Definition
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is a branch of computer science concerned with creating systems capable of performing tasks that typically require human intelligence. These tasks include learning, reasoning, problem-solving, perception, natural language understanding, and decision-making. AI spans a range of capabilities, from simple automation to complex autonomous reasoning and adaptation.
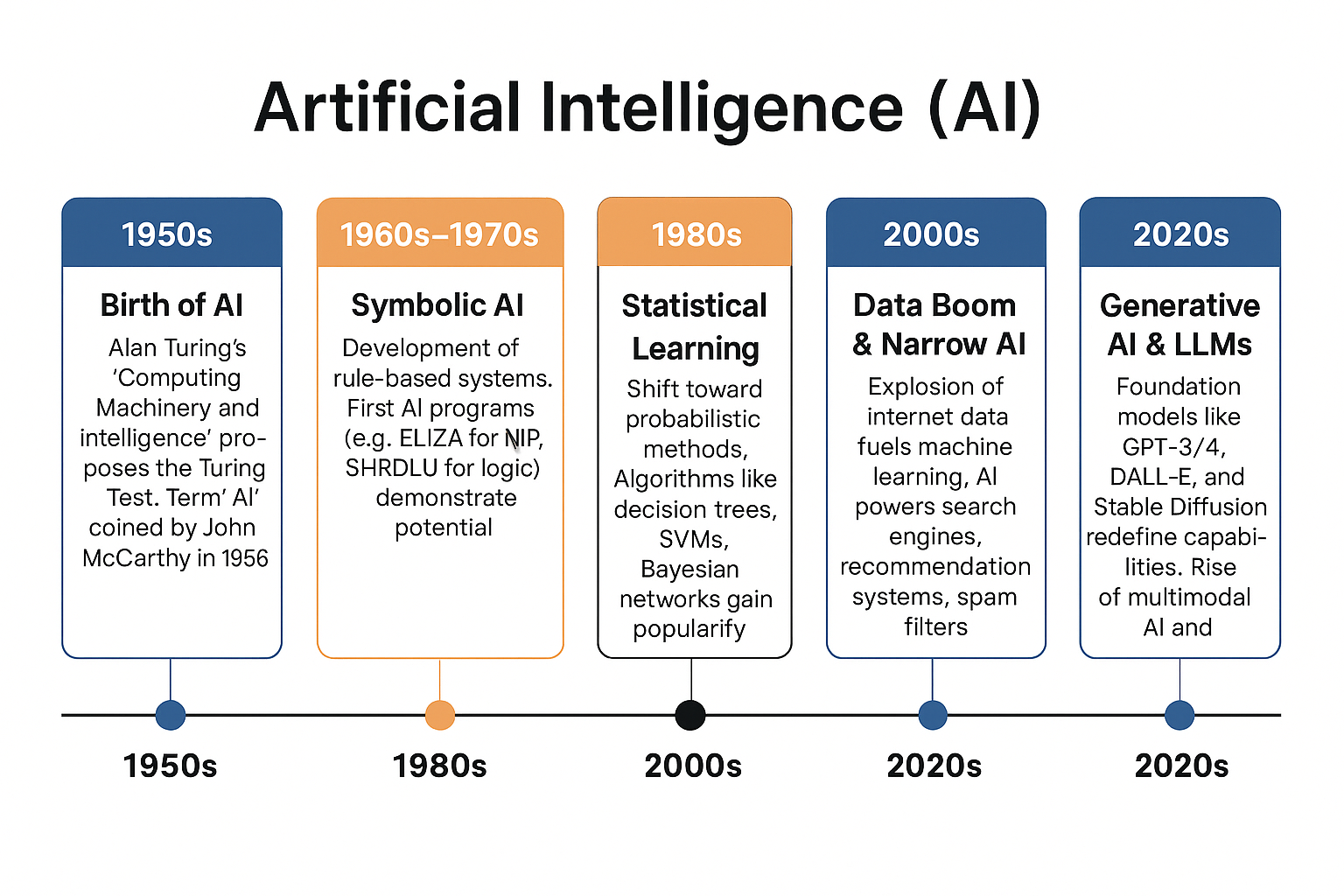
Historical Timeline of AI
| Era | Milestone | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1950s | Birth of AI | Alan Turing’s “Computing Machinery and Intelligence” proposes the Turing Test. Term “AI” coined by John McCarthy in 1956 at the Dartmouth Conference. |
| 1960s–1970s | Symbolic AI | Development of rule-based systems. First AI programs (e.g., ELIZA for NLP, SHRDLU for logic) demonstrate potential. |
| 1980s | Expert Systems | Commercialization of AI via rule-based expert systems (e.g., XCON at DEC). High expectations, but scalability issues arise. |
| 1990s | Statistical Learning | Shift toward probabilistic methods. Algorithms like decision trees, SVMs, Bayesian networks gain popularity. |
| 2000s | Data Boom & Narrow AI | Explosion of internet data fuels machine learning. AI powers search engines, recommendation systems, spam filters. |
| 2010s | Deep Learning Revolution | Neural networks (especially CNNs and RNNs) outperform traditional methods. ImageNet success (AlexNet, 2012) sparks AI renaissance. |
| 2020s | Generative AI & LLMs | Foundation models like GPT-3/4, DALL·E, and Stable Diffusion redefine capabilities. Rise of multimodal AI and autonomous agents. |
Core Subfields of AI
1. Machine Learning (ML)
A method where computers learn patterns from data to make decisions without explicit programming.
-
Supervised learning: Learns from labeled data (e.g., classification, regression).
-
Unsupervised learning: Discovers structure in unlabeled data (e.g., clustering).
-
Reinforcement learning: Learns via trial-and-error in dynamic environments (e.g., AlphaGo, robotics).
2. Deep Learning
A subfield of ML using deep neural networks with many layers:
-
CNNs: Used for images.
-
RNNs/LSTMs/Transformers: Used for sequences and language.
-
Transformers (e.g., GPT, BERT): Now dominant across modalities.
3. Natural Language Processing (NLP)
AI’s ability to understand and generate human language.
-
Examples: translation, summarization, sentiment analysis, chatbots, code generation.
4. Computer Vision
Enables machines to interpret visual data (images, video).
-
Tasks: object detection, facial recognition, OCR, scene understanding.
5. Robotics
Integration of AI with mechanical systems to enable real-world action.
-
Applications: industrial robots, autonomous vehicles, drones.
6. Planning & Reasoning
AI that simulates logic-based problem solving and decision-making.
-
Techniques: symbolic AI, constraint solvers, knowledge graphs.
AI Paradigms
Narrow AI (Weak AI)
-
Specialized for a specific task.
-
Examples: Alexa, Netflix recommender, self-driving software.
Artificial General Intelligence (AGI)
-
Hypothetical AI with broad cognitive capabilities like a human.
-
Still under research; subject of ethical and existential debate.
Applications of AI by Industry
| Sector | Use Cases |
|---|---|
| Healthcare | Disease diagnosis, medical imaging, drug discovery, virtual assistants, patient monitoring |
| Finance | Fraud detection, algorithmic trading, credit scoring, chatbots, compliance monitoring |
| Retail & E-Commerce | Personalized recommendations, inventory prediction, dynamic pricing, customer service |
| Transportation | Autonomous vehicles, traffic management, logistics optimization, drone delivery |
| Manufacturing | Predictive maintenance, quality assurance, robotics, supply chain optimization |
| Education | Adaptive learning platforms, grading automation, content personalization, tutoring systems |
| Media & Entertainment | Deepfakes, content generation, real-time translation, voice cloning |
| Government & Defense | Surveillance, cybersecurity, threat analysis, military robotics |
Leading AI Companies and Labs
Technology Giants
-
OpenAI – GPT series, DALL·E, Codex
-
Google DeepMind – AlphaGo, AlphaFold, Gemini
-
Microsoft AI – Copilot, Azure OpenAI integration
-
Meta AI – LLaMA models, FAIR research
-
Amazon – AWS AI tools, Alexa
-
IBM – Watson, Project Debater
-
NVIDIA – AI hardware and platforms, CUDA, generative AI SDKs
Startups
-
Anthropic – Claude family of LLMs
-
Cohere – Enterprise LLMs and retrieval-augmented generation (RAG)
-
Mistral AI – Open-weight generative models
-
xAI – Elon Musk’s AI company focused on “truthful” reasoning
-
Runway ML – Creative tools for video, art, design using generative AI
Academic Institutions
-
Stanford AI Lab (SAIL)
-
MIT CSAIL
-
UC Berkeley BAIR
-
CMU Machine Learning Department
-
Oxford and Cambridge AI research centers
Key Technologies and Architectures
-
Transformers: Dominant neural network architecture (Vaswani et al., 2017)
-
Large Language Models (LLMs): GPT-4, Claude, PaLM, LLaMA
-
Multimodal Models: Combine text, image, audio, and video (e.g., Gemini, GPT-4o)
-
Reinforcement Learning from Human Feedback (RLHF): Aligns AI with human preferences
-
Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG): Combines generative AI with external knowledge bases
-
Neurosymbolic AI: Merges deep learning with symbolic reasoning
AI Ethics and Policy
Concerns
-
Bias and Discrimination: Trained on biased data, AI can reproduce and amplify societal inequalities.
-
Privacy: Data-driven models may expose personal or sensitive information.
-
Misinformation: Deepfakes, fake news generation, and AI-generated spam are rising threats.
-
Autonomy & Control: Risks from misaligned agents or self-directed systems.
-
Economic Impact: Potential for job displacement, especially in routine and clerical sectors.
Key Principles
-
Fairness
-
Transparency
-
Accountability
-
Explainability
-
Safety and Robustness
-
Human-centeredness
Regulatory Initiatives
-
EU AI Act – Risk-based framework regulating AI use in the European Union.
-
U.S. Executive Order on AI – Introduces safety, civil rights, and innovation directives.
-
China AI Governance Guidelines – Emphasis on alignment with socialist values.
-
OECD AI Principles – International standards for trustworthy AI.
Future of AI
Trends
-
Scaling Laws: Bigger models continue to outperform smaller ones, but costs rise.
-
Model Compression: Techniques like quantization and pruning to deploy AI on edge devices.
-
Synthetic Data: AI-generated data used to train or augment datasets.
-
Autonomous Agents: AI systems capable of long-term planning, execution, and collaboration.
-
Open-Source AI: Tools like Hugging Face, Mistral, and OpenLLM democratize access.
-
AI + Robotics: Embodied intelligence merges digital and physical reasoning.
-
Brain-Computer Interfaces (BCIs): Long-term integration of AI with neural activity.
AGI Outlook
-
Experts remain divided on timeline and feasibility.
-
Consensus: even narrow AI will profoundly impact every industry.
-
AGI safety and alignment research becoming central.













Things From Intel 10K That Make You Go …. Hmmmm