmeet Walia and Manuel Mota, both senior product marketing managers at Synopsys. These gentlemen have both been at Synopsys for more than 11 years and both have over 20 years of industry experience, so you’re in good hands for the tour.
The webinar begins with an overview of the various communication regimes – inside the box, box-to-box and enterprise, data center and telco applications. The technical requirements and interface standards relevant to each area are discussed. At an application level, the required IP components for a computing and networking SoC are discussed. It turns out there are four key “pillars of technology” that must work together to address the demands of these applications. Synopsys presents a nice diagram that summarizes this.
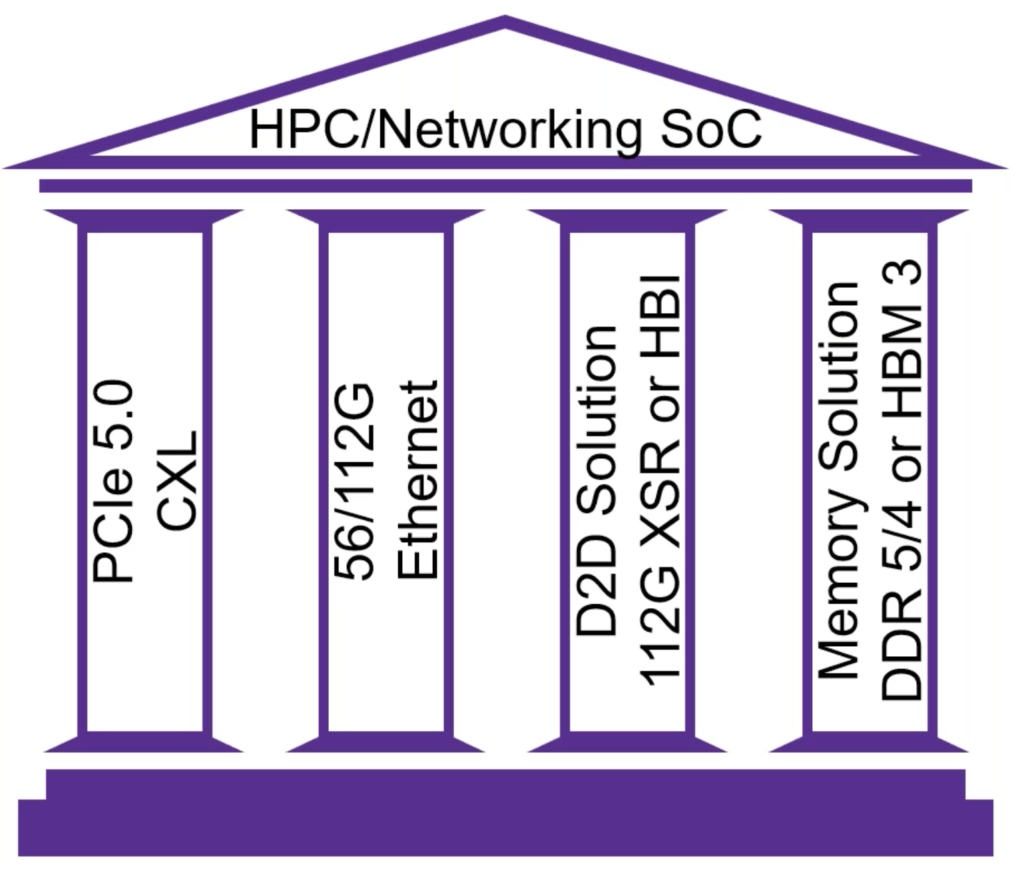
The presenters next examine some of the integration and layout requirements for these types of SoCs. The specifications that define requirements from ultra-short reach to long reach applications are also reviewed. The move from NRZ to PAM4 encoding has had a huge impact on data communications. The specific requirements and challenges of PAM4 are discussed in detail as well, along with eye diagrams to illustrate the points discussed. Various architectural approaches to implement the required technology are also reviewed, along with a discussion of which architecture delivers the best performance from a low-latency point of view.
Many high-end SoCs for large data center applications will integrate hundreds of SerDes lanes. This creates significant packaging and signal integrity design challenges. These are discussed during the webinar as well. Crosstalk and jitter are discussed in detail with example data presented. Methods for performing lab measurements and the use of eval boards are also discussed.
The webinar then turns to die-to-die communications. The design challenges and standards efforts underway are reviewed in detail. There are basically four primary use cases for die-to-die technology:
- Various configurations of homogenous dies for to serve different markets
- Split very large (reticle size) die into multiple parts for yield enhancement
- Aggregate multiple functions from different process nodes to reduce power and improve form factor
- Disaggregate a large SoC to facilitate migration of core functions to a new process node
Example design are discussed. The various multi-chip packaging options available today are also reviewed in detail. The different approaches to implement ultra-short, very short and medium/long reach communication are also presented with the benefits and challenges of each. Design and validation flows for multi-die connectivity are discussed, along with diagnostic approaches.
The webinar concludes with an overview of Synopsys products and support for 56G and 112G applications. There is also a short Q&A session. If high-speed communication is part of your design requirements, I urge you to register for this webinar, you will likely learn something new. The webinar will be broadcast on August 4, 2020 from 10AM – 11AM PDT. You can register for the High-Speed SerDes PHY IP for Up to 800G Hyperscale Data Centers webinar here.
Also Read:
Accelerating High-Performance Computing SoC Designs with Synopsys IP
Quantifying the Benefits of AI in Edge Computing
Synopsys Introduces Industry’s First Complete USB4 IP Solution
Share this post via:






Comments
There are no comments yet.
You must register or log in to view/post comments.