In the first part we covered AI as the first line of defense for cybersecurity, the goal was to keep the cyber-criminals at bay, but in case they managed to get-in and infiltrate the network we need to initiate the second line of defense; #Blockchain. With the fact that cybercrime and cyber security attacks hardly seem to be out of the news these days and the threat is growing globally. Nobody would appear immune to malicious and offensive acts targeting computer networks, infrastructures and personal computer devices. Firms clearly must invest to stay resilient. Gauging the exact size of cybercrime and putting a precise US dollar value on it is nonetheless tricky. But one thing we can be sure about is that the number is big and probably larger than the statistics reveal.
Read: First Line of Defense for Cybersecurity: AI
The global figure for cyber breaches had been put at around $200 billion annually.
New blockchain platforms are stepping up to address security concerns in the face of recent breaches. Since these platforms are not controlled by a singular entity, they can help ease the concerns created by a spree of recent breach disclosures. Services built on top of #blockchain have the potential to inspire renewed trust due to the transparency built into the technology.
Developments in blockchain have expanded beyond recordkeeping and cryptocurrencies. The integration of smart contract development in blockchain platforms has ushered in a wider set of applications, including cybersecurity.
By using blockchain, transaction details are kept both transparent and secure. Blockchain’s decentralized and distributed network also helps businesses to avoid a single point of failure, making it difficult for malicious parties to steal or tamper with business data.
Transactions in the blockchain can be audited and traced. In addition, public blockchains rely on distributed network to run, thus eliminating a single point of control. For attackers, it is much more difficult to attack a large number of peers distributed globally as opposed to a centralized data center.
Implementing Blockchain in Cybersecurity
Since a blockchain system is protected with the help of ledgers and cryptographic keys, attacking and manipulating it becomes extremely difficult. Blockchain decentralizes the systems by distributing ledger data on several systems rather than storing them on one single network. This allows the technology to focus on gathering data rather than worrying about any data being stolen. Thus, decentralization has led to an improved efficiency in blockchain-operated systems.
For a blockchain system to be penetrated, the attacker must intrude into every system on the network to manipulate the data that is stored on the network. The number of systems stored on every network can be in millions. Since domain editing rights are only given to those who require them, the hacker won’t get the right to edit and manipulate the data even after hacking a million of systems. Since such manipulation of data on the network has never taken place on the blockchain, it is not an easy task for any attacker.
While we store our data on a blockchain system, the threat of a possible hack gets eliminated. Every time our data is stored or inserted into blockchain ledgers, a new block is created. This block further stores a key that is cryptographically created. This key becomes the unlocking key for the next record that is to be stored onto the ledger. In this manner, the data is extremely secure.
Furthermore, the hashing feature of blockchain technology is one of its underlying qualities that makes it such a prominent technology. Using cryptography and the hashing algorithm, blockchain technology converts the data stored in our ledgers. This hash encrypts the data and stores it in such a language that the data can only be decrypted using keys stored in the systems. Other than cybersecurity, blockchain has many applications in several fields that help in maintaining and securing data. The fields where this technology is already showing its ability are finance, supply chain management, and blockchain-enabled smart contracts.
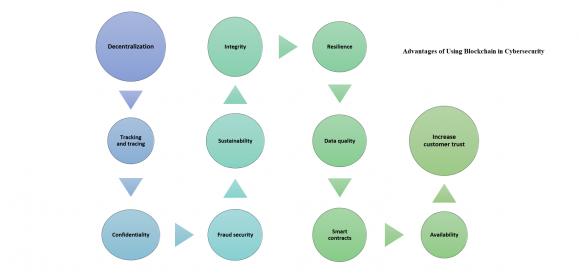
The main advantages of blockchain technology for cyber security are the following:
Decentralization
Thanks to the peer-to-peer network, there’s no need for third-party verification, as any user can see network transactions.
Tracking and tracing
All transactions in blockchains are digitally signed and time-stamped, so network users can easily trace the history of transactions and track accounts at any historical moment. This feature also allows a company to have valid information about assets or product distribution.
Confidentiality
The confidentiality of network members is high due to the public-key cryptography that authenticates users and encrypts their transactions.
Fraud security
n the event of a hack, it’s easy to define malicious behavior due to the peer-to-peer connections and distributed consensus. As of today, blockchains are considered technically ‘unhackable’, as attackers can impact a network only by getting control of 51% of the network nodes.
Sustainability
Blockchain technology has no single point of failure, which means that even in the case of DDoS attacks, the system will operate as normal thanks to multiple copies of the ledger.
Integrity
The distributed ledger ensures the protection of data against modification or destruction. Besides, the technology ensures the authenticity and irreversibility of completed transactions. Encrypted blocks contain immutable data that is resistant to hacking.
Resilience
The peer-to-peer nature of the technology ensures that the network will operate round-the-clock even if some nodes are offline or under attack. In the event of an attack, a company can make certain nodes redundant and operate as usual.
Data quality
Blockchain technology can’t improve the quality of your data, but it can guarantee the accuracy and quality of data after it’s encrypted in the blockchain.
Smart contracts
Software programs that are based on the ledger. These programs ensure the execution of contract terms and verify parties. Blockchain technology can significantly increase the security standards for smart contracts, as it minimizes the risks of cyber-attacks and bugs.
Availability
There’s no need to store your sensitive data in one place, as blockchain technology allows you to have multiple copies of your data that are always available to network users.
Increase customer trust
Your clients will trust you more if you can ensure a high level of data security. Moreover, blockchain technology allows you to provide your clients with information about your products and services instantly.
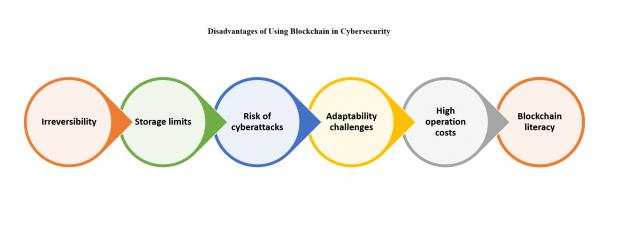
Disadvantages of Using Blockchain in Cybersecurity
Irreversibility
There’s a risk that encrypted data may be unrecoverable in case a user loses or forgets the private key necessary to decrypt it.
Storage limits
Each block can contain no more than 1 Mb of data, and a blockchain can handle only 7 transactions per second in average.
Risk of cyberattacks
Though the technology greatly reduces the risk of malicious intervention, it’s still not a panacea to all cyber threats. If attackers manage to exploit the majority of your network, you may lose your entire database.
Adaptability challenges
Though blockchain technology can be applied to almost any business, companies may face difficulties integrating it. Blockchain applications can also require complete replacement of existing systems, so companies should consider this before implementing the blockchain technology.
High operation costs
Running blockchain technology requires substantial computing power, which may lead to high marginal costs in comparison with existing systems.
Blockchain literacy
There are still not enough developers with experience in blockchain technology and with deep knowledge of cryptography.
Conclusion
Blockchain’s decentralized approach to cybersecurity can be seen as a fresh take on the issues that the industry faces today. The market could only use more solutions to combat the threats of cyberattacks. And, the use of blockchain may yet address the vulnerabilities and limitations of current security approaches and solutions.
Throwing constant pots of money at the problem and knee-jerk reactions is not the answer. Firms need to sort out their governance, awareness, organizational culture and critically look at the business purpose and processes before they invest in systems to combat cybercrime.
The roster of these new services provided by Blockchain may be limited for now and of course they face incumbent players in the cybersecurity space. But this only offers further opportunity for other ventures to cover other key areas of cybersecurity. Blockchain also transcends borders and nationalities, which should inspire trust in users. And, with the growth of these new solutions, the industry may yet restore some of the public’s trust they may have lost in the midst of all these issues.
Overall, blockchain technology is a breakthrough in cyber security, as it can ensure the highest level of data confidentiality, availability, and security. However, the complexity of the technology may cause difficulties with development and real-world use.
Implementation of blockchain applications requires comprehensive, enterprise- and risk-based approaches that capitalize on cybersecurity risk frameworks, best practices, and cybersecurity assurance services to mitigate risks. In addition, cyber intelligence capabilities, such as cognitive security, threat modeling, and artificial intelligence, can help proactively predict cyber threats to create counter measures, that’s why AI considered as the first line of defense while Blockchain is the second line.
Ahmed Banafa Named No. 1 Top VoiceTo Follow in Tech by LinkedIn in 2016
Read more articles at IoT Trends by Ahmed Banafa
References
https://www.ibm.com/blogs/insights-on-business/government/convergence-blockchain-cybersecurity/
http://www.technologyrecord.com/Article/cybersecurity-via-blockchain-the-pros-and-cons-62035
https://www.allerin.com/blog/blockchain-cybersecurity
All figures: Ahmed Banafa







CEO Interview with Jerome Paye of TAU Systems