And if, like me, you don’t go to MWC, that’s the right time to get your version of the MIPI IP survey, the 3[SUP]rd[/SUP] version since the first launch in 2010, because IPNEST will give you a good reason to buy it during MWC: you will get it at a lower price. That will apply now and during the event, but only from today, and up to the 3[SUP]rd[/SUP] of March… But let’s have a look at the latest status about MIPI. MIPI is hot, MIPI is coming to the mainstream, don’t miss it!
MIPI follows the trends in the Electronic industry: the massive move from parallel to serial interconnect, as illustrated by PCI Express replacing PCI, SATA replacing PATA, HDMI or DisplayPort replacing LVDS based interconnect to Display material (computer screen or HDTV) etc… Using similar technologies in Mobile Devices is a natural move, but a specific attention has been taken to power consumption. MIPI has been specifically designed for portable electronic devices, battery powered, and lowering the power consumption is a key feature.
MIPI’s defined charter focusing on mobile platforms defines the markets addressed by the standards and the target products for those standards. That market is mobile handsets, from basic low-end, full-featured phones, to Smartphone. Since 2009, the MIPI alliance has decided to promote MIPI use in every kind of mobile Application, like Mobile Internet Devices (MID) and Media Tablet in the PC segment, or Handheld game console, Digital still camera and potentially all portable system in the Consumer Electronic segment.
In this survey, we have started to look at the MIPI use in the Mobile Handset segment and first derive a forecast in term of Integrated Circuits (IC) because we think that the more widely MIPI will be used in chips in production, the more stable and easier to manage the protocol will be. When more IC is in production means more efficient –and cheaper- test program, leading to a null or marginal impact on yield. More identical IC in production also means cheaper production cost and consequently a lower Average Selling Price (ASP).
Such a virtuous cycle is expected to lead to a wider adoption for MIPI technology. When MIPI was introduced and started to be used in the high end of the wireless handset segment, most of the early adopters had both the knowhow and the resource needed to develop the solution internally (or enough money to use design service) instead of sourcing MIPI externally as a standard IP. They probably also prefer at that time not to depend to external sourcing for a function to be integrated into strategic IC like Application Processor, or Camera Controller whatever is their core business. This was the first phase for MIPI, being considered as an emerging technology, which also means more expansive to integrate, and more risky.
With the success of this first phase, illustrated by the number of MIPI powered IC in production passing the one billion range (in 2011 according with our forecast) will come the second phase, in 2012-2013, where MIPI will be integrated in the majority of the smartphone segment, some of the featured phone and being considered in design starts serving other segments than the wireless handset segment. This second phase will lead to several consequences: the early adopters may start to use externally sourced MIPI functions (MIPI is no more a strategic differentiator) instead of internal design; the many followers, attracted by the very high volumes in the wireless handset industry, many of them in China or Taiwan, will certainly decide to “buy” instead of “make” MIPI function, for TTM or knowhow related reasons; the chip makers developing IC to serve other market segment will also prefer to buy, for the same reasons.
All of them selecting the technology to get full benefit, on top of the low power consumption, from MIPI usage:
- Standardized Interconnect protocol: an OEM can run seamless integration in the system of the different IC, providing they comply with the same MIPI Interfaces.
- Interchange suppliers at low risk: an OEM can easily move from one IC supplier to another for the same function (for example a camera controller IC), at least at the Interface level
- There are different specifications for the Controller (CSI, DSI, LLI and so on), but only two for the PHY (D-PHY and M-PHY): many specifications, but an easier learning curve to physically interface the application processor with Camera, Display, Modem, Mass Storage, WLAN, Remote Coprocessor…!
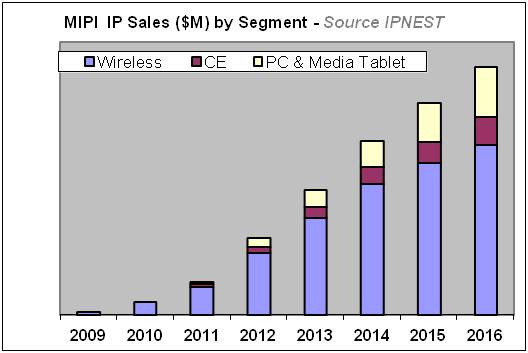
We expect this second phase to lead to high growth sales of MIPI IP; we propose a forecast for the IP licenses sales for the 2010-2016 periods, including “actual” results from IP vendors whenever it’s possible.
We have also proposed a review of the different IP vendors actively marketing MIPI PHY IP, or Controller IP or both. This competitive analysis could benefit to:
- MIPI new adopters, or the chip makers integrating MIPI in devices serving wireless handset segment (smartphone or not), Media Tablet and PC and Consumer Electronic segments,
- IP vendors, who desire to develop a new IP business or consolidating existing business and invest resources on line with MIPI IP business potential.
- VIP vendors who invest into this new source of business, after having supported USB, SATA, PCI Express…
This MIPI IP survey or one of the two previous versions has been sold to IP vendors (already supporting MIPI or in the decision process to support these specifications), VIP vendor and chip makers. This report is unique: it’s the only one where the reader can find both an IC and an IP forecast for MIPI, as well as a competitive analysis of the IP –and VIP- vendors. As such, if your company is or will be involved into MIPI, you need to have it.
Eric Esteve from IPNEST– Table of Content for “MIPI IP Forecast 2011-2016” available here