Overview
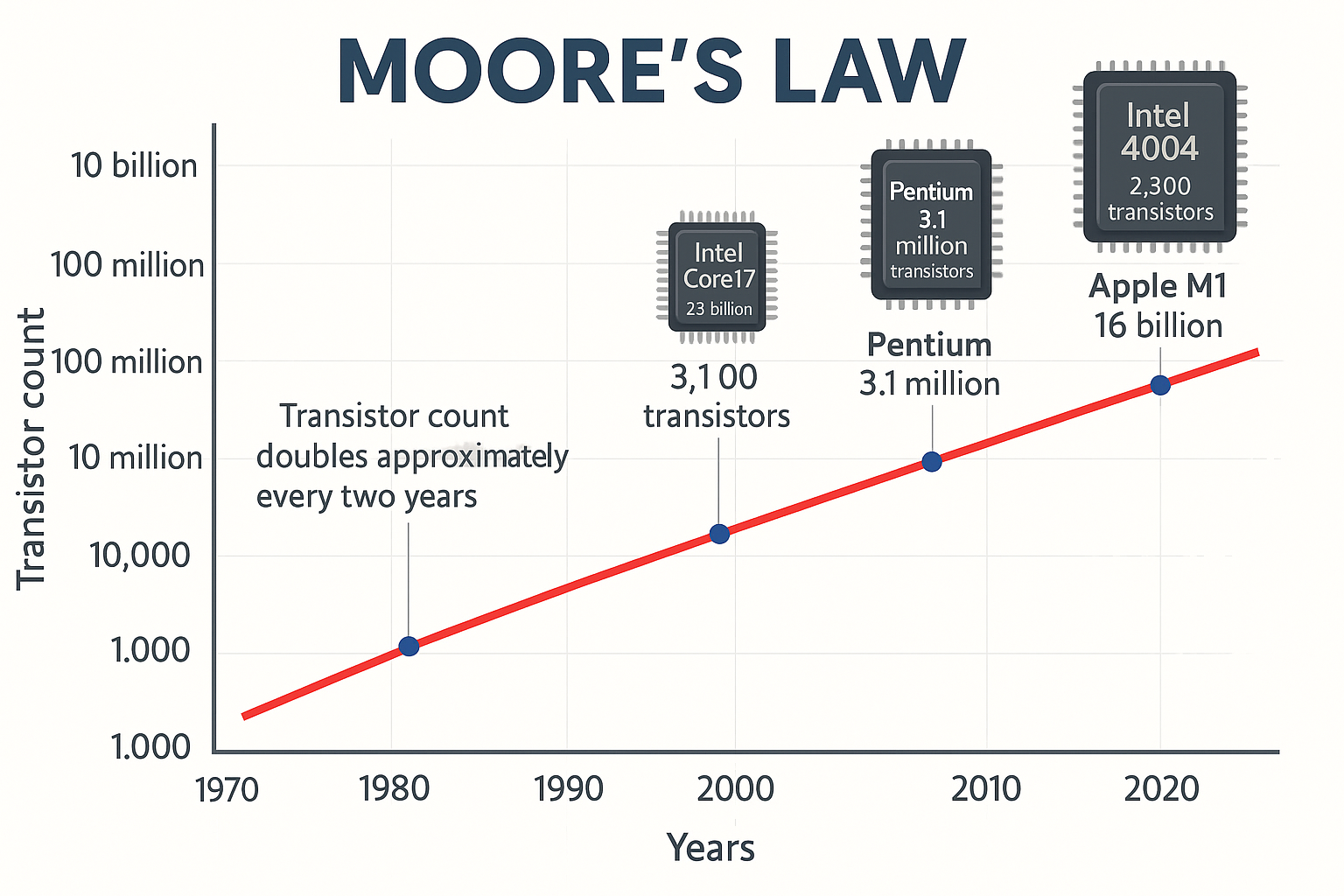
Moore’s Law is an empirical observation stating that the number of transistors on a microchip doubles approximately every two years, leading to exponential improvements in computing performance, efficiency, and cost per function. It has been a guiding principle for the semiconductor industry for over five decades, driving innovation in microprocessors, memory, and system-on-chip (SoC) designs.
Although not a physical law of nature, Moore’s Law has served as a roadmap and self-fulfilling prophecy, inspiring advancements in lithography, materials, packaging, and architectural techniques.
Origin
-
Coined by: Gordon E. Moore, co-founder of Intel Corporation.
-
Original prediction (1965): Transistors would double every year.
-
Revised (1975): The doubling rate slowed to every two years.
-
Published in Electronics Magazine, Moore’s article projected growth for about a decade—but the trend persisted far longer.
Implications of Moore’s Law
| Domain | Impact |
|---|---|
| Performance | Faster CPUs, GPUs, DSPs, and AI accelerators |
| Power Efficiency | More operations per watt enabling mobile and edge devices |
| Cost per Function | Lower price per transistor and lower system cost |
| Miniaturization | Enabled smartphones, wearables, and embedded AI |
| Innovation Cycles | Pushed fabs and chipmakers to adopt smaller process nodes regularly |
Moore’s Law and Semiconductor Scaling
| Generation | Approx. Node (nm) | Transistor Count Example |
|---|---|---|
| 1970s | 10,000 nm (10 µm) | Intel 4004 (2,300 transistors) |
| 1990s | ~350–180 nm | Pentium processors (1–5M transistors) |
| 2010s | 32–7 nm | Intel Core / Apple A-series (1–10B+) |
| 2020s | 5–2 nm | Apple M3, NVIDIA Hopper, TSMC N2 |
| Future | <2 nm | Gate-All-Around (GAA), CFET, 3D stacking |
Extensions of Moore’s Law
To sustain Moore’s Law, the industry began innovating beyond pure transistor shrinking:
1. More-than-Moore (MtM)
-
Adds functionality via heterogeneous integration: sensors, RF, analog, photonics.
2. 3D IC / Advanced Packaging
-
Technologies like TSMC CoWoS, Intel Foveros, and chiplets/UCIe increase effective transistor density through vertical and modular scaling.
3. Design Technology Co-Optimization (DTCO)
-
Co-designing devices, standard cells, EDA tools, and libraries for each process node.
4. System Technology Co-Optimization (STCO)
-
System-level optimization including power delivery, thermals, interconnect, and memory hierarchy.
Physical and Economic Limits
Moore’s Law has slowed due to multiple constraints:
| Constraint | Description |
|---|---|
| Quantum effects | Electrons tunnel at very small scales |
| Heat dissipation | Power density increases with scaling |
| Complexity and cost | Sub-5nm fabs cost $20B+ and require EUV |
| Design challenges | Verification, DFM, and yield losses escalate |
Despite these, innovations like EUV lithography, GAA-FETs, AI-driven design, and chiplets are extending its relevance.
Is Moore’s Law Dead?
While classic scaling has slowed, many argue Moore’s Law is evolving, not ending:
-
Intel, TSMC, and Samsung continue roadmap development through 2nm, GAA-FETs, and 3D packaging.
-
NVIDIA, Apple, AMD, and others drive performance-per-watt via architecture and software optimization.
-
AI acceleration, heterogeneous compute, and domain-specific architectures are enabling post-Moore growth.
Related Concepts
| Concept | Description |
|---|---|
| Dennard Scaling | Voltage and power scaled with size (broken around 2006) |
| Wright’s Law | Cost declines with cumulative production |
| Koomey’s Law | Compute per joule doubles ~2 years |
| Bell’s Law | New classes of computing emerge every decade |
| More-than-Moore | System-level enhancements beyond transistor scaling |
Organizations Driving Moore’s Law
-
Intel: Moore’s Law originator and process scaling leader.
-
TSMC: Leading foundry enabling 3nm and below nodes.
-
Samsung: Pioneer of GAA transistor implementation.
-
ASML: Developer of EUV lithography tools.
-
IBM: Advanced node R&D, including 2nm and 3D chip stacking.
Famous Quotes
Gordon E. Moore (Co-founder of Intel)
“The number of transistors on a chip will double approximately every two years.”
– Gordon Moore, 1965“It can’t continue forever. The nature of exponentials is that you push them out and eventually disaster happens.”
– Gordon Moore, on the eventual limits of Moore’s Law“What drove me was a strong desire to solve technical problems… It’s nice to have your name associated with something that’s meaningful.”
– Gordon Moore, reflecting on Moore’s Law
Share this post via:“Moore’s Law is alive and well.”— Pat Gelsinger, Intel CEO, 2023
Moore’s Law is not a law of physics; it’s a law of human ingenuity.”
– Brian Krzanich, former CEO of Intel“The end of Moore’s Law is not the end of progress.”
– Jensen Huang, CEO of NVIDIA“Even if Moore’s Law slows down, there’s no law preventing us from innovating in other dimensions.”
– Lisa Su, CEO of AMD“Moore’s Law is alive, but it’s getting harder and more expensive to sustain.”
– Tsu-Jae King Liu, Dean of UC Berkeley College of EngineeringMoore’s Law is what allowed Apple to shrink a room-sized computer into your pocket.”
– Popular tech media paraphrase“Moore’s Law isn’t dead. It’s evolved.”
– Common industry refrain as innovation shifts to 3D ICs, chiplets, and new architectures“If the automobile had followed Moore’s Law, a Rolls-Royce would cost $3 today and go 2 million miles per gallon.”
– Comparison often cited to show the exponential nature of Moore’s Law“We will keep Moore’s Law alive for the next decade.”
– Raja Koduri, former Intel Chief Architect“The roadmaps may no longer double transistors every 18–24 months, but innovation isn’t slowing down.”
– Jim Keller, microprocessor architect (Intel, AMD, Tesla)“With 3D packaging, Moore’s Law becomes more of a system-level law.”
– Lisa Su, AMD CEO“Moore’s Law is more alive than ever — it’s just not in two dimensions anymore.”
– Mark Liu, former TSMC Chairman“Moore’s Law became a self-fulfilling prophecy — a target for the industry to hit.”
– Anonymous engineer, quoted in IEEE Spectrum“It’s the economic engine of the modern world.”
– Marc Andreessen, investor, on Moore’s Law and its influence“The most important trend in technology history.”
– Ray Kurzweil, futurist and author“Moore’s Law enabled the software revolution by supplying exponential hardware improvements.”
– Bill Gates, Microsoft founder“Moore’s Law is why computers became invisible — and indispensable.”
– Paul Saffo, technology forecasterAlso Read:














Advancing Automotive Memory: Development of an 8nm 128Mb Embedded STT-MRAM with Sub-ppm Reliability