PCI Express 3.0 increased the supported data rate to 8 Gbps, which effectively doubles the data rate supported by PCI Express 2.0. While the data rate was increased, no improvement was made to the channels. As such, an 8 Gbps channel in PCIe 3.0 experiences significantly more loss than one implemented in PCIe 2.0. To compensate for this increased loss, PCI Express 3.0 specifies enhanced equalization in the PHY with improved TX equalization, improved RX equalization, and equalization training.
It is critical that designers who plan to implement PCIe 3.0 understand these equalization changes and their impacts. After attending this webinar from Synopsys, registrants will understand:
- Why improved levels of equalization are necessary at higher data rates
- Types of equalization enhancements required for optimal performance at 8 Gbps
- The difference between decision feedback equalization (DFE) and continuous time linear equalization (CTLE)
- The need for equalization training and adaptability in PCIe 3.0
- The importance of proven interoperability between the PHY and the controller
Who should attend:SoC designers and system architects. They may register here… do it quickly, as the webinar will be heeld on January 24 (this Thursday).
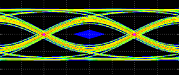
I remember, back in 2008, when Snowbush designers were implementing these advanced equalization techniques (DFE, CTLE), that one of the critical point was the number of “taps” in the equalization strategy: is two taps enough or should we implement three taps? I would certainly ask this question to Synopsys when attending this webinar! If you don’t know the mathematical (or Digital Signal Processing-DSP) principles of equalization and would like to learn, it will take you some brain gas, and time, my advice would be to find a good teacher. I was lucky enough 20 years ago to learn Equalization when working in a DSP oriented ASIC design team with DSP experts… it took me several 3 hours set to start (only start) understanding it! You can see one of the numerous steps on the above picture…
Coming back to Synopsys PCIe gen-3 PHY IP, not only the design is 100% compliant with PCI Express specification, but the test strategy is also very solid:
The test features include:
- Unique built-in diagnostics enables visibility into link performance
- Automatic Test Equipment (ATE) test vectors for complete, at-speed production testing
- Built-in per channel BERTs
- Flexible fixed and random pattern generation
- Error counting on patterns or disparity
- Digital phase or voltage margining (bathtub curves)
- Built-in per channel non-destructive scopes: captures eye diagrams and coherently captures periodic signals in situ without disrupting link operation
- Additional loopbacks:
- Serial analog (for wafer probe)
- Parallel Tx to Rx
- Supports full analog ATE test on low cost digital tester using only pass/fail JTAG vectors
Presenters:

Rita Horner, Senior Technical Marketing Manager for Analog/Mixed Signal IP, Synopsys
Rita Horner has more than 20 years’ experience in mixed-signal circuit design, interconnect, test, and packaging of high-speed integrated circuits for consumer, computing, and high-end networking ASSP and ASIC products. As a technical and product marketing manager, she has experience in ASSP, ASIC and Fiber Optic products, focusing on High Speed Serial Interconnect. She participated and presented in multiple standards bodies including ANSI T11, IEEE 802.3, OIF, and SFF Multi Sourcing Agreements.

David Rennie, Senior Analog Design Engineer for Mixed-Signal Interface IP, Synopsys
David Rennie is a Senior Analog Design Engineer for Synopsys’ Mixed-Signal IP, developing next-generation high-speed PCIe and Ethernet SerDes technologies. David has authored and co-authored fifteen IEEE conference and journal papers and holds five granted and three pending patents. He has presented at several industry and IEEE conferences, and is an active member in the IEEE.
Eric Esteve from IPNEST
Share this post via:







Comments
There are no comments yet.
You must register or log in to view/post comments.