At the 2025 RISC-V Summit, amid debates over cloud scaling and AI cost, DeepComputing CEO Yuning Liang offered a radical view: the future of intelligence isn’t in the cloud at all — it’s already in your pocket. His lunchtime conversation began with iPhones and ended with the death of the operating system. In between, he sketched … Read More
Tag: Jonah McLeod
GlobalFoundries, MIPS, and the Chiplet Race for AI Datacenters
GlobalFoundries’ (GF) acquisition of MIPS in 2025 wasn’t a nostalgic move to revive a legacy CPU brand. It was a calculated step into one of the most lucrative frontiers in semiconductors: AI, high-performance computing (HPC), and datacenters. As Nvidia, AMD, Intel, and hyperscalers embrace chiplet architectures, GF is betting… Read More
Rapidus, IBM, and the Billion-Dollar Silicon Sovereignty Bet
Can cash and IBM collaboration put Japan into premier-league chipmaking? Rapidus is betting billions it can.
When Japan announced the creation of Rapidus in 2022, the news was met with a mix of enthusiasm and skepticism. The company would enter the market at a time of escalating demand for semiconductor fabrication capacity to… Read More
Basilisk at Hot Chips 2025 Presented Ominous Challenge to IP/EDA Status Quo
At Hot Chips 2025, Philippe Sauter of ETH Zürich presented Basilisk, a project that may redefine what’s possible with open-source hardware. Basilisk is a 34 mm² RISC-V SoC fabricated at IHP Microelectronics on its open-source 130nm BiCMOS process in Germany. Basilisk, named after the Greco-Roman mythical creature known… Read More
Flynn Was Right: How a 2003 Warning Foretold Today’s Architectural Pivot
In 2003, legendary computer architect Michael J. Flynn issued a warning that most of the industry wasn’t ready to hear. The relentless march toward more complex CPUs—with speculative execution, deep pipelines, and bloated instruction handling—was becoming unsustainable. In a paper titled “Computer Architecture … Read More
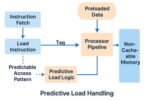
Predictive Load Handling: Solving a Quiet Bottleneck in Modern DSPs
When people talk about bottlenecks in digital signal processors (DSPs), they usually focus on compute throughput: how many MACs per second, how wide the vector unit is, how fast the clock runs. But ask any embedded AI engineer working on always-on voice, radar, or low-power vision—and they’ll tell you the truth: memory stalls … Read More
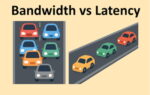
Even HBM Isn’t Fast Enough All the Time
Why Latency-Tolerant Architectures Matter in the Age of AI Supercomputing
High Bandwidth Memory (HBM) has become the defining enabler of modern AI accelerators. From NVIDIA’s GB200 Ultra to AMD’s MI400, every new AI chip boasts faster and larger stacks of HBM, pushing memory bandwidth into the terabytes-per-second range. … Read More
RISC-V’s Privileged Spec and Architectural Advances Achieve Security Parity with Proprietary ISAs
Because of its open and modular nature, RISC-V has faced recognizable security challenges stemming from fragmentation, performance inefficiencies, and inherent vulnerabilities. Fragmentation across implementations leads to inconsistencies, making it difficult to enforce uniform security measures. Performance… Read More
Harnessing Modular Vector Processing for Scalable, Power-Efficient AI Acceleration
The dominance of GPUs in AI workloads has long been driven by their ability to handle massive parallelism, but this advantage comes at the cost of high-power consumption and architectural rigidity. A new approach, leveraging a chiplet-based RISC-V vector processor, offers an alternative that balances performance, efficiency,… Read More