HDMI (High-Definition Multimedia Interface) is a proprietary digital interface standard used to transmit high-quality audio and video signals between a wide range of consumer electronics, computing, and embedded devices. Developed in the early 2000s, HDMI has become the dominant AV interconnect standard, replacing older analog standards such as VGA, DVI, and component video.
HDMI is widely used in televisions, gaming consoles, PCs, laptops, AV receivers, projectors, cameras, and SoCs for consumer, automotive, and industrial applications.
📜 Overview
-
Introduced: December 2002
-
Developed by: HDMI Forum & HDMI Licensing Administrator, Inc.
-
Current Version: HDMI 2.1a (as of 2024)
-
Transmission: Digital uncompressed video and multi-channel audio
-
Connector Types: Type A (standard), C (mini), D (micro), Type E (automotive)
-
Replaces: DVI, VGA, Component, SCART (analog AV)
🔌 Key Features
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Uncompressed Video | Supports up to 10K resolution at 120Hz (HDMI 2.1) |
| Multi-Channel Audio | PCM, DTS, Dolby Digital, Dolby Atmos, eARC |
| Consumer Electronics Control (CEC) | Remote control interoperability |
| High-Bandwidth Digital Content Protection (HDCP) | DRM for protected content |
| Display Stream Compression (DSC) | Optional compression for ultra-high resolutions |
| Audio Return Channel (ARC / eARC) | Sends audio upstream to AV receivers/soundbars |
| Variable Refresh Rate (VRR) | Reduces screen tearing in gaming |
| Quick Frame Transport (QFT) | Lower latency for games and VR |
| Quick Media Switching (QMS) | Eliminates black screen when switching modes |
🔁 Evolution of HDMI Versions
| Version | Year | Max Resolution | Bandwidth | Key Additions |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1.0–1.2 | 2002–2005 | 1080p | 4.95 Gbps | Basic HD video/audio |
| 1.3–1.4 | 2006–2009 | 4K@30Hz | 10.2 Gbps | Deep Color, Ethernet over HDMI, ARC |
| 2.0 | 2013 | 4K@60Hz | 18 Gbps | 32 audio channels, HDR, BT.2020 |
| 2.1 | 2017 | 10K@120Hz | 48 Gbps | VRR, eARC, ALLM, DSC, QFT, QMS |
| 2.1a | 2022 | Same | Same | Source-Based Tone Mapping (SBTM) |
🎞️ Video Capabilities
-
Supported Formats:
-
SD, HD, FHD (1080p), UHD (4K), 8K, 10K
-
3D video (Frame Packing)
-
-
HDR Support:
-
HDR10, HDR10+, Dolby Vision, HLG
-
-
Color Formats:
-
RGB, YCbCr 4:4:4 / 4:2:2 / 4:2:0
-
10-bit, 12-bit (Deep Color)
-
🔊 Audio Features
-
Up to 32 channels of audio
-
High bit rate audio: DTS:X, Dolby TrueHD, Atmos
-
LPCM: Multi-channel lossless audio
-
ARC / eARC:
-
ARC (HDMI 1.4): Compressed formats, stereo
-
eARC (HDMI 2.1): Supports uncompressed 192kHz/24-bit up to 8 channels
-
🔐 Content Protection
-
HDCP (High-bandwidth Digital Content Protection):
-
Version 1.x: Used in early HD systems
-
Version 2.2: Required for 4K UHD content (Blu-ray, streaming)
-
Version 2.3: Used in HDMI 2.1 systems
-
🎮 Gaming & Advanced Use Cases
-
Variable Refresh Rate (VRR): Prevents screen tearing (like FreeSync, G-Sync)
-
Auto Low Latency Mode (ALLM): Switches TV to Game Mode automatically
-
QFT (Quick Frame Transport): Reduces latency
-
QMS (Quick Media Switching): Eliminates black screen during content format switches
-
DSC (Display Stream Compression): Enables higher resolutions over 48 Gbps bandwidth
🧩 Connectors and Pinouts
| Type | Description | Use |
|---|---|---|
| Type A | Standard 19-pin | TVs, monitors, GPUs |
| Type C (Mini) | Smaller 19-pin | Tablets, cameras |
| Type D (Micro) | Very compact | Smartphones, action cameras |
| Type E | Automotive lockable | In-vehicle HDMI use |
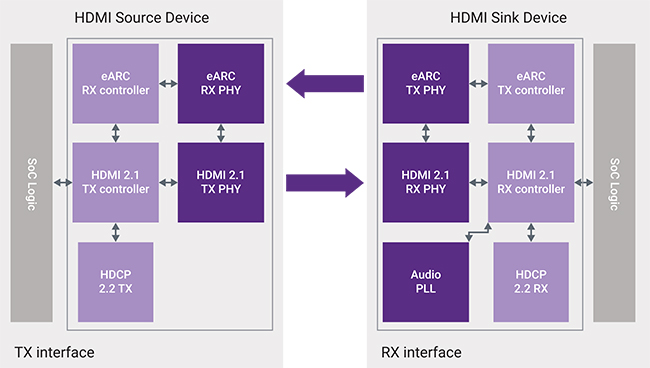
🧠 Semiconductor IP and Silicon Integration
HDMI functionality is typically implemented in SoCs or via dedicated HDMI PHY + controller IP.
HDMI IP Blocks:
-
TX Controller: HDMI source (e.g., set-top box, GPU)
-
RX Controller: HDMI sink (e.g., TV, monitor)
-
PHY Interface: High-speed differential transmitter/receiver
-
HDCP Engine: Encryption and key management
-
CEC Controller: Optional, for device inter-control
Leading IP Vendors:
-
Synopsys – HDMI PHY and controller IP (up to HDMI 2.1)
-
Cadence – HDMI RX/TX subsystems
-
Analogix (ANX) – HDMI/DisplayPort PHYs
-
Invecas, Rambus, Lontium – HDMI PHY and converter IP
-
Implements in: SoCs for TVs, game consoles, mobile, laptops, STBs, AVRs
🔄 HDMI vs Other Interfaces
| Interface | Max Bandwidth | Key Features | Primary Use |
|---|---|---|---|
| HDMI 2.1 | 48 Gbps | Audio+Video, eARC, HDR, HDCP | TVs, consoles, AVRs |
| DisplayPort 2.1 | 80 Gbps | Higher refresh rates, daisy-chaining | Monitors, PCs |
| DVI | 3.96 Gbps | Legacy video only | Monitors (older) |
| USB-C Alt Mode (DP/HDMI) | Up to 40 Gbps | Multi-protocol | Laptops, tablets |
| VGA/Component | Analog | Obsolete | Legacy systems |
🚗 HDMI in Automotive
-
Type E connector with locking mechanism for vibration resistance
-
Used in infotainment systems, rear-seat entertainment, digital mirrors
-
Competes with MIPI A-PHY and Automotive Ethernet
📜 Compliance and Certification
-
Devices using HDMI must be certified and licensed
-
HDMI Licensing Administrator (HDMI LA) governs:
-
HDMI Adopters program
-
Logo usage
-
Specification access
-
-
Testing by HDMI Authorized Test Centers (ATCs) for:
-
Electrical compliance
-
Interoperability
-
HDCP enforcement
-
🛠️ Tools and Development Aids
-
HDMI Analyzer/Generator Tools for signal validation (e.g., Teledyne LeCroy, Keysight)
-
Simulation IP for pre-silicon HDMI verification
-
Compliance test benches available from EDA vendors and silicon validation suites
🔮 Future Trends
-
Integration with DisplayPort 2.1 / USB4 Alt Mode
-
Dynamic HDR metadata and per-frame tone mapping (SBTM)
-
More eARC adoption for soundbars and home theater
-
HDMI over IP in AV distribution (using HDBaseT, AVB)
-
Integration with AI chips for on-device HDMI output (e.g., smart cameras, vision systems)













TSMC N3 Process Technology Wiki