Advanced Microcontroller Bus Architecture (AMBA) is an open-standard, on-chip interconnect specification for the connection and management of functional blocks in system-on-chip (SoC) designs. Developed and maintained by Arm Ltd., AMBA is the de facto standard bus protocol used across a wide range of embedded systems, microcontrollers, and mobile processors.
AMBA facilitates IP reuse, modular SoC design, and interoperability between processors, peripherals, memory interfaces, and accelerators from multiple vendors.
Overview
-
Developer: Arm Ltd.
-
Initial Release: 1996
-
Current Version: AMBA 5 and AMBA CHI (as of 2024)
-
License: Open, royalty-free specification
-
Primary Purpose: High-speed, low-latency, low-power communication between SoC components
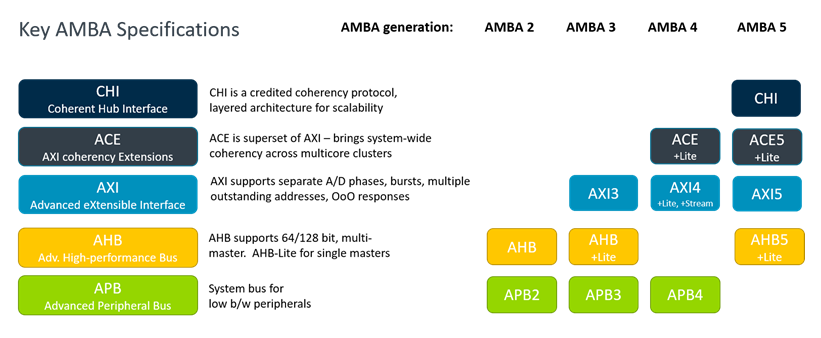
Key AMBA Protocol Families
| Protocol | Description | Use Case |
|---|---|---|
| APB (Advanced Peripheral Bus) | Simple low-bandwidth bus for peripherals | GPIO, UART, timers |
| AHB (Advanced High-performance Bus) | High-performance, single bus master system | Legacy microcontrollers |
| AXI (Advanced eXtensible Interface) | High-speed, burst-based, multi-master system | Modern SoCs, AI/ML accelerators |
| CHI (Coherent Hub Interface) | Cache-coherent interconnect for multi-core SoCs | Server-class cores, cache-coherent fabrics |
Protocol Summary
1. APB – Advanced Peripheral Bus
-
Version: APB3, APB4
-
Simplicity-focused: Low power and low complexity
-
No pipelining or burst transfers
-
Used for: UARTs, GPIOs, low-speed timers
-
Master-Slave: Always single master
2. AHB – Advanced High-performance Bus
-
Version: AHB, AHB-Lite
-
Supports: Burst transfers, split transactions, pipelining
-
Used in: Legacy systems and MCUs
-
Master-Slave: Multiple bus masters supported (except in AHB-Lite)
3. AXI – Advanced eXtensible Interface
-
Version: AXI3, AXI4, AXI4-Lite, AXI4-Stream
-
Key Features:
-
Separate address/control and data phases
-
Support for out-of-order transactions
-
Multiple outstanding and parallel transactions
-
Burst-based transfers
-
-
Variants:
-
AXI4 – High-speed memory-mapped
-
AXI4-Lite – Simple single-word access (low area)
-
AXI4-Stream – Streaming, non-addressed data for DSP/AI
-
-
Used in: High-end SoCs, FPGA IP, AI accelerators
4. CHI – Coherent Hub Interface
-
Used in: High-performance, multi-core, server-grade SoCs
-
Supports: Cache coherency, directory-based snoop filtering
-
Alternative to: Intel’s CCI, interconnects like CCIX, CXL (at SoC level)
-
Primarily used by: Arm Neoverse-based server chips
Why AMBA Matters
Benefits of AMBA:
-
Promotes IP interoperability from multiple vendors
-
Enables hierarchical SoC design with standardized interfaces
-
Supports multi-core, multi-master, and asynchronous domain crossing
-
Eases integration, verification, and debug of complex designs
-
Works across CPU cores, DSPs, accelerators, and memory
Use Cases
| Application | Role of AMBA |
|---|---|
| Embedded MCUs | AHB/APB for connecting peripherals |
| Mobile SoCs | AXI interconnects between GPU, CPU, DSP |
| Automotive SoCs | Deterministic bus structure, isolation domains |
| AI Accelerators | AXI4-Stream for high-bandwidth, low-latency data feeds |
| Server SoCs | CHI for coherence and scalability |
| FPGAs | AXI is standard interface in Xilinx and Intel IP cores |
AMBA in Practice
IP and Tools Support:
-
Vendors: Arm, Cadence, Synopsys, SiFive, Andes, Arteris
-
Tools:
-
EDA IP interconnect generators (e.g., Arm CoreLink, Arteris FlexNoC)
-
Simulation/Verification: UVM-based AXI VIPs
-
AMBA-compliant transaction monitors and bus analyzers
-
Evolution Timeline
| Year | Version | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| 1996 | AMBA 1.0 | Introduced AHB and APB |
| 1999 | AMBA 2.0 | Improved pipelining, split transaction |
| 2003 | AMBA 3.0 | Introduced AXI (AXI3) |
| 2010 | AMBA 4.0 | AXI4, AXI4-Lite, AXI4-Stream |
| 2013 | AMBA 5.0 | Introduced CHI |
| 2016+ | AMBA 5 updates | Performance tuning, QoS support |
Related Standards and Interconnects
| Standard | Relation to AMBA |
|---|---|
| Wishbone | Open-source bus used in open silicon |
| TileLink | RISC-V interconnect developed by SiFive |
| NoC (Network-on-Chip) | AMBA-compliant NoCs are common |
| UCIe | AMBA used inside chiplets with external UCIe |
| CXL / CCIX | Inter-chip coherent protocols; CHI is intra-chip equivalent |
Challenges
-
Legacy vs Modern: Integrating AHB/APB with AXI4/CHI in SoCs with mixed IP
-
Verification complexity: AXI and CHI involve many handshakes, QoS paths
-
Latency management: In deep-pipelined systems with multiple masters
-
Security and isolation: Tightly coupled with bus firewalls and TrustZone














Quantum Computing Technologies and Challenges