Overview
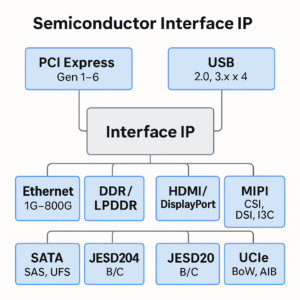
Semiconductor Interface IP refers to pre-verified, reusable IP blocks that implement industry-standard communication protocols in System-on-Chip (SoC) or ASIC designs. These IPs include both the controller and PHY (physical layer) and are critical for enabling high-speed communication between chips, memory, peripherals, and external devices.
Interface IP allows SoC designers to integrate standard interfaces like PCI Express, USB, DDR, Ethernet, HDMI, and MIPI without designing them from scratch, reducing risk, development time, and cost.
🧱 Key Components
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Protocol Controller | Digital logic handling the interface layer (e.g., packetizing, link management) |
| PHY IP | Mixed-signal/analog block that handles electrical signaling and timing |
| Verification IP | Testbenches, assertions, and stimulus used to validate the interface |
Some vendors offer combo IPs (controller + PHY), while others license them separately for flexibility.
📡 Common Interface IP Types
| Interface | Use Case | Data Rate |
|---|---|---|
| PCIe (Gen 1–6) | High-speed host-to-device I/O | Up to 64 GT/s |
| USB (2.0, 3.x, 4) | Universal I/O for data, charging, display | Up to 40 Gbps |
| Ethernet (1G–800G) | Networking, data centers, automotive | Up to 800 Gbps |
| DDR / LPDDR | DRAM interfaces for compute/memory | Up to LPDDR5X/DDR5 |
| HDMI / DisplayPort | Audio/video display interfaces | Up to 48 Gbps |
| MIPI (CSI, DSI, I3C) | Mobile cameras, sensors, displays | Up to 6+ Gbps/lane |
| SATA / SAS / UFS | Storage interfaces | Up to 24 Gbps |
| JESD204B/C | High-speed ADC/DAC interfaces | Up to 32 Gbps/lane |
| UCIe / BoW / AIB | Chiplet and die-to-die interconnects | >100 Gbps/mm |
🧠 Why Interface IP Matters
-
Reduces time-to-market for SoCs
-
Ensures compliance with global standards (USB-IF, JEDEC, PCI-SIG, etc.)
-
Enables interoperability with external components (DRAM, SSD, displays)
-
Offloads complex protocol management from the main CPU
-
Improves signal integrity and power efficiency via optimized PHYs
🏭 Leading Interface IP Vendors
| Vendor | Notable IPs |
|---|---|
| Synopsys | PCIe, USB, DDR, HDMI, Ethernet, UCIe PHY |
| Cadence Design Systems | DDR, PCIe, LPDDR, MIPI, USB |
| Rambus | DDR, SerDes, HBM, LPDDR |
| Alphawave Semi | High-speed SerDes and Ethernet |
| Arasan | MIPI (CSI, DSI, I3C), USB, storage |
| Mixel | MIPI PHY IP |
| Silvaco / Dolphin Design | Mixed-signal and low-power interface IP |
| eMemory / Kilopass | Secure fuses, eFuse interface blocks |
| AnalogX / Kandou | Ultra-low-power chiplet PHYs and USB4 IPs |
🧪 Verification and Compliance
Interface IP must meet strict industry compliance standards:
-
PCI-SIG, USB-IF, JEDEC, HDMI Forum, MIPI Alliance, etc.
-
IP vendors often provide pre-certified IPs with:
-
Compliance logs
-
Interoperability test results
-
Silicon validation and test chip results
-
📈 Trends in Interface IP
| Trend | Impact |
|---|---|
| High-Speed SerDes (56G/112G/224G) | Enables 800G/1.6T Ethernet and AI chiplet links |
| Chiplet Connectivity (UCIe) | Interface IP evolving to support die-to-die protocols |
| AI/ML SoCs | Require low-latency I/O (PCIe, HBM, LPDDR, SerDes) |
| Automotive Ethernet/IP | Functional safety-compliant PHY and MAC IP |
| Security Integration | Embedded cryptography and side-channel protection in PHYs |
🛠️ Design Considerations
-
Process Node Optimization: PHYs must be tailored to FinFET and advanced nodes (5nm, 3nm)
-
Signal Integrity and Jitter: Equalization, pre-emphasis, and clock recovery are critical
-
Die Area and Power: Especially important for mobile, edge, and chiplet designs
-
Custom Configurability: IPs may be tailored for lane count, voltage swing, channel length













Things From Intel 10K That Make You Go …. Hmmmm