By Ujjwal Negi – Siemens EDA
Multi-die architectures are redefining the limits of chip performance and scalability through the integration of multiple dies into a single package to deliver unprecedented computing power, flexibility, and efficiency. At the heart of this transformation is the Universal Chiplet Interconnect Express (UCIe) protocol, which enables high-bandwidth, low-latency communication between dies. But with innovation comes complexity: inter-die interactions, evolving protocol features, and the need to verify behavior across multiple abstraction layers create significant verification challenges.
This article examines the core verification hurdles in UCIe-based multi-die systems and explains how Questa™ One Avery™ Verification IP (Avery VIP) provides a protocol-aware, automated, and layered verification framework. It supports block-level to full system-level validation—combining automation, advanced debug tools, and AI-driven coverage analysis to accelerate verification closure.
Verification Hurdles in Multi-Die Systems
In traditional verification, individual design blocks are validated in isolation. Multi-die architectures require a shift toward verifying the entire system, ensuring that inter-die communication, synchronization, and interoperability between protocols, such as PCIe, CXL, CHI, and UCIe, function seamlessly. The challenge grows as the UCIe specification evolves—UCIe 2.0 and later versions introduce features such as the management transport protocol, lane repair, autonomous link training, and advanced sideband handling—all of which require verification environments to remain adaptable and up to date.
The test environment must also offer flexibility to simulate both standard operating conditions (such as steady-state data transfers and control signaling) and edge cases (like misaligned lanes or failed link training). Fine-grained controllability is essential, allowing errors to be injected and traffic patterns manipulated to test robustness—especially since faults can propagate across dies and protocol layers.
In addition, system-level performance metrics like cross-die latency, throughput, and bandwidth must be monitored in real time to ensure the design meets its performance targets under diverse workloads. This performance validation needs to be continuous and consistent across various traffic patterns and system states.
Configuration space management presents another challenge, as multi-die systems require synchronized register updates across dies, including real-time error reporting and runtime reconfiguration. Finally, verification must be able to scale from simulation, where deep debug visibility is possible, to emulation and hardware prototyping, for speed and real-world validation.
Accelerating Multi-Die Verification with Questa One Avery UCIe VIP
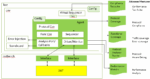
The Questa One Avery UCIe VIP is built to handle the full spectrum of multi-die verification needs through a layered, configurable framework.
It supports multiple bus functional models (BFM) across diverse DUT types. At the block level, Avery VIP can verify standalone components, such as the Logical PHY (LogPHY), D2D adapter, and protocol layers. At the die or system level, it operates in two modes: a full-stack mode for end-to-end testing of the D2D adapter, LogPHY, mainband, and sideband (with or without raw die-to-die interface (RDI), and a No-LogPHY/RDI2RDI mode for direct, higher-level protocol testing without physical link dependencies.
To accelerate customer testbench deployment, the Questa One VIP Configurator can generate a UVM-compliant testbench in just a few clicks, enabling verification to begin almost immediately. It allows visual DUT–VIP connectivity mapping with automatic signal binding, intuitive GUI-based BFM configuration, and selection of pre-built sequences aligned with the DUT’s use model. This eliminates extensive manual set up and provides a ready-to-run environment from the outset.
Avery VIP also provides layer-specific and feature-specific callbacks, enabling on-the-fly traffic manipulation and precise error injection, whether that means corrupting FLITs, altering parameter exchanges, or testing abnormal traffic patterns. Real-time monitoring and dynamic score boarding help track system reactions to these injected conditions.
For compliance and coverage, Avery VIP includes a comprehensive Compliance Test Suites (CTS) framework. Questa™ One Avery CTS is organized by DUT type, protocol mode, and direct specification references. The protocol test suite contains more than 500 checks for UCIe core layers and approximately 3,000 checks for PCIe, CXL, and AXI interactions. Runtime configurability allows protocol features, FLIT formats, or topology to be adjusted on the fly without rebuilding the environment.
The Avery CTS smart API layer further simplifies test creation, offering high-level functions to monitor link training, access configuration or memory spaces, control link state transitions, generate placeholder protocol traffic, and inject packets at precise protocol states.
Debugging and performance tracking are built in. Avery VIP features protocol-aware transaction recording, correlating transactions across layers and highlighting errors with associated signal activity. FSM recording logs internal state transitions such as LTSSM, FDI, and RDI events, complete with timestamps and annotations. Layer-specific debug trackers focus on LogPHY, the D2D adapter, FDI/RDI drivers, parity checks, and configuration space accesses. The performance logger provides real-time throughput, latency, and bandwidth measurements, and can focus on specific simulation phases for targeted analysis.
Finally, an AI-driven verification co-pilot is integrated through Questa One Verification IQ, acting as an intelligent assistant throughout the verification cycle. The Questa One Verification IQ Coverage Analyzer leverages machine learning to automatically identify and prioritize coverage gaps, rank tests based on their contribution to overall coverage, and detect recurring failure signatures for faster root-cause analysis. The system visualizes coverage data through intuitive heatmaps and bin distribution charts, enabling teams to make data-driven decisions, focus effort on high-impact areas, and continuously refine their verification strategy for maximum efficiency.
Driving the Future of Multi-Die with UCIe Verification
As an open standard, UCIe is rapidly becoming the cornerstone of heterogeneous integration, allowing chipmakers to combine chiplets from different vendors into a single package with seamless interoperability. By standardizing the interconnect layer, UCIe unlocks a new wave of innovation in data centers, AI accelerators, and high-performance computing, paving the way for designs that are more scalable, energy-efficient, and cost-optimized than traditional monolithic approaches.
The Questa One Avery UCIe VIP is built to handle the demands of this rapidly evolving landscape. It scales effortlessly from block-level to full system-level verification, streamlines environment set up, allows precise error injection, and brings in AI-driven coverage analysis to speed up closure. With its mix of compliance suites, flexible runtime configuration, and powerful debug tools, it gives verification teams the confidence to hit performance, compliance, and reliability goals, helping the industry move toward a future where multi-die systems aren’t the exception, but the standard.
For a deeper dive into the full verification architecture, download the complete whitepaper: Accelerating UCIe Multi-Die Verification with a Scalable, Smart Framework.
Ujjwal Negi is a senior member of the technical staff at Siemens EDA based in Noida, specializing in storage and interconnect technologies. With over two years of hands-on experience, she has contributed extensively to NVMe, NVMe over Fabrics, and UCIe Verification IP solutions. She graduated with a Bachelor of Technology degree from Bharati Vidyapeeth College of Engineering in 2023.
Also Read:
Orchestrating IC verification: Harmonize complexity for faster time-to-market
Perforce and Siemens at #62DAC
Breaking out of the ivory tower: 3D IC thermal analysis for all