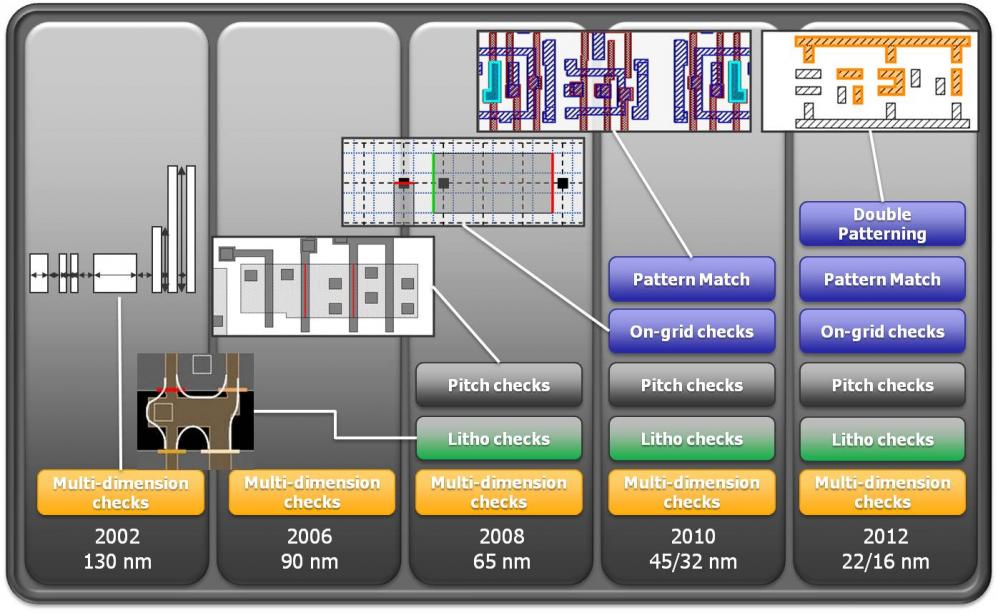
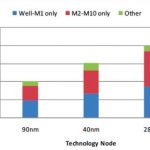
With each process generation, the design rules get more and more complex. One datapoint: there are twice as many checks at 28nm as there are at 90nm. In fact, the complexity of the rules is outpacing the ability to describe them using the simplified approaches used in the DRCs built-into layout editors or formats like LEF.
Worse still, at 28nm and below the rules are really too complicated for a designer to understand. As Richard Rouse of MoSys said “at 28nm, even the metal rules are incomprehensible.” It goes without saying that the rules for the even more critical layers for transistor formation are even more opaque.
It is going to get worse too, since at 22nm and below we will need to use double patterning for the most critical layers, which means that it is not really even possible to know whether a design is in compliance, that depends on the double patterning algorithm being able to assign shapes to the two patterns in a way that the lithography will work.
It used to be that analog designers were comfortable staying a couple of nodes behind the digital guys but that is no longer possible. 70% of designs are mixed-signal SoCs, driven by the communications market in particular. Mobile consumer chips need analog, and even some of the digital, such as graphics accelerators, typically require custom design datapaths.
Digital designs are about scaling, using simplified rules to be able to handle enormous designs. Custom and analog design is about optimization and so need to push to the limits of what the process can deliver.
The only solution to this problem is to run the real signoff DRC with the real signoff rules. The signoff DRC is pretty much universally Mentor’s Calibre (sorry Cadence and Synopsys). But running Calibre from within theLaker™ Custom Layout Automation System is inconveniently slow and disruptive. So Mentor have created an integratable version called Calibre RealTime (and by the way, doesn’t Mentor know that Oasys have a product already called RealTime Designer) which operates on top of the OpenAccess (OA) database and Laker is the first, and so far only, layout editor to do the integration. Rules are continuously checked in parallel with editing. A full check takes about 0.2 to 0.3 seconds. In the demonstration I saw at Springsoft’s booth it was almost instantaneous, rather like the spell-checker in a word processor. In fact at 28nm it was checking 6649 shapes in 0.3 second. Laker optimizes which checks are required based on what changes were made to the design (if you don’t change the metal you don’t need to run those metal checks again, for example) which further improves performance.
Historically, layout designers have been very reluctant to adopt anything that might slow them down. But the complexity of the rules in modern process nodes along with the high performance and unobtrusiveness of the integration, has a good chance of immediate adoption of the Laker signoff-driven layout flow.