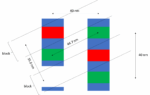
For the so-called “2nm” node or beyond, the minimum metal pitch is expected to be 20 nm or even less, while at the same time, contacted gate pitch is being pushed to 40 nm [1]. Therefore, we expect via connections that can possibly be as narrow as 10 nm (Figure 1)! For this reason, it is natural to expect High-NA EUV lithography as the go-to
Tag: euv lithography
EUV Resist Degradation with Outgassing at Higher Doses
Dosing for EUV lithography walks a fine line between productivity and defectivity. Fabs can choose higher-dose exposures to suppress photon shot noise [1]. However, higher doses require EUV machines to scan the wafer at slower speeds, degrading throughput [2].
On the other hand, there is the threat of resist thickness loss that… Read More
Edge Roughness Differences Among EUV Resists
EUV resists are a key component in the implementation and optimization of EUV lithography. By converting a limited number of absorbed EUV photons into a variable number of released migrating electrons, the resist becomes the final determinant of resolution. There are two kinds of resist which are seriously considered: chemically… Read More
Facing the Quantum Nature of EUV Lithography
The topics of stochastics and blur in EUV lithography has been examined by myself for quite some time now [1,2], but I am happy to see that others are pursuing this direction seriously as well [3]. As advanced node half-pitch dimensions approach 10 nm and smaller, the size of molecules in the resist becomes impossible to ignore for… Read More
A Perfect Storm for EUV Lithography
Electron blur, stochastics, and now polarization, are all becoming stronger influences in EUV lithography as pitch continues to shrink
As EUV lithography continues to evolve, targeting smaller and smaller pitches, new physical limitations continue to emerge as formidable obstacles. While stochastic effects have long been… Read More
CEO Interview with Jonas Sundqvist of AlixLabs
Jonas Sundqvist received his PhD in inorganic chemistry from Uppsala University, Department for Materials Chemistry at The Ångström Laboratory in 2003 where he developed ALD and CVD processes for metal oxide ALD and CVD processes using metal iodides. Jonas is in charge of the daily business at AlixLabs – as a co-founder, he’s… Read More
CEO Interview with Dinesh Bettadapur of Irresistible Materials
Dinesh Bettadapur serves as the Chief Executive Officer of Irresistible Materials Ltd. Dinesh has over 20 years of executive management experience in the semiconductor industries and has held significant leadership roles encompassing general management, P&L management, sales, business development, strategic alliances,… Read More
Resist Loss Model for the EUV Stochastic Defectivity Cliffs
The occurrences of notorious stochastic defects in EUV lithography have resulted in CD or corresponding dose windows with the lower and higher bounds being characterized as “cliffs” [1-3], since the defect density increases exponentially when approaching these bounds. The defects at lower doses have been attributed to the… Read More
Stochastic Effects Blur the Resolution Limit of EUV Lithography
Conventionally, the resolution limit of a lithography system with wavelength l and numerical aperture NA is given by half-pitch = 0.25 wavelength/NA. With the use of EUV lithography, however, electron blur needs to be added [1]. The impact of this blur is to reduce the contrast [2]. Blur reduces the modulation amplitude by a factor… Read More
Stochastic Pupil Fill in EUV Lithography
Pupil fill tradeoff again
EUV lithography continues to be plagued by its stochastic nature.
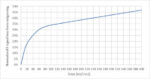
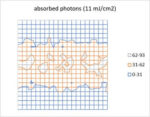
This stochastic nature is most clearly portrayed by the random fluctuation of the absorbed photon number at a given location. For example, consider an absorbed dose of 10 mJ/cm2 amounts to 6.8 photons of energy 92 eV absorbed in a square … Read More