Non-Volatile Memory (NVM) refers to a broad category of memory technologies that retain stored data even when power is removed. NVM is fundamental to persistent storage in consumer electronics, embedded systems, automotive applications, data centers, and advanced computing. Unlike volatile memory (such as DRAM or SRAM), NVM is used to store code, configuration, firmware, and user data in everything from microcontrollers to solid-state drives (SSDs).
📜 Overview
-
Definition: Memory that preserves data without continuous power
-
Core Feature: Retention of information after power loss
-
Primary Uses: Boot code, firmware, data logging, application storage
-
Categories: Embedded NVM, removable NVM, stand-alone NVM
🔑 Key Properties of NVM
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
| Data Retention | Typically 10–100 years depending on type |
| Endurance | Number of write/erase cycles before failure (can vary from ~10³ to 10¹⁵) |
| Access Speed | Slower than SRAM/DRAM but improving |
| Density | Generally higher than SRAM, varies across types |
| Power Efficiency | Low power consumption at rest |
| Scalability | Emerging technologies improving scaling for sub-10nm nodes |
🧩 Types of NVM Technologies
1. Conventional NVMs
| Type | Description | Common Use |
|---|---|---|
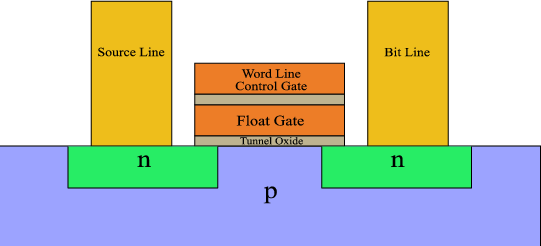
| Flash Memory (NAND, NOR) | Electrically erasable, block/page-based | SSDs, microcontrollers |
| EEPROM | Byte-addressable electrically erasable memory | MCU config storage |
| Mask ROM | Programmed during manufacturing | Fixed firmware |
| PROM / EPROM | One-time or UV-erasable | Legacy embedded devices |
2. Emerging NVMs (Next-Gen)
| Type | Technology | Characteristics |
|---|---|---|
| MRAM (Magnetoresistive RAM) | Uses magnetic states | Fast, durable, non-destructive |
| FRAM (Ferroelectric RAM) | Uses ferroelectric material | Very low power, low latency |
| ReRAM (Resistive RAM) | Changes resistance states | High speed, low write energy |
| PCM (Phase-Change Memory) | Uses amorphous/crystalline states | High endurance, scalable |
| 3D XPoint (Intel Optane) | Proprietary (discontinued 2023) | DRAM-like speed, Flash-like persistence |
🖥️ Applications
| Market | Use Case |
|---|---|
| Consumer Electronics | Firmware storage in TVs, game consoles, phones |
| Embedded Systems | Boot code, device calibration, parameters |
| Automotive | OTA updates, secure key storage, ECU logs |
| Data Center | SSDs (NAND), persistent memory (e.g., MRAM, Optane) |
| AI/ML Accelerators | Weight storage, checkpointing |
| IoT Devices | Low-power data logging, secure identity storage |
📦 NVM in SoCs and Embedded Design
🔹 Embedded NVM
-
Used in: Microcontrollers, secure elements, smartcards
-
Examples:
-
On-chip Flash (e.g., Arm Cortex-M MCUs)
-
EEPROM blocks in automotive MCUs
-
OTP (One-Time Programmable) fuses for secure ID
-
🔹 External NVM
-
SPI/QSPI NOR Flash
-
eMMC / UFS / SD for mobile storage
-
NAND Flash in SSDs or USB drives
⚙️ Technical Comparison
| Memory Type | Volatility | Density | Speed | Endurance | Common Use |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SRAM | Volatile | Low | Very fast | 10¹⁶+ | Cache, registers |
| DRAM | Volatile | Medium | Fast | ~10⁸ | Main memory |
| Flash | Non-Volatile | High | Moderate | 10⁴–10⁵ | SSDs, embedded |
| EEPROM | Non-Volatile | Low | Slow | 10⁶ | MCU parameters |
| MRAM | Non-Volatile | Medium | Fast | 10¹⁵ | Cache-like persistent memory |
| FRAM | Non-Volatile | Low | Fast | 10¹⁴ | Medical, wearables |
| ReRAM | Non-Volatile | High | Fast | 10⁸–10¹² | In-memory computing (emerging) |
🛡️ Reliability & Security
-
ECC (Error Correction Code) often used in NAND-based storage
-
Wear leveling to extend NAND Flash lifespan
-
Data retention aging must be modeled for automotive/aerospace
-
Tamper resistance: EEPROM and embedded Flash in secure elements
-
Secure boot: NVM often stores hash roots and public keys
🌍 Industry Standards and Ecosystem
| Area | Standard / Group |
|---|---|
| Flash Memory | JEDEC JESD47, ONFI (Open NAND Flash Interface) |
| Automotive | AEC-Q100 qualification, ISO 26262 |
| Security | NIST SP 800-193 (firmware integrity), FIPS 140-3 |
| Storage Interfaces | SPI, QSPI, eMMC, UFS, NVMe |
| Persistent Memory | SNIA NVM programming model, CXL-PM (future) |
🔬 Challenges and Trends
⚠️ Challenges
-
Endurance limits in Flash (especially NAND)
-
Scaling of cell size at sub-10nm nodes
-
Retention degradation over temperature and time
-
Emerging NVM adoption hindered by cost and process integration
🚀 Trends
-
Adoption of MRAM in automotive MCUs (e.g., NXP S32 family)
-
Embedded ReRAM and FRAM for ultra-low-power IoT
-
3D NAND scaling beyond 300+ layers for SSDs
-
In-memory compute using ReRAM and PCM for neuromorphic workloads
-
NVM-backed SRAM caches for always-on AI inference devices
🧾 NVM IP Providers and Foundry Support
| Vendor | Technology | Notable Features |
|---|---|---|
| TSMC | Embedded Flash, ReRAM | Available down to 22nm ULP |
| GlobalFoundries | Embedded MRAM, ReRAM | Used in MCU and AI SoCs |
| UMC | EEPROM, OTP, Flash | Low-cost embedded NVM |
| Samsung Foundry | MRAM, NAND | Advanced memory for AI and HPC |
| Infineon | Embedded Flash MCUs | Automotive-grade Flash |
| Adesto (Dialog/Renesas) | CBRAM, EEPROM | IoT and low-power NVM |
| Weebit Nano | ReRAM | Open foundry model |
| Everspin | Discrete MRAM | High-endurance NVM SSDs and caches |













Facing the Quantum Nature of EUV Lithography