Overview
AI/ML IP refers to specialized semiconductor intellectual property blocks designed for accelerating artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) workloads, particularly in SoCs (System-on-Chip), ASICs, and edge devices. These IP blocks include neural processing units (NPUs), tensor engines, vector processors, and AI-optimized DSPs, enabling efficient, low-power, and real-time execution of AI inference tasks.
These IPs are critical for use cases such as image recognition, voice processing, object detection, sensor fusion, NLP, and autonomous control, in everything from edge AI devices to datacenter accelerators.
🧱 Types of AI/ML IP
| Category | Description | Example Vendors |
|---|---|---|
| Neural Processing Unit (NPU) | Specialized IP for CNNs, RNNs, transformers | Arm Ethos, CEVA NeuPro, Cadence DNA |
| AI-enhanced DSP | DSP with AI extensions and vector math | Cadence Tensilica Vision DSPs, CEVA SensPro |
| Matrix/Tensor Engines | MAC-optimized IP for matrix multiplications | Imagination AXE, Synopsys ARC NPX |
| Low-power Edge AI IP | Ultra-efficient AI cores for wearables/IoT | Syntiant NDP, BrainChip Akida, GreenWaves GAP9 |
| RISC-V AI Extensions | Custom RISC-V cores with AI/ML vector ops | Andes NX27V, Codasip, SiFive Intelligence Series |
🧠 Core Capabilities
| Feature | Function |
|---|---|
| MAC Units (Multiply-Accumulate) | Enables matrix ops for DNN inference |
| SIMD / Vector Engines | Perform parallel operations on arrays |
| Weight Compression / Sparsity Support | Reduces model size and memory bandwidth |
| Winograd / FFT Transforms | Optimizations for convolution layers |
| Dataflow / Reconfigurable Architecture | Custom execution for different layers |
| Low-bit Quantization (INT8/INT4/FP8) | Enhances performance and energy efficiency |
| On-chip Memory Buffers | Minimize latency and power by avoiding DRAM |
📲 Use Cases
| Application | Details |
|---|---|
| Smartphones | Face unlock, AI photography, speech enhancement |
| Edge IoT | Voice command, anomaly detection, smart sensors |
| Automotive | ADAS, radar object detection, driver monitoring |
| Wearables / Hearables | Audio AI, biometric tracking |
| Surveillance / Cameras | Object detection, motion tracking |
| Industrial AI | Predictive maintenance, machine vision |
| Datacenter AI | Low-power inference accelerators for edge-cloud hybrid deployments |
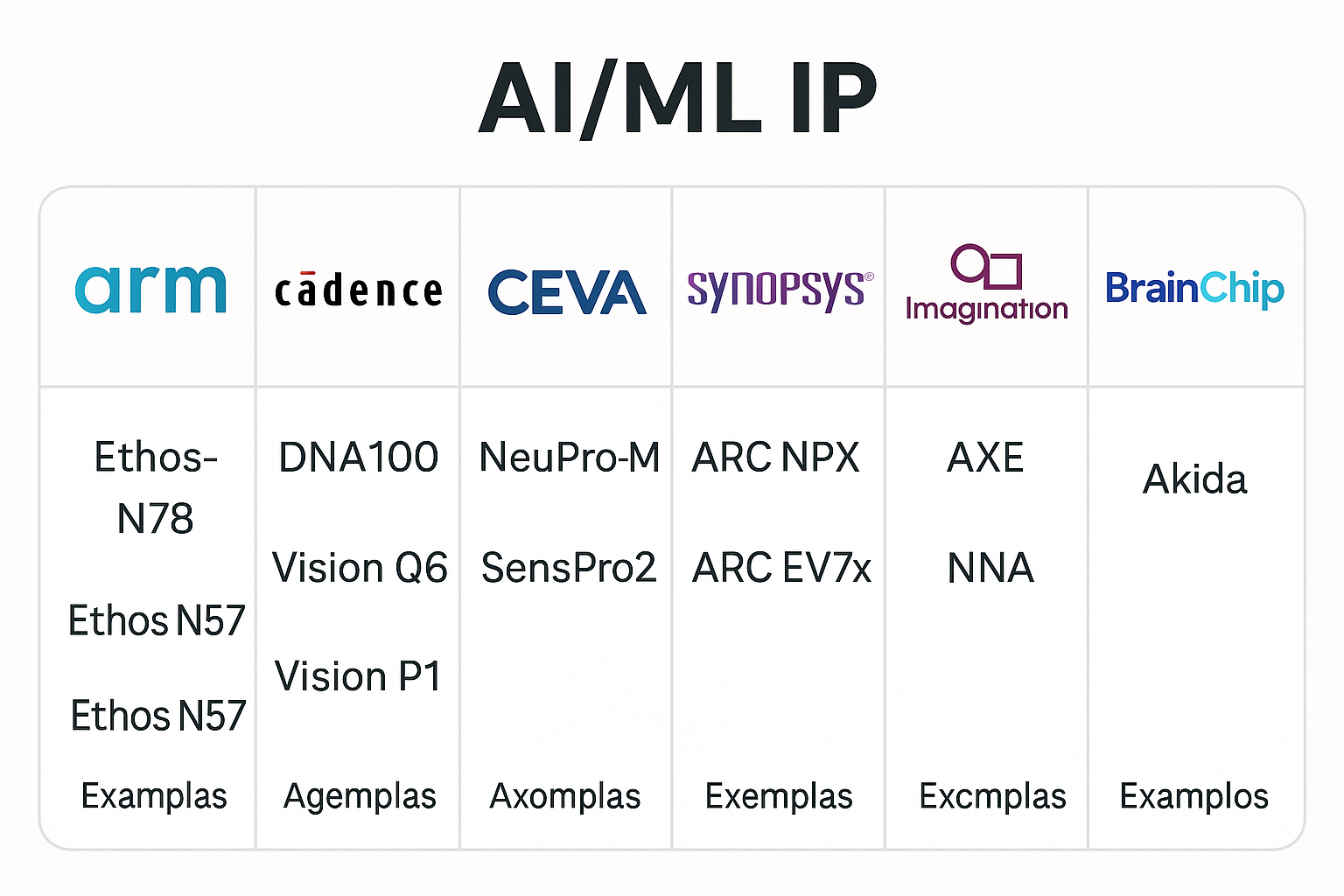
🏢 Key Vendors
| Vendor | Notable IP |
|---|---|
| Arm | Ethos-N78/N57/N37 NPUs |
| Cadence (Tensilica) | DNA100, Vision Q6, Vision P1 |
| CEVA | NeuPro-M, SensPro2 |
| Synopsys | ARC EV7x, ARC NPX series |
| Imagination Technologies | AXE tensor engines, NNA cores |
| BrainChip | Akida neuromorphic IP |
| Syntiant | TinyML-class neural processors |
| GreenWaves | GAP9 for ultra-low-power edge AI |
| SiFive / Andes | RISC-V-based vector AI cores |
🔁 Toolchain & Software Support
Most AI/ML IP comes with SDKs and tools for:
-
Model import (TensorFlow, ONNX, PyTorch)
-
Quantization and pruning
-
Compiler toolchains
-
Runtime APIs (C/C++)
-
Simulation & performance profiling
-
Support for standard ops (e.g., ReLU, Conv2D, Softmax)
Vendors also offer:
-
Neural compilers (e.g., CEVA NetDeploy, Cadence nCompiler)
-
Reference networks and tuning tools
📈 Trends in AI/ML IP
| Trend | Impact |
|---|---|
| TinyML | AI IP optimized for <1 mW inference on microcontrollers |
| Transformer & LLM acceleration | Specialized matrix cores for NLP workloads |
| Chiplets + AI IP | Modular IPs for chiplet-based inference engines |
| Sparsity-aware acceleration | Dynamic workload reduction for DNNs |
| Secure AI IP | AI inference with built-in data encryption, model protection |
| Post-quantum + AI fusion | Combined use of PQ crypto and edge ML for secure AI devices |
📜 Licensing Models
| Model | Notes |
|---|---|
| Upfront License + Royalty | Common in production SoCs |
| Subscription | For rapid prototyping and startups |
| Low-Royalty Edge IP | Growing demand in TinyML market |
| Bundled SDK + IP | Tools, compilers, and runtime often included with core IP |














Advancing Automotive Memory: Development of an 8nm 128Mb Embedded STT-MRAM with Sub-ppm Reliability